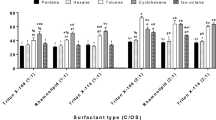
In the oil production process, a large amount of generated oily sludge causes considerable pollution to the environment. In this paper, the oil sludge samples obtained from the Jidong oilfield in China are treated by the microemulsion system containing sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) as a surfactant. The microemulsion system contains kerosene as the oil phase and an aqueous solution containing SDBS, n-butanol, and sodium chloride as the water phase. This study is focused on the effects of the system’s composition and treatment process on the efficiency of oil removal. The results show that when the volume ratio of kerosene to water is 1:1 and the weight concentrations of SDBS, n-butanol, and sodium chloride are 4.92%, 2.59%, and 3.94% respectively, the system provides the highest oil removal efficiency. When the initial sample mass is 10 g and the water content in the microemulsion is 100 mL, the treatment provides the removal of 79.3% of oil from the sludge. The oil removal efficiency is further optimized to 82.5% by treating the sludge at the temperature of 30°C for 2 h.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. A. Zharov and V. L. Lavrov, “Modern methods of oil sludge processing,” Ekol. Proizvodstva, 5, 43-51 (2004).
N. Buyukkamaci and E. Kucuksilek, “Improvement of dewatering capacity of a petrochemical sludge,” J. Hazard. Mater., 144, 323-327 (2007).
A. A. Vikarchuk, I. I. Rastegaeva, and E. Yu. Chernokhaeva, “Technology and equipment for oil treatment and processing of solid and liquid petrochemical sludge,” Vektor Nauki TGU, 3(21), 70-75 (2012).
G. Jing, M. Luan, and T. Chen, “Prospects for the development of oily sludge treatment,” Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils, 4, 44-54 (2011).
A. Yu. Tsivadze, A. L. Maksimov, A. Ya. Fridman, et al., “Processing of oil-tank sludge by hydrothermal dispersion using polycomplexants and amino-acid salts,” Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils, 2, 199-204 (2020).
A. Yu. Tsivadze, A. Ya. Fridman, B. P. Tumanyan, et al., “Prospective preparations for accelerated bioremediation of oilcontaminated soils,” Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils, 4, 588-592 (2020).
S. V. Egazar’yants, V. A. Vinokurov, A. V. Vutolkina, et al., “Oil sludge treatment processes,” Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils, 5, 506-515 (2015).
F. F. Viana, T. N. Dantas, C. G. Rossi, et al., “Aged oil sludge solubilization using new microemulsion systems: design of experiments,” J. Mol. Liq., 210(1), 44-50 (2015).
H. E. Liu, X. P. Zhang, C. Q. Ding, et al., “Phase behavior of sodium dodecylsulfate-n-butanol-kerosene-water microemulsion system,” Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 22(6), 699-705 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 96–99, November-December, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Qiang, L., Wu, X. et al. Oil Sludge Treatment by a Microemulsion System Containing Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 57, 1000–1004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01337-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01337-z