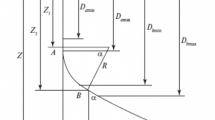
Drilling applications involve a number of global optimization problems that require finding the best extremum value of a nonlinear function of many variables. One of such problems is the choice of the optimal well drilling trajectory. Various trajectory optimization algorithms have been previously proposed, but they all suffer from some shortcomings. In the present paper, the shortest well length is used as the objective function, and optimization is performed by the artificial fish swarm algorithm (AFSA). The calculations have been carried out in the Matlab environment. Comparison of our calculations with previously published data suggests that AFSA optimization produces the best numerical results and the shortest trajectory, while in addition ensuring high stability and reliability. The algorithm has a simple structure and fast convergence, quickly producing a global optimum. AFSA thus may be used to calculate the optimal drilling trajectory.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Xilu and Jiang Shengzong, Optimization model for designing the trajectory of 2-D horizontal well and its algorithms, Appl. Found. Eng. Sci., 7(2), 111-116 (1999).
Tong Changhai, Optimization calculation method for well trajectory design, Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 12(1), 60-62 (2005).
Qiu Guohu and Fu Jianhong, Optimization design for 3-D directional well trajectory, Drill. Prod. Technol., 20(5), 26-29 (1997).
Jiang Shengzong, and Feng Enmin, Optimization model for designing the trajectory of 3-D horizontal well and its algorithms, J. Dalian Univ. Technol., 42(3), 261-264 (2002).
Zhang Yan, Liu Kunfang, Cao Limin, et al., Well trajectory optimization design for horizontal well while drilling, Acta Pet. Sin., 22(1), 100-104 (2001).
Sui Mancang, Zhang Da, and Cheng Weilan, Optimizing for horizontal well hole trajectory, J. Jianghan Pet. Inst., 22(2), 25-26 (2000).
Zhang Yuejun, Zhao Ziren, and Cui Jiangjie, Study on optimization design technology for horizontal well drilling, West-China Exploration Engineering, 7(01) (1995).
Tian Yaowen, Study on optimization methods of directional well trajectory, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007.
Zhang Yan, Li Ji, Liu Kunfang, et al., Study on optimization design method for directional well trajectory, Nat. Gas Ind., 20(1),57-60 (2000).
Wu Shilei, Feng Enmin, and Jiang Shengzong, Optimized trajectory of two-dimension directional well and analysis of applied instance, Appl. Found. Eng. Sci., 9(2), 125-132 (2001).
Ding Hua, Wang Xiukun, and Sun Tao, Research on optimization of well trajectory based on PSO algorithm. J. Dalian Univ. Technol., 45(3), 449-452 (2005).
Li Xiaolei, A new type of intelligent optimization methods - artificial fish-swarm algorithm, Zhejiang University, 2003.
Wu Yueping and Du Yi, Parameters analysis of improved artificial fish swarm algorithm, Comput. Eng. Appl. (2012-2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel No. 2 pp. 61 — 64 March —April 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Zhang, H., Gao, D. et al. Application of the Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm to Well Trajectory Optimization. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 55, 213–218 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-019-01023-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-019-01023-7