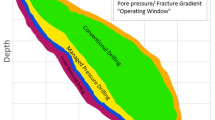
Overflow accidents are frequent in deepwater managed-pressure drilling, and the monitoring basis and control methods of risks are vague, necessitating the establishment of a suitable risk matrix. Based on the traditional risk matrix analysis method, this paper establishes a overflow-backpressure risk matrix with overflow size and backpressure threshold as judgment criteria, and formulates 11-level backpressure application plans and backpressure application calculation models. The results show that the overflow-backpressure risk matrix with overflow size and backpressure threshold as judgment criteria meets the requirements of deepwater managed-pressure drilling design and can significantly determine the risk level of overflow occurrence. The formulated backpressure application calculation model refines the backpressure control situation of managed-pressure drilling and can apply different backpressure according to different risk levels. After applying risk control measures, the maximum allowable drilling speed and backpressure in different working conditions of the 3950-4130 m wellbore section were designed on-site at well A1, and the risk level was reduced to 0. This overflow-backpressure risk matrix can classify and control the risk of overflow in deepwater managed-pressure drilling.


Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Gao Yonghai, Sun Baojiang, Wang Zhiyuan, et al. Calculation and analysis of wellbore Temperature fi eld in deep water drilling [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2008(02): 58-62.
Li Mengbo, Liu Gonghui, Li Jun, et al. Research on wellbore temperature fi eld considering spiral fl ow of non-Newtonian fl uid [J]. Petroleum Drilling T echniques, 2014, 42(05): 74-79.
Lai Minbin, Fan Honghai, Peng Qi, et al. Hydraulic parameter optimization design of deep-water double gradient submarine lift drilling system [J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2015, 37(01): 68-71.
Sun Tengfei, et al. Annular Pressure Buildup Calculation When Annulus Contains Gas [J]. Chemistry & Technology of Fuels & Oils, 2018, 54 (4):57-61.
Kong Xiangwei, Liu Zuocai, Jin Yanxin. Study on Multiphase Pressure Wave Velocity Characteristics of Automatic Kill Annulus in Chuanyu Fractured Formation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(12):1370-1379.
Sun Tengfei, Gao Deli, et al. A New Well Profile Design Method for Extended-Reach Drilling[J]. Cmes-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 2013, 90(1):37-45, 2013.
Wiktorski E., Cobbah C., Sui D, Mahmound K. Experimental study of temperature effects on wellbore material properties to enhance temperature profi le modeling for production wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 176: 689-701.
Kong Xiangwei, Lin Yuanhua, Qiu Yijie. Research of mechanism for the gas invasion and gravity replacement in drilling operations [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2015, 32(02): 317-322+358.
Tang Haixiong, Yin Zhiming, Chen Fengyou. Research on material planning risk assessment and control technology for deepwater drilling [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2009, 31(05): 155-157.
Li Huan, Han Song. Drilling risk assessment based on HAZOP analysis [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 15(S1): 17-20.
Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Quantitative risk analysis of offshore drilling operations: a Bayesian approach[J]. Safety Science, 2013, 57: 108-117.
Acknowledgments
“Research and engineering demonstration of offshore precise pressure-controlled drilling technology” (Project Number: YXKY-2021-HN-01) of China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) Technology Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 2, pp. 66–69 March– April, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Ren, M., Yang, X. et al. Study of Risk Matrix for Overflow-Backpressure-Based Deepwater Managed Pressure Drilling. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 59, 305–310 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01530-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01530-8