Abstract
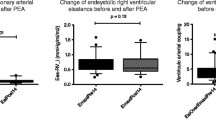
Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI) offers a range of surrogate markers to quantify the hemodynamic changes associated with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Our aim was to noninvasively monitor effects of pulmonary vascular remodeling before and after endarterectomy (PEA) in patients with CTEPH by using PC-MRI. Fifty-seven consecutive patients (mean age 56.7 ± 16, 28 female) underwent PC-MRI before and after PEA as part of their peri-operative routine workup. Pulmonary artery (PA) maximum flow velocity (maxV), acceleration time/ejection time (AT/ET), distensibility [(PA maximum area − PA minimum area)/PA minimum area], mid-systolic flow deceleration (notch), and the timing of deceleration (notch ratio) were recorded. Mean PA pressure was obtained from standard right heart catheter procedures. maxV and AT/ET were decreased before PEA and significantly improved afterwards (60.8 ± 16 vs. 73.8 ± 19 cm/s, p = 0.007; 0.32 ± 0.06 vs. 0.36 ± 0.09, p = 0.0015). Surprisingly, distensibility did not change significantly (30 ± 19 vs. 26 ± 12 %, p = 0.11). Forty-five patients (78 %) had a systolic notch before PEA that persisted in only 10 (18 %; p = 0.00001). Among patients with a persisting notch, the notch ratio did not significantly increase (1.3 ± 0.2 vs. 1.6 ± 1.5, p = 0.32). Our data show early PA reverse remodeling after PEA. Flow velocities increase while PA flow wave reflections represented by mid-systolic flow deceleration are abolished. In some patients a mid-systolic notch persists, suggesting increased downstream resistance as a consequence of small vessel arteriopathy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Krishna Kumar R, Landzberg M, Machado RF, Olschewski H, Robbins IM, Souza R (2013) Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 62(25 Suppl):D34–D41. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.029
Pengo V, Lensing AW, Prins MH, Marchiori A, Davidson BL, Tiozzo F, Albanese P, Biasiolo A, Pegoraro C, Iliceto S, Prandoni P, Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Study G (2004) Incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 350(22):2257–2264. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032274
Moser KM, Auger WR, Fedullo PF (1990) Chronic major-vessel thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 81(6):1735–1743
Jamieson SW, Kapelanski DP (2000) Pulmonary endarterectomy. Curr Probl Surg 37(3):165–252
Mayer E, Dahm M, Hake U, Schmid FX, Pitton M, Kupferwasser I, Iversen S, Oelert H (1996) Mid-term results of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Ann Thorac Surg 61(6):1788–1792. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(96)00169-5
Archibald CJ, Auger WR, Fedullo PF, Channick RN, Kerr KM, Jamieson SW, Kapelanski DP, Watt CN, Moser KM (1999) Long-term outcome after pulmonary thromboendarterectomy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160(2):523–528
Lang I (2010) Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Br J Haematol 149(4):478–483. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08142.x
Frazier AA, Galvin JR, Franks TJ, Rosado-De-Christenson ML (2000) From the archives of the AFIP: pulmonary vasculature: hypertension and infarction. Radiographics 20(2):491–524. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.2.g00mc17491
Blauwet LA, Edwards WD, Tazelaar HD, McGregor CG (2003) Surgical pathology of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy: a study of 54 cases from 1990 to 2001. Hum Pathol 34(12):1290–1298
Kafi SA, Mélot C, Vachiery JL, Brimioulle S, Naeije R (1998) Partitioning of pulmonary vascular resistance in primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 31(6):1372–1376
Kim NHS, Fesler P, Channick RN, Knowlton KU, Ben-Yehuda O, Lee SH, Naeije R, Rubin LJ (2004) Preoperative partitioning of pulmonary vascular resistance correlates with early outcome after thromboendarterectomy for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 109(1):18–22. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000111841.28126.D4
Kreitner K-F, Wirth GM, Krummenauer F, Weber S, Pitton MB, Schneider J, Mayer E, Dueber C (2013) Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary hemodynamics in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by high temporal resolution phase-contrast MRI: correlation with simultaneous invasive pressure recordings. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 6(5):722–729. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.000276
Ley S, Mereles D, Puderbach M, Gruenig E, Schöck H, Eichinger M, Ley-Zaporozhan J, Fink C, Kauczor H-U (2007) Value of MR phase-contrast flow measurements for functional assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Radiol 17(7):1892–1897. doi:10.1007/s00330-006-0559-9
Naeije R, Huez S (2007) Right ventricular function in pulmonary hypertension: physiological concepts. Eur Heart J Suppl 9(Suppl H):H5–H9. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sum023
Sanz J, Kuschnir P, Rius T, Salguero R, Sulica R, Einstein AJ, Dellegrottaglie S, Fuster V, Rajagopalan S, Poon M (2007) Pulmonary arterial hypertension: noninvasive detection with phase-contrast MR imaging. Radiology 243(1):70–79. doi:10.1148/radiol.2431060477
