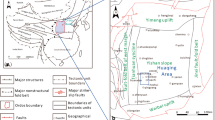
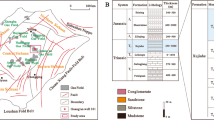
In this paper, fractal characteristics of sandstone in the Chang 7 section of the Triassic Yanchang Formation of the Dingbian oilfield, Ordos Basin, China were analyzed by high pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry and the fractal model. The influence offractal parameters on rock permeability is discussed. Results show that fractal dimensions (Df) of sandstone samples range within 2.759-2.987, with an average of 2.890, and the mean capillary tortuosity fractal dimension (DT) ranges within 1.194-1.553, with an average of 1.391; Df is larger than Dr There is a strong negative correlation between rock permeability and Df or Dr Both Df and DT decrease with decreasing porosity of sandstone samples, indicating that connectivity between rock sample pores becomes poor and capillary tortuosity increases. The seepage path in low-permeability (tight) sandstone is much longer than in moderate-permeability sandstone, which is an important reason for the low permeability of the tight sandstone oil reservoir Meanwhile, the fractal model is an effective predictor of the permeability of tight sandstone oil reservoirs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 March 2019
The corresponding author of the article is Guo Ying, E-mail: majian258741@163.com.
15 March 2019
The corresponding author of the article is Guo Ying, E-mail: majian258741@163.com.
15 March 2019
The corresponding author of the article is Guo Ying, E-mail: majian258741@163.com.
References
S. Khajooie, R. Roghanian, A. Shahrabadi, et al., Petrol. Sci. Technol, 30, No. 23, 1330-1332 (2012).
H. Zhang, Y. M. Zhu, S. B. C. L. Hu, Petrol. Sci. Technol., 32, No. 24,2930-2937 (2014).
H. Y. Zhu, X. C. Jin, J. C. Guo, et al., Int. J. Oil Gas Coal T, 13, No. 4,359-387 (2016).
P. Pfeifer and D. Avnir, J. Phys. Chem., 79,3369-3558 (1983).
P. Xu and B. M. Yu, Chinese Phys. Lett., 31, No. 1,74-81 (2008).
J. H. M. Thomeer, J. Petrol. Technol., 12,73-77 (1960).
Y. J. Gong, S. B. Liu, R. K. Zhu, et al., Petrol. Explor. Dev, 42, No. 5,681-688 (2015).
Z. Y. Zhang and A. Weller, Geophysics, 79, No. 6, D377—D387 (2014).
Z. M. Fang and X. C. Li, Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol., 6, No. 5,567-577 (2013).
F. Yang, Z. F. Ning, and H. Q. Liu, Fuel, 115,378-384 (2014).
P. C. Carman, T Am. Inst. Chem. Eng., 15,150-156 (1937).
R. T. Bai, Z. P. Li, J. X. Nan, et al., Natural Gas Geoscience, 27, No. 1,142-148 (2016).
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2017PD001) and Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Depositional Mineralization and Sedimentary Minerals at the Shandong University of Science and Technology (DMSM2017018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 5, pp. 74 — 78, September — October, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Changhua, Y., Ying, G., Xiangyang, S. et al. High Pressure Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry Analysis of the Influence of Fractal Dimensions on the Permeability of Tight Sandstone Oil Reservoirs. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 54, 641–649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0970-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0970-3