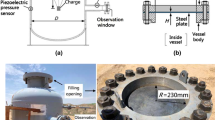
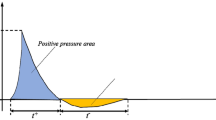
A new safety-valve construction was developed and tested by studying combined dynamic and static loads between powered supports and surrounding rocks. The gas—air mixture explosion conditions were modeled to test the dynamic load. Explosion properties of the gas-air mixtures (including maximum explosion pressure, maximum rise rate of explosion pressure, explosion rime, deflagration index) were investigated experimentally at room temperature in a cylindrical chamber with top-center ignition. The results showed that the maximum explosion pressure, maximum rate of pressure rise, and deflagration index were linearly correlated to the initial pressure. On the other hand, the explosion time depended mainly on the ratio of gases and only in a limited range on the initial pressure. The experimentally measured explosion properties of LPG—air mixtures could be used in practice to study safe operation of safety valves.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. G. Qian, X. X. Miao, F. L. He, et al., J. China Coal Soc., 21, No. 1, 40-44 (1996) [in Chinese].
Z. S Lian, Y. C. Guo, D. Y. Wang, et al., "A large flow safety valve test device," CN Patent, ZL201510190240.7. 2017.
T. Mogi and S. Horiguchi, J Hazard. Mater, 164, No. 1, 114-119 (2009).
A. S. Huzayyin, H. A. Moneib, M. S. Shehatta, et al., Fuel, 87, No. 1, 39-57 (2008).
M. Mita, V. Giurcan, D. Razus, et al., Energy Fuels, 26, No. 8, 4840-4848 (2012).
D. Razus, V. Brinzea, M. Minn, et al., J Hazard. Mater, 165, No. 1-3, 1248-1252 (2009).
Y. Koshiba, T. Nishida, N. Morita, et al., Process Saf. Environ. Prot., 98, 11-15 (2015).
D. Razus, C. Movileanu, V. Brinzea, et al., J Hazard. Mater., 135, No. 1-3, 58-65 (2006).
D. Razus, C. Movileanu, and D. Oancea, J Hazard. Mater., 139, No. 1, 1-8 (2007).
B. Zhang and H. D. Ng, Fuel, 157, 56-63 (2015).
D. Razus, V. Brinzea, M. Mitu, et al., Rev. Chim. (Bucharest, Rom.), 60, No. 8, 750-754 (2009).
D. Razus, C. Movileanu, V. Brinzea, et al., Fuel, S6. No. 12-13, 1865-1872 (2007).
Z. L. Zhang, B. Q. Lin, G. M. Li, et al., Combust. Set Technol., 185, No. 3, 514-531 (2013).
D. Razus, V. Brinzea, M. Mitu et al., J Hazard. Mater., 190, No. 1-3, 891-896 (2011).
D. Razus, V. Brinzea, M. Mitu, et al., J Hazard. Mater., 174, No. 1-3, 548-555 (2010).
Q. Q. Li, Y. Cheng, and Z. H. Huang, J. Loss Prey. Process Ind., 37, 91-100 (2015).
Q. Q. Li, Y. Cheng, W. Jin, et al., Fuel, 161, 78-86 (2015).
Q. Zhang, W. Li, and H. M. Liang, Saf. Sci., 50, No. 9, 1715-1721 (2012).
Q. Zhang, W. Li, Y. Huang, et al., Process Saf. Prog., 31, No. 2, 148-151 (2012).
Y. D. Jo and D. A. Crowl, Process Saf. Prog., 29, No. 3, 216-223 (2010).
C. L. Tang, Z. H. Huang, C. Jin, et al., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 34, No. 1, 554-561 (2009).
F. Cammarota, A. D. Benedetto, P. Russo, et al., Process Sat Environ. Prot., 88, No. 5, 341-349 (2010).
R. K. Vishwakarma, V. Ranjan, and J. Kumar, J. Loss Prevent. Process Ind., 31, No. 31, 82-81 (2014).
C. L. Tang, S. Zhang, Z. B. Si, et al., J Hazard. Mater., 278, 520-528 (2014).
Q. Z. Li, B. Q. Lin, H. M. Dai, et al., Powder Technol, 229,222-228 (2012).
M. Mitua and E. Brandes, Fuel, 158, 217-223 (2015).
C. Movileanu, V. Gosa, and D. Razus, J Hazard. Mater., 235-236, No. 2, 108-115 (2012).
D. Li, Q. Zhang, Q. J. Ma, et al, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 40, No. 28, 8761-8768 (2015).
T. S. Lee, J. Y. Sung, and D. J. Park, Fire Saf J., 49, No. 49, 62-66 (2012).
K. Lee and J. Ryu, Fuel, 84, No. 9, 1116-1127 (2005).
F. S. Li, G X. Li, and Z. Y. Sun, Energies, 10, No. 7, 915 (2017).
D. P. Mishra and A. Rahman, Fuel, 82, No. 32, 863-866 (2003).
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by the Foundation for Scientific and Technological Projects for the Coal-Mining Industry of Shanxi Province, PRC (No. MJ2014-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Xiang, H., Lian, Z. et al. Explosion Properties of LPG—Air Mixtures in a Cylindrical Vessel with Top-Center Ignition. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 54, 591–598 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0964-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0964-1