Abstract
Purpose of the study
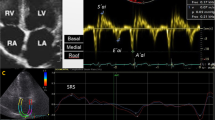
The study was done to determine the clinical feasibility and reproducibility of tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE) with strain rate imaging (SRI) at rest and under physical exercise in healthy young individuals and to report normal values for parameters of regional myocardial function under exercise.
Methods
Forty-five young volunteers (age 9–29 years) underwent echocardiography with TDE/SRI at rest and during a bicycle exercise test (2 W/kg body weight).
Results
Velocities could be obtained in 93% of segments, whereas strain rate was measurable at least in 80% of segments. Inter- and intraobserver variability for measurement of velocities under exercise was 14% and 9%, respectively for strain rate 28% and 20%. Except for peak strain, values for all other parameters were higher during exercise with the clearest response in the left lateral and the right ventricular wall.
Conclusions
(1) Tissue Doppler with strain rate imaging is a practical and robust method for assessment of regional function of both ventricles under exercise. (2) Systolic motion, local myocardial relaxation and contractility increased significantly under physical exercise. These normal values obtained from healthy young subjects can serve as a reference database for further clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HR:
-
heart rate
- LAX:
-
parasternal long axis
- LV:
-
left ventricle
- RV:
-
right ventricle
- SAX:
-
parasternal short axis
- SRA :
-
peak late diastolic strain rate
- SRE :
-
peak early diastolic strain rate
- SRS :
-
peak systolic strain rate
- SRI:
-
strain rate imaging
- TDE:
-
tissue Doppler echocardiography
- V A :
-
peak late diastolic myocardial velocity
- V E :
-
peak early diastolic myocardial velocity
- V S :
-
peak systolic myocardial velocity
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
peak overall strain
References
Sawada SG, Segar DS, Ryan T et al (1991) Echocardiographic detection of coronary artery disease during dobutamine infusion. Circulation 83:1605–1614
Geleijnse ML, Fioretti PM, Roelandt JR (1997) Methodology, feasibility, safety and diagnostic accuracy of dobutamin stress echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:595–606
Beleslin BD, Ostojic M, Stepanovic J et al (1994) Stress echocardiography in the detection of myocardial ischemia: Head-to-head comparison of exercise, dobutamine and dipyridamole tests. Circulation 90:1168
Hoffman R, Lethen H, Marvick T et al (1996) Analysis of inter-institutional observer agreement in interpretation of dobutamine stress echocardiograms. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:330–336
Cain P, Khoury V, Short L et al (2003) Usefulness of quantitative echocardiographic techniques to predict recovery of regional and global left ventricular function after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 91:391–396
Fraser AG, Payne N, Mädler CF et al (2003) Feasibility and reproducibility of offline tissue Doppler measurements of regional myocardial function during dobutamine stress echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 4:43–53
Boettler P, Hartmann M, Watzl K et al (2005) Heart rate effects on strain and strain rate in healthy children. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1121–1130
Urheim S, Edvardsen T, Torp H et al (2000) Myocardial strain by Doppler echocardiography validation of anew method to quantify regional myocardial function. Circulation 102:1158–1164
Heimdal A, Stoylen A, Torp H et al (1998) Real-time strain rate imaging of the left ventricle by ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 11:1013–1019
Weidemann F, Jamal F, Sutherland GR et al (2002) Myocardial function defined by strain rate and strain during alterations in inotropic states and heart rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H792–H799
Voigt JU, Arnold MF, Karlsson M et al (2000) Assessment of regional longitudinal myocardial strain rate derived from Doppler myocardial imaging indices in normal and infarcted myocardium. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 13:588–598
Jamal F, Kukulski T, Strotmann J et al (2001) Quantification of the spectrum of changes in regional myocardial function during acute ischemia in closed chest pigs: an ultrasonic strain rate and strain study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 14:874–884
Kapusta L, Thijssen JM, Cuypers MH et al (2000) Assessment of myocardial velocities in healthy children using tissue Doppler imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 26:229–37
Davidavicius G, Kowalski M, Williams et al (2003) Feasibility and reproducibility of offline tissue Doppler measurements of regional myocardial function during dobutamine stress echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 4:43–53
Quintana M, Saha SK, Rohani M et al (2004) Assessment of the longitudinal and circumferential left ventricular function at rest and during exercise in healthy elderly individuals by tissue-Doppler echocardiography: relationship with heart rate. Clin Sci 106:451–457
Kowalski M, Kukulski T, Jamal F et al (2001) Can natural strain and strain rate quantify regional myocardial deformation? A study in healthy subjects. Ultrasound Med Biol 8:1087–1097
Wilkenshoff UM, Sovany A, Wigstrom L et al (1998) Regional mean systolic myocardial velocity estimation by real-time colour Doppler myocardial imaging: a new technique for quantifying regional systolic function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 11:683–92
Stoylen A, Heimdal A, Bjornstad K et al (2000) Strain rate imaging by ultrasonography in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 13:1053–1064
Hanekom L, Lundberg V, Leano R et al (2004) Optimization of strain rate imaging for application to stress echocardiography. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:1451–1460
Storaa C, Lind B, Brodin LA (2004) Distribution of left ventricular longitudinal peak systolic strain and impact of low frame rate. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:1049–55
Munagala VK, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW et al (2003) Association of newer diastolic function parameters with age in healthy subjects: a population-based study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16:1049–1056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Björn Goebel and Raoul Arnold have contributed equally to this work
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9159-7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goebel, B., Arnold, R., Koletzki, E. et al. Exercise tissue Doppler echocardiography with strain rate imaging in healthy young individuals: feasibility, normal values and reproducibility. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 23, 149–155 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9130-7