Abstract
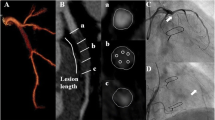
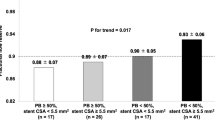
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of vascular response assessed by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) imaging on clinical outcomes in elderly patients (≥75 years) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for de novo lesions with sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) implantation. Repeat coronary angiography with IVUS was performed 1 year after SES-based PCI for de novo lesions in 136 elderly patients (≥75 years) and 427 younger counterparts (<75 years) (219 lesions and 635 lesions, respectively). Major adverse cardiac events (MACE) including cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and target lesion revascularization (TLR) during 2-year follow-up were recorded. Despite similar angiographic in-stent restenosis and TLR and IVUS-detected incomplete stent apposition (ISA), absolute intimal hyperplasia and percentage of volumetric obstruction were lower in elderly than in younger patients. At 2-year follow-up, cumulative survival freedom from composite death and myocardial infarction or MACE was significantly reduced in elderly patients, but very late stent thrombosis was similar in the two groups. Cox proportional hazards model identified age, diabetes, left ventricular ejection fraction, lesion length,minimal stent cross-sectional area and plaque progression as independent predictors of non-fatal myocardial infarction or mortality. In elderly patients undergoing SES-based PCI, despite similar TLR, neointimal hyperplasia was significantly lower than in younger patients. IVUS measurements except for minimal stent cross-sectional area did not correlate with stent thrombosis and clinical outcomes at 2 years.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O’Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y (2009) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 119(3):480–486. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.191259
Vijayakumar M, Lemos PA, Hoye A, Ong AT, Aoki J, Granillo GR, McFadden EP, Sianos G, Hofma SH, Smits PC, van der Giessen WJ, de Feyter P, van Domburg RT, Cummins PA, Serruys PW (2004) Effectiveness of sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for the treatment of coronary artery disease in octogenarians. Am J Cardiol 94(7):909–913. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.06.036
Hassani SE, Wolfram RM, Kuchulakanti PK, Xue Z, Gevorkian N, Suddath WO, Satler LF, Kent KM, Pichard AD, Weissman NJ, Waksman R (2006) Percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents in octogenarians: characteristics, clinical presentation, and outcomes. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 68(1):36–43. doi:10.1002/ccd.20768
Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, Fajadet J, Ban Hayashi E, Perin M, Colombo A, Schuler G, Barragan P, Guagliumi G, Molnar F, Falotico R (2002) A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 346(23):1773–1780. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012843
Holmes DR Jr, Leon MB, Moses JW, Popma JJ, Cutlip D, Fitzgerald PJ, Brown C, Fischell T, Wong SC, Midei M, Snead D, Kuntz RE (2004) Analysis of 1-year clinical outcomes in the SIRIUS trial: a randomized trial of a sirolimus-eluting stent versus a standard stent in patients at high risk for coronary restenosis. Circulation 109(5):634–640. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000112572.57794.22
Varani E, Aquilina M, Balducelli M, Vecchi G, Frassineti V, Maresta A (2009) Percutaneous coronary interventions in octogenarians: Acute and 12 month results in a large single-centre experience. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 73(4):449–454. doi:10.1002/ccd.21852
Finn AV, Joner M, Nakazawa G, Kolodgie F, Newell J, John MC, Gold HK, Virmani R (2007) Pathological correlates of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: strut coverage as a marker of endothelialization. Circulation 115(18):2435–2441. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.693739
Cook S, Wenaweser P, Togni M, Billinger M, Morger C, Seiler C, Vogel R, Hess O, Meier B, Windecker S (2007) Incomplete stent apposition and very late stent thrombosis after drug-eluting stent implantation. Circulation 115(18):2426–2434. doi:101161/CIRCULATIONNAHA.106.658237
Tahara S, Chamie D, Baibars M, Alraies C, Costa M (2011) Optical coherence tomography endpoints in stent clinical investigations: strut coverage. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27(2):271–287. doi:10.1007/s10554-011-9796-3
Berry C, L’Allier PL, Gregoire J, Lesperance J, Levesque S, Ibrahim R, Tardif JC (2007) Comparison of intravascular ultrasound and quantitative coronary angiography for the assessment of coronary artery disease progression. Circulation 115(14):1851–1857. doi:CIRCULATIONAHA.106.655654
Degertekin M, Serruys PW, Tanabe K, Lee CH, Sousa JE, Colombo A, Morice MC, Ligthart JM, de Feyter PJ (2003) Long-term follow-up of incomplete stent apposition in patients who received sirolimus-eluting stent for de novo coronary lesions: an intravascular ultrasound analysis. Circulation 108(22):2747–2750. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000103666.25660.77
Cutlip DE, Baim DS, Ho KK, Popma JJ, Lansky AJ, Cohen DJ, Carrozza JP Jr, Chauhan MS, Rodriguez O, Kuntz RE (2001) Stent thrombosis in the modern era: a pooled analysis of multicenter coronary stent clinical trials. Circulation 103(15):1967–1971
Tsuchida K, Garcia–Garcia HM, Ong AT, Valgimigli M, Aoki J, Rademaker TA, Morel MA, van Es GA, Bruining N, Serruys PW (2006) Revisiting late loss and neointimal volumetric measurements in a drug-eluting stent trial: analysis from the SPIRIT FIRST trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 67(2):188–197. doi:10.1002/ccd.20581
Serruys PW, Degertekin M, Tanabe K, Abizaid A, Sousa JE, Colombo A, Guagliumi G, Wijns W, Lindeboom WK, Ligthart J, de Feyter PJ, Morice MC (2002) Intravascular ultrasound findings in the multicenter, randomized, double-blind RAVEL (RAndomized study with the sirolimus-eluting VElocity balloon-expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery Lesions) trial. Circulation 106(7):798–803
Matsumoto D, Shite J, Shinke T, Otake H, Tanino Y, Ogasawara D, Sawada T, Paredes OL, Hirata K, Yokoyama M (2007) Neointimal coverage of sirolimus-eluting stents at 6-month follow-up: evaluated by optical coherence tomography. Eur Heart J 28(8):961–967. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl413
Kim BK, Kim JS, Oh C, Ko YG, Choi D, Jang Y, Hong MK (2011) Major determinants for the uncovered stent struts on optical coherence tomography after drug-eluting stent implantation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. doi:10.1007/s10554-011-9896-0
Kim TH, Kim JS, Kim BK, Ko YG, Choi D, Jang Y, Hong MK (2010) Long-term (>/=2 years) follow-up optical coherence tomographic study after sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation: comparison to 9-month follow-up results. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. doi:10.1007/s10554-010-9729-6
Jeremias A, Sylvia B, Bridges J, Kirtane AJ, Bigelow B, Pinto DS, Ho KK, Cohen DJ, Garcia LA, Cutlip DE, Carrozza JP Jr (2004) Stent thrombosis after successful sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation 109(16):1930–1932. doi:101161/01.CIR.0000127105.99982.21
Farb A, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R (2003) Pathological mechanisms of fatal late coronary stent thrombosis in humans. Circulation 108(14):1701–1706. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000091115.05480.B0
Hartmann M, von Birgelen C, Mintz GS, van Houwelingen GK, Eggebrecht H, Bose D, Wieneke H, Verhorst PM, Erbel R (2006) Relation between plaque progression and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol during aging as assessed with serial long-term (> or = 12 months) follow-up intravascular ultrasound of the left main coronary artery. Am J Cardiol 98(11):1419–1423. doi:S0002-9149(06)01612-2
Mintz GS, Shah VM, Weissman NJ (2003) Regional remodeling as the cause of late stent malapposition. Circulation 107(21):2660–2663. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000074778.46065.24
Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, Park DW, Park KM, Lee BK, Kim YH, Song JM, Han KH, Kang DH, Cheong SS, Song JK, Kim JJ, Park SW, Park SJ (2006) Late stent malapposition after drug-eluting stent implantation: an intravascular ultrasound analysis with long-term follow-up. Circulation 113(3):414–419. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.563403
Ozaki Y, Okumura M, Ismail TF, Naruse H, Hattori K, Kan S, Ishikawa M, Kawai T, Takagi Y, Ishii J, Prati F, Serruys PW (2010) The fate of incomplete stent apposition with drug-eluting stents: an optical coherence tomography-based natural history study. Eur Heart J 31(12):1470–1476. doi:ehq066
Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, Park DW, Lee SW, Kim YH, Kang DH, Cheong SS, Song JK, Kim JJ, Park SW, Park SJ (2007) Impact of late drug-eluting stent malapposition on 3-year clinical events. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(15):1515–1516. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.038
Hoffmann R, Morice MC, Moses JW, Fitzgerald PJ, Mauri L, Breithardt G, Schofer J, Serruys PW, Stoll HP, Leon MB (2008) Impact of late incomplete stent apposition after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation on 4-year clinical events: intravascular ultrasound analysis from the multicentre, randomised, RAVEL, E-SIRIUS SIRIUS trials. Heart 94(3):322–328. doi:10.1136/hrt.2007.120154
Hassan AK, Bergheanu SC, Stijnen T, van der Hoeven BL, Snoep JD, Plevier JW, Schalij MJ, Wouter Jukema J (2010) Late stent malapposition risk is higher after drug-eluting stent compared with bare-metal stent implantation and associates with late stent thrombosis. Eur Heart J 31(10):1172–1180. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn553
Vlaar PJ, Lennon RJ, Rihal CS, Singh M, Ting HH, Bresnahan JF, Holmes DR Jr (2008) Drug-eluting stents in octogenarians: early and intermediate outcome. Am Heart J 155(4):680–686. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2007.11.007
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rui Yan Zhang contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, R., Zhang, R.Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Assessment of the relation between IVUS measurements and clinical outcome in elderly patients after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for de novo coronary lesions. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28, 1653–1662 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-0007-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-0007-z