Abstract
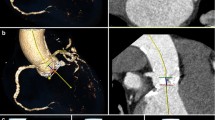
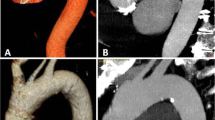
Purpose Computed tomography (CT) is increasingly being used for planning purposes prior to trans-arterial valve implantation (TAVI). High-pitch protocols using a 2nd generation dual-source CT (DSCT) allow for a comprehensive assessment of the aortic valve anulus, its distance to the coronary artery ostia, the aortic bulbus and the iliofemoral arteries with very low radiation exposure and low amount of contrast agent. The aim of this study was to evaluate the image quality of a comparable high-pitch scan mode in a modern single-source CT (SSCT) system. Methods 40 patients with severe symptomatic aortic valve stenosis have been examined for planning purposes prior to TAVI. The first 20 consecutive patients were examined with a 2nd generation DSCT system using a high-pitch scan mode (pitch value 3.4) and 60 ml of contrast agent. The second group of 20 consecutive patients were examined with a 128-slice SSCT system, using a high-pitch scan mode (pitch value of 1.7) and 60 ml of contrast agent. Image quality of the aortic valve, the ascending aorta, the coronary artery ostia, the iliofemoral arteries and overall image quality were graded in a blinded fashion using a 4-point-grading-scale. Furthermore, signal intensity and image noise were derived in the ascending aorta and in the ilio-femoral arteries. Results There was a minor but significant difference in the overall image quality score with lower image quality in SSCT (3.5 ± 0.6) when compared to DSCT (3.85 ± 0.4; p = 0.037). The mean image quality score was significantly higher in patients examined in DSCT when compared to SSCT regarding the evaluability of the coronary ostia (4.0 vs. 3.5; p < 0.01) and the image quality of the ascending aorta (4.0 vs. 3.5; p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in evaluation of the aortic valve and its anulus (3.85 for DSCT and 3.65 for SSCT; p = 0.149) and image quality of the iliofemoral arteries (3.65 for DSCT and 3.85 for SSCT; p = 0.140). Signal intensity and image noise did not differ significantly between both groups. Conclusions This study presents a novel high-pitch protocol for modern SSCT scanners, which allows CT angiography for TAVI planning with a similar radiation dose and contrast agent exposition and only small compromises in image quality compared to a high-pitch protocol on a DSCT scanner.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nkomo VT et al (2006) Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Lancet 368(9540):1005–1011
Webb JG et al (2007) Percutaneous transarterial aortic valve replacement in selected high-risk patients with aortic stenosis. Circulation 116(7):755–763
Moat NE et al (2011) Long-term outcomes after trans.catheter aortic valve implantation in high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis: the U.K. TAVI (United Kingdom Trans.catheter Aortic Valve Implantation) registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(20):2130–2138
Plank F et al (2012) Benefits of high-pitch 128-slice dual-source computed tomography for planning of trans.catheter aortic valve implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 94(6):1961–1966
Wuest W et al (2011) Dual source multidetector CT-angiography before trans.catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) using a high-pitch spiral acquisition mode. Eur Radiol 22(1):51–58
Leipsic J et al (2011) Multidetector computed tomography in trans.catheter aortic valve implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 4(4):416–429
Blanke P et al (2010) Combined assessment of aortic root anatomy and aortoiliac vasculature with dual-source CT as a screening tool in patients evaluated for trans.catheter aortic valve implantation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195(4):872–881
Menzel H, Schibilla H,Teunen D (2000) European guidelines for quality criteria for computed tomography
Beeres M et al (2012) High-pitch dual-source CT angiography of the whole aorta without ECG synchronisation: initial experience. Eur Radiol 22(1):129–137
Karlo C et al (2011) High-pitch dual-source CT angiography of the aortic valve–aortic root complex without ECG-synchronization. Eur Radiol 21(1):205–212
Bolen MA et al (2012) Image quality, contrast enhancement, and radiation dose of ECG-triggered high-pitch CT versus non-ECG-triggered standard-pitch CT of the thoracoabdominal aorta. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198(4):931–938
Pontone G et al (2011) Feasibility and accuracy of a comprehensive multidetector computed tomography acquisition for patients referred for balloon-expandable trans.catheter aortic valve implantation. Am Heart J 161(6):1106–1113
Shiran A et al (2009) Accuracy and reproducibility of left ventricular outflow tract diameter measurement using transthoracic when compared with transesophageal echocardiography in systole and diastole. Eur J Echocardiogr 10(2):319–324
Tops LF et al (2008) Noninvasive evaluation of the aortic root with multislice computed tomography implications for trans.catheter aortic valve replacement. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 1(3):321–330
Lehmkuhl L et al. Inter-individual variance and cardiac cycle dependency of aortic root dimensions and shape as assessed by ECG-gated multi-slice computed tomography in patients with severe aortic stenosis prior to trans.catheter aortic valve implantation: is it crucial for correct sizing? J Am Coll Cardiol Img
Bolen MA et al (2012) Prospective ECG-triggered, axial 4-D imaging of the aortic root, valvular and left ventricular structures: a lower radiation dose option for preprocedural TAVR imaging. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 6(6):393–398
Achenbach S et al (2012) SCCT expert consensus document on computed tomography imaging before trans.catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI)/trans.catheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 6(6):366–380
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bischoff, B., Meinel, F.G., Reiser, M. et al. Novel single-source high-pitch protocol for CT angiography of the aorta: comparison to high-pitch dual-source protocol in the context of TAVI planning. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29, 1159–1165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0182-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0182-1