Gan CT-J, Lankhaar J-W, Westerhof N, Marcus JT, Becker A, Twisk JWR, Boonstra A, Postmus PE, Vonk Noordegraaf A (2007) Noninvasively assessed pulmonary artery stiffness predicts mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 132(6):1906–1912. doi:10.1378/chest.07-1246
Kang KW, Chang HJ, Kim YJ, Choi BW, Lee HS, Yang WI, Shim CY, Ha J, Chung N (2011) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging-derived pulmonary artery distensibility index correlates with pulmonary artery stiffness and predicts functional capacity in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ J 75(9):2244–2251
Sanz J, Kariisa M, Dellegrottaglie S, Prat-González S, Garcia MJ, Fuster V, Rajagopalan S (2009) Evaluation of pulmonary artery stiffness in pulmonary hypertension with cardiac magnetic resonance. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2(3):286–295. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.08.007
Hardziyenka M, Reesink HJ, Bouma BJ, de Bruin-Bon HACMR, Campian ME, Tanck MWT, van den Brink RBA, Kloek JJ, Tan HL, Bresser P (2007) A novel echocardiographic predictor of in-hospital mortality and mid-term haemodynamic improvement after pulmonary endarterectomy for chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J 28(7):842–849. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl534
Klok FA, Romeih S, Westenberg JJ, Kroft LJ, Huisman MV, de Roos A (2011) Pulmonary flow profile and distensibility following acute pulmonary embolism. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13:14. doi:10.1186/1532-429X-13-14
Bonderman D, Skoro-Sajer N, Jakowitsch J, Adlbrecht C, Dunkler D, Taghavi S, Klepetko W, Kneussl M, Lang IM (2007) Predictors of outcome in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 115(16):2153–2158. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.661041
Kreitner K-FJ, Ley S, Kauczor H-U, Mayer E, Kramm T, Pitton MB, Krummenauer F, Thelen M (2004) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: pre- and postoperative assessment with breath-hold MR imaging techniques. Radiology 232(2):535–543. doi:10.1148/radiol.2322030945
Ley S, Kramm T, Kauczor H-U, Mayer E, Heussel CP, Thelen M, Kreitner K-F (2003) Pre- and postoperative assessment of hemodynamics in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by MR techniques. RoFo Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Rontgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin 175(12):1647–1654. doi:10.1055/s-2003-45340
Jardim C, Rochitte CE, Humbert M, Rubenfeld G, Jasinowodolinski D, Carvalho CRR, Souza R (2007) Pulmonary artery distensibility in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an MRI pilot study. Eur Respir J 29(3):476–481. doi:10.1183/09031936.00016806
Swift AJ, Rajaram S, Hurdman J, Hill C, Davies C, Sproson TW, Morton AC, Capener D, Elliot C, Condliffe R, Wild JM, Kiely DG (2013) Noninvasive estimation of PA pressure, flow, and resistance with CMR imaging: derivation and prospective validation study from the ASPIRE registry. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 6(10):1036–1047. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.01.013
Helderman F, Mauritz GJ, Andringa KE, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Marcus JT (2011) Early onset of retrograde flow in the main pulmonary artery is a characteristic of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(6):1362–1368. doi:10.1002/jmri.22581
Swift AJ, Rajaram S, Condliffe R, Capener D, Hurdman J, Elliot C, Kiely DG, Wild JM (2012) Pulmonary artery relative area change detects mild elevations in pulmonary vascular resistance and predicts adverse outcome in pulmonary hypertension. Invest Radiol 47(10):571–577. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e31826c4341
Furuno Y, Nagamoto Y, Fujita M, Kaku T, Sakurai S, Kuroiwa A (1991) Reflection as a cause of mid-systolic deceleration of pulmonary flow wave in dogs with acute pulmonary hypertension: comparison of pulmonary artery constriction with pulmonary embolisation. Cardiovasc Res 25(2):118–124
Torbicki A, Kurzyna M, Ciurzynski M, Pruszczyk P, Pacho R, Kuch-Wocial A, Szulc M (1999) Proximal pulmonary emboli modify right ventricular ejection pattern. Eur Respir J 13(3):616–621
Castelain V, Hervé P, Lecarpentier Y, Duroux P, Simonneau G, Chemla D (2001) Pulmonary artery pulse pressure and wave reflection in chronic pulmonary thromboembolism and primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 37(4):1085–1092
Lankhaar J-W, Westerhof N, Faes TJC, Marques KMJ, Marcus JT, Postmus PE, Vonk Noordegraaf A (2006) Quantification of right ventricular afterload in patients with and without pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291(4):H1731–H1737. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00336.2006
Conflict of interest
The authors declare, that they have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rolf, A., Rixe, J., Kim, W.K. et al. Pulmonary vascular remodeling before and after pulmonary endarterectomy in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a cardiac magnetic resonance study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 31, 613–619 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-014-0580-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-014-0580-z