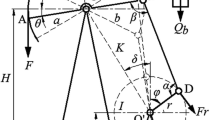
Deep and superdeep reservoirs over 5000 m deep are continually being discovered and developed in Western China, particularly in the Tarim Basin. The low pressure in these reservoirs makