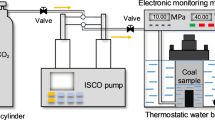
In order to clarify the characteristics of coal rock pore fracture changes after CO2 gas injection into coal seams, the Dafosi coalfield in Binchang mining area was taken as the research object. The changes in CT scanning surface, pseudo color, grayscale mean, and porosity of coal and rock samples were studied under different CO2 injection pressures. Through CT scanning experiments, combined with ORS visual and Matlab software. The main reasons for the changes in pore fracture characteristics of coal and rock after injecting CO2 gas were studied from three aspects: compressive deformation of coal and rock, crack width, and number of cracks. The experimental results showed that, as the injection pressure of CO2 gas increases, the color of coal rock CT scan images and pseudo color images becomes lighter, the mean gray level increases, and the porosity decreases; The compression deformation of coal rock is not the main reason for the changes in the characteristics of coal rock pores and fractures; The more CO2 gas is adsorbed by coal and rock, the narrower the cracks gradually, and the number of pores and fractures decreases. CO2 adsorption is the main reason for the decrease in porosity of coal and rock. The research results provide a technical boundary reference for the development of coalbed methane injection CO2.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu Jin-jun, Liu Jing, Wang Jin-an. Experimental Research and Exploration of New Technologies for Coalbed Methane Development[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(5): 43-45.
Wu Di, Hao Shu-ping, Liang Wei-guo. Development of the displacement technique of by carbon dioxide coal bed methane[J]. Shanxi Coal, 2008, 28(3):10-13.
Lian Li-ming, Qi Ji-shun, Yang Si-yu,et al. Research progress and development directions on mathematical models of CO2 flooding[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2013, 20(2):77-82.
Tang Shu-heng, Ma Cai-xia, Ye Jian-ping,et al. A modeling experiment of enhancing coalbed methane recovery by carbon dioxide injection [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2006, 35(5):607-611.
Wu Shi-yue, Guo Yong-yi. Study of the mechanism of increasing production of exploitation coal bed methane by gas injection[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2001, 26(2):199-203.
Ma Dong-ming, Li Lai-xin, Li Xiao-ping,et al. Contrastive experiment of absorption-desorption between CH4 and CO2 in Coal Seam 4 of Dafosi Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Coal Science, 2014, 39(9):1938-1944.
Zhou De-feng, Yai Guang-qin, Tang Zhong-hua. Economic Evaluation and Sensitivity Analysis of Enhanced Coalbed Methane Production with CO2 and N2 Injection [J]. CHINA Coalbed Methane, 2009, 6(3):40-45.
Fang Zhi-ming, Li Xiao-chun, Bai Bing. Study of method of simultaneously measuring adsorption-deformation-permeability of coal[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(9):1828-1833.
Jiang Chun-yue, Yuan Ji, Tan Xun-qiang,et al. Development of Measurements for the coal swelling strain of coal matrix in CO2-ECBM[J]. Chemical Times Magazine, 2010, 24(10):46-51.
Wang You-an, Tao Yu-mei. Adsorption deformation and adsorption deformation force of coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 1993(6):19-26.
Zhu Jie, Tang Jun, Chuan Li-jing, et al. A Mechanical model of coal strain induced by gas sorption/desorption[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2015(17):2090-2094.
Zhu Jie, Zhang Min, Jiang Yao-dong, et al. Experimental study of coal strain induced by carbon dioxide sorption/desorption[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(5):1081-1086.
Zhou Lai, Feng Qi-dong, Chen Zhong-wei, et al,Effects of coal swelling on modeling of CO2 sorption on the coal and correction approaches[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009(5): 673-677.
Hao Nai, Mao Ling-tao, Wei Feng, et al. Experimental study on coal associated with carbondioxide sorption by CT[J]. CT Theory and Applications, 2014, 23(3):425-433.
Yu Yan-mei, Hu Yao-qing, Liang Wei-guo,et al. Study on pore characteristics of lean coal at different temperature by CT technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(2):637-644.
Fan Liu-ming, Li Ning, Ding Wei-hua. Application of pseudo color enhancement method to geotechnical CT image analysis[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2004, 23(13):2257-2261.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation Project “Adhesion and deposition mechanism of Nano polymer microspheres on the inner wall of pore throat and migration and diversion mechanism, No.2021JM-408”, the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum, Beijing (No. PRP/open-2112), and Shaanxi Province Post-doctoral Fund Project “Study on the Mechanism and Numerical Simulation of Crude Oil Displacement by Different Medium in tight Reservoir Matrix, No. 2018BSHYDZZ53”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 3, pp. 158–163 May – June, 2023
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, C., Junbin, C., Han, W. et al. The Influence Law and Mechanism of CO2 Injection Pressure on Coal Rock Pore-Fracture Characteristics. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 59, 638–646 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01564-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01564-y