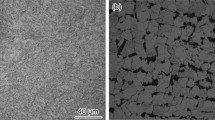
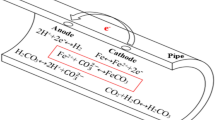
Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas flooding for enhancement of oil recovery is known to face challenges such as corrosion and scaling of oil-gathering facilities and environmental pollution. The corrosion behavior of the gathering facilities must be studied to select the optimum measures for protecting them from the corrosive effect of CO2. Surface corrosion of the separator, a key problem with using CO2, is evaluated in the present work. The corrosion characteristics, corrosion rate, and corrosion products in different functional areas of the facility were determined by the weight-loss method, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and x-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. The results indicate that pitting corrosion is the main characteristic of Fe-360 A steel facilities and that the average corrosion rate in vulnerable areas can reach 0.1358 mm/yr with formation of Fe2O3 and FeS. The combined effects of contact time and CO2 volume in conjunction with the activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria influence the corrosion kinetics and mechanism of Fe-360 A steel. The results are of great significance for minimizing corrosion using chemical inhibition and proper selection of materials that come into contact with CO2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Q. Niu, J. W. Liang, and S. Z. Wang, Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils, 50, No. 6, 494-500 (2015).
H. Y. Zhong, Z. H. Wang, and E. M. Cao, Int. J. Oil, Gas Coal Technol., 6, No. 5, 507-516 (2013).
O. Arjmand and A. Roostaei, Res J. Appl. Sci., Eng. Technol., 4, No. 17, 3065-3068 (2012).
B. T. Hoffman and S. Shoaib, J. Energy Resour. Technol., 136, No. 2, 1-10 (2014).
R. B. Alston, G. P. Kokolis, and C. F. James, SPE J., 25, No. 2, 268-274 (1985).
S. H. Stevens and J. Gale, Oil Gas J., No. 20, 40 (2000).
K. Su, X. W. Liao, and X. L. Zhao, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 125, 128-135 (2015).
F. Gozalpour, S. R. Ren, and B. Tohidi, Oil Gas Sci. Technol., 60, No. 3, 537-546 (2005).
B. S. Ju, T. L. Fan, and Z. X. Jiang, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 109, 144-154 (2013).
Y. Liu, J. X. Li, Z. H. Wang, et al., Environ. Earth Sci., 73, No. 10, 5891-5904 (2015).
A. H. Mustafa, B. Ari-Wahjoedi, and M. C. Ismail, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 22, No. 6, 1748-1755 (2013).
G. X. Zhao, X. H. Lu, J. M. Xiang, et al., J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 16, No. 4, 89-94 (2009).
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by the State Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51534004) and the University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. UNPYSCT-2015074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 79 – 84, November – December, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Yu, T. et al. Study of Corrosion Behavior of Oil Gathering Facilities with Co2 Flooding In Low-Permeability Oilfields. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 53, 933–942 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0883-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-018-0883-1