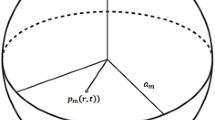
Experiments to characterize the constant-rate gas depleted production behavior in core samples were performed to study the areal gas flowing mechanism of a high-pressure low-permeability heterogeneous gas reservoir, including a newly designed long-core experiment on areal heterogeneity constant-rate gas depleted production considering fracturing. In the experiments, the fluid pressure increased up to 45 MPa, and the cores of the near-wellbore high permeability area before and after fracturing and the cores of the low permeability non fractured area were connected in series to simulate the gas flowing process of the dual-area composite gas reservoir. When the irreducible water saturation is considered, the gas permeability in a high permeability area cater fracturing increased threefold. Experimental results indicated that the pressure difference in the near-wellbore high permeability area decreased rapidly after fracturing and increased in the low permeability area. The recovery:factor of each area increased titter fracturing. Fracturing could have a significant effect on increasing the recovery factor when the average permeability is relatively low. The greater the gas rate, the higher is the built-up pressure alter shut-in. Fracturing in the near-wellbore area may cause a significant decrease in the shut-in built-up pressure value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Zhao, H. M. Tang, Y. F. Meng, et al., “Damage evaluation for water—based underbalanced drilling in low—permeability and tight sandstone gas reservoirs,” Pet. Explor. Dev., 36(1), 113-119 (2009).
R. Sander, Z. J. Pan, and L. D. Connell, “Laboratory measurement of low permeability unconventional gas reservoir rocks: A review of experimental methods,” J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng., 37, 248-279 (2017).
A. Su, H. H. Chen, X. Chen, et al., “The characteristics of low permeability reservoirs, gas origin, generation and charge in the central and western Xihu depression, East China Sea Basin,”J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng., 53, 94-109 (2018).
W. C. Liu, “Exact analytical solution of a generalized multiple moving boundary model of one—dimensional non-Darcy flow in heterogeneous multilayered low-permeability porous media with a threshold pressure gradient,”Appl. Math. Model., 81, 931-953 (2020).
P. Wei, W. F. Pu, L. Sun, et al., “Oil recovery enhancement in low permeable and severe heterogeneous oil reservoirs via gas and foam flooding,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 163, 340-348 (2018).
J. Zeng, X. Z. Wang, J. C. Guo, et al., “Modeling of heterogeneous reservoirs with damaged hydraulic fractures,” J. Hydrol., 574, 774-793 (2019).
A. N. Baykin and S. V. Golovin, “Application of the fully coupled planar 3D poroelastic hydraulic fracturing model to the analysis of the permeability contrast impact on fracture propagation,” Rock Mech. Rock Eng., 51(10), 3205-3217 (2018).
Q. Sang, Y. J. Li, C. F. Zhu, et al., “Experimental investigation of shale gas production with different pressure depletion schemes,” Fuel, 186, 293-304 (2016).
R. S. Nie, F. Xie, Y. L. ha, et al., “Experimental study on the pressure—depleted flow of natural gas in a cluster of combined tight cores with a certain water saturation,” J Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng., 33. 821-829 (2016).
P. Guo, J. F. Du, Z. H. Wang, et al., “Method for determining fracture permeability in fracture-pore type flowing experiments,” China Patent CN102619502A, issued August 1. 2012.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (NO. 2016ZX05027-004-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 2, pp. 110 — 116, March—April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, P., Dong, C., Wang, Z. et al. Experimental Study on Areal Flowing During Depletion of a High-Pressure Heterogeneous Gas Reservoir. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 57, 406–414 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-021-01259-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-021-01259-2