Abstract
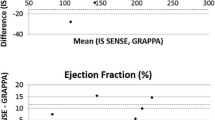
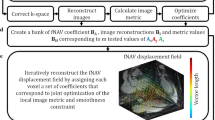
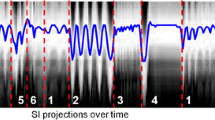
To evaluate parallel-imaging methods in free-breathing whole-heart 3D coronary magnetic resonance angiography and assess the navigator techniques and visualization rates of the major coronary arteries. We compared key parameters of the generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisition and modified sensitive encoding images in vitro phantom MRI; performed the MRA with GRAPPA parallel imaging in healthy volunteers; compared 1D- and 2D-prospective acquisition correction and analyzed the differences; and evaluated the visualization of major coronary arterial branches. GRAPPA images had higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio and fewer aliasing artifacts. The coronary arteries were adequately visualized in 38 volunteers. 2D-PACE had a higher navigator efficiency, shorter scan time, and gave clearer reconstructed images in comparison with 1D-PACE. GRAPPA images were superior to mSENSE images. Whole-heart 3D coronary MRA along with parallel-imaging technique is a potential clinical method, and 2D-PACE is a better navigation technique than 1D-PACE.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1D/2D PACE:
-
One/two-dimensional prospective acquisition correction
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise ratio
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- GRAPPA:
-
Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisition
- LAD:
-
Left anterior descending artery
- LCX:
-
Left circumflex artery
- LM:
-
Left main coronary artery
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- mSENSE:
-
Modified sensitive encoding
- RCA:
-
Right coronary artery
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- TrueFISP:
-
True fast imaging with steady-state precession
References
Edelman RR (2004) Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the heart: overview of the literature. Radiology 232(3):653–668. doi:10.1148/radiol.2323031558
Finn JP, Nael K, Deshpande V et al (2006) Cardiac MR imaging state of the technology. Radiology 241(2):338–354. doi:10.1148/radiol.2412041866
Ropers D, Baum U, Pohle K et al (2003) Detection of coronary artery stenoses with thin-slice multi-detector row spiral computed tomography and multiplanar reconstruction. Circulation 107(5):664–666. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000055738.31551.A9
Abdulla J, Abildstrom SZ, Gotzsche O et al (2007) 64-multislice detector computed tomography coronary angiography as potential alternative to conventional coronary angiography: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 28(24):3042–3050. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm466
Jahnke C, Paetsch I, Achenbach S et al (2006) Coronary MR imaging: breath-hold capability and patterns, coronary artery rest periods, and beta-blocker use. Radiology 239(1):71–78. doi:10.1148/radiol.2383042019
Nehrke K, Bornert P, Mazurkewitz P et al (2006) Free-breathing whole-heart coronary MR angiography on a clinical scanner in four minutes. J Magn Reson Imaging 23(5):752–756. doi:10.1002/jmri.20559
Prakken NH, Vonken EJ, Velthuis BK et al (2006) 3D MR coronary angiography: optimization of the technique and preliminary results. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 22(3–4):477–487. doi:10.1007/s10554-005-9053-8
Gharib AM, Ho VB, Rosing DR et al (2008) Coronary artery anomalies and variants: technical feasibility of assessment with coronary MR angiography at 3 T. Radiology 247(1):220–227
Pruessmann KP (2006) Encoding and reconstruction in parallel MRI. NMR Biomed 19(3):288–299. doi:10.1002/nbm.1042
Hunold P, Maderwald S, Ladd ME et al (2004) Parallel acquisition techniques in cardiac cine magnetic resonance imaging using TrueFISP sequences: comparison of image quality and artifacts. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(3):506–511. doi:10.1002/jmri.20125
Ruel L, Brugieres P, Luciani A et al (2004) Comparison of in vitro and in vivo MRI of the spine using parallel imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182(3):749–755
Niendorf T, Hardy CJ, Giaquinto RO et al (2006) Toward single breath-hold whole-heart coverage coronary MRA using highly accelerated parallel imaging with a 32-channel MR system. Magn Reson Med 56(1):167–176. doi:10.1002/mrm.20923
Klessen C, Asbach P, Kroencke TJ et al (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging of the upper abdomen using a free-breathing T2-weighted turbo spin echo sequence with navigator triggered prospective acquisition correction. J Magn Reson Imaging 21(5):576–582. doi:10.1002/jmri.20293
Weber OM, Martin AJ, Higgins CB (2003) Whole-heart steady-state free precession coronary artery magnetic resonance angiography. Magn Reson Med 50(6):1223–1228. doi:10.1002/mrm.10653
Sakuma H, Ichikawa Y, Suzawa N et al (2005) Assessment of coronary arteries with total study time of less than 30 min by using whole-heart coronary MR angiography. Radiology 237(1):316–321. doi:10.1148/radiol.2371040830
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Zeng, MS., Ge, MY. et al. A study of in vitro and in vivo MR of free-breathing whole-heart 3D coronary angiography using parallel imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 25 (Suppl 1), 121–129 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-008-9415-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-008-9415-0