Abstract
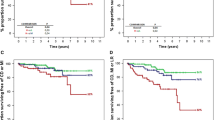
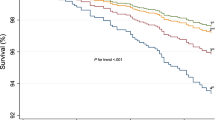
The prognostic value of dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) for risk stratification of patients aged ≥80 years is not clearly defined. A follow-up of 3 ± 2 years for major cardiac events and all-cause mortality was obtained in 227 patients, age ≥80 years, who underwent DSE for known or suspected coronary artery disease. Stress function index (SFI), calculated as the ratio of peak wall motion score index to left ventricular ejection fraction, was analyzed both as continuous variable and categorized using the mean value of 5 as the cut-off. Only 95 patients (42%) of this group underwent a cycloergometer exercise stress test (EST). During DSE 118 patients developed inducible ischemia; SFI was 4.9 ± 2.6 and 60 subjects showed a value higher than 5. EST gave a positive result in 12 patients and a negative result in 8 patients; it was inconclusive for inadequate increase in heart rate in 75 (79%) subjects. Advanced age (HR: 1.184/year, 95% CI: 1.073–1.306, p = 0.001) and SFI ≥ 5 (HR: 2.682, 95% CI: 1.429–5.035, p = 0.002) were independent predictors of all-cause mortality; advanced age (HR: 1.252/year, 95% CI: 1.064–1.473, p = 0.007), SFI ≥ 5 (HR: 3.181, 95% CI: 1.174–8.621, p = 0.02) and presence of left bundle branch block (HR: 3.060, 95% CI: 1.057–8.862, p = 0.039) independently predicted an increased occurrence of major cardiac events. No parameter derived from EST showed an independent prognostic role. DSE showed a significant prognostic value in octogenarians, both for all-cause mortality and major cardiac events.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lye M, Donnellan C (2000) Heart disease in the elderly. Heart 84:560–566
Biagini E, Elhendy A, Schinkel AF et al (2005) Long-term prediction of mortality in elderly persons by dobutamine stress echocardiography. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:1333–1338
Riley CP, Oberman A, Lampton TD, Hurst DC (1970) Submaximal exercise testing in a random sample of an elderly population. Circulation 42:43–52
Anthopoulos LP, Bonou MS, Kardaras FG et al (1996) Stress echocardiography in elderly patients with coronary artery disease: applicability, safety and prognostic value of dobutamine and adenosine echocardiography in elderly patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:52–59
Poldermans D, Fioretti PM, Boersma E et al (1994) Dobutamine-atropine stress echocardiography in elderly patients unable to perform an exercise test. Hemodynamic characteristics, safety, and prognostic value. Arch Intern Med 154:2681–2686
Hiro J, Hiro T, Reid CL, Ebrahimi R, Matsuzaki M, Gardin JM (1997) Safety and results of dobutamine stress echocardiography in women versus men and in patients older and younger than 75 years of age. Am J Cardiol 80:1014–1020
Poldermans D, Fioretti PM, Boersma E et al (1999) Long-term prognostic value of dobutamine-atropine stress echocardiography in 1737 patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease: a single-center experience. Circulation 99:757–762
Sicari R, Pasanisi E, Venneri L, Landi P, Cortigiani L, Picano E (2003) Stress echo results predict mortality: a large-scale multicenter prospective international study. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:589–595
Armstrong WF, Zoghbi WA (2005) Stress echocardiography: current methodology and clinical applications. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1739–1747
Bangalore S, Yao SS, Chaudhry FA (2005) Stress function index, a novel index for risk stratification and prognosis using stress echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1335–1342
Xu B, Li JJ, Yang YJ et al (2007) Age-based clinical and angiographic outcomes after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation in patients with coronary artery disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 120:447–451
Rathore S, Rhys J, Buchalter MB, Gerning NO, Groves PH, Penny W (2006) Impact of age on the outcomes of women following percutaneous coronary intervention in the bare-metal stent era. J Interv Cardiol 19:245–249
Messinger-Rapport B, Pothier Snader CE, Blackstone EH, Yu D, Lauer MS (2003) Value of exercise capacity and heart rate recovery in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 51:63–68
Era P, Schroll M, Hagerup L, Schultz-Larsen JK (2001) Changes in bicycle ergometer test performance and survival in men and women from 50 to 60 and from 70 to 80 years of age: two longitudinal studies in the Glostrup (Denmark) population. Gerontology 47:136–144
Myers J, Prakash M, Froelicher V, Do D, Partington S, Atwood JE (2002) Exercise capacity and mortality among men referred for exercise testing. N Engl J Med 346:793–801
Prakash M, Myers J, Froelicher VF et al (2001) Clinical and exercise test predictors of all-cause mortality: results from > ; 6, 000 consecutive referred male patients. Chest 120:1003–1013
Kallinen M, Kauppinen M, Era P, Heikkinen E (2006) The predictive value of exercise testing for survival among 75-year-old men and women. Scand J Med Sci Sports 16:237–244
Tsutsui JM, Xie F, Cloutier D, Kalvaitis S, Elhendy A, Porter TR (2008) Real-time dobutamine stress myocardial perfusion echocardiography predicts outcome in the elderly. Eur Heart J 29:377–385
Cortigiani L, Bigi R, Sicari R, Landi P, Bovenzi F, Picano E (2007) Prognostic implications of dipyridamole or dobutamine stress echocardiography for evaluation of patients > or = 65 years of age with known or suspected coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol 99:1491–1495
Baudhuin T, Marwick T, Melin J, Wijns W, D’Hondt AM, Detry JM (1993) Diagnosis of coronary artery disease in elderly patients: safety and efficacy of dobutamine echocardiography. Eur Heart J 14:799–803
Chaudhry FA, Qureshi EA, Yao SS, Bangalore S (2007) Risk stratification and prognosis in octogenarians undergoing stress echocardiographic study. Echocardiography 24:851–859
Solomon SD, Anavekar N, Skali H et al (2005) Influence of ejection fraction on cardiovascular outcomes in a broad spectrum of heart failure patients. Circulation 112:3738–3744
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Innocenti, F., Totti, A., Baroncini, C. et al. Prognostic value of dobutamine stress echocardiography in octogenarians. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27, 65–74 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9655-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9655-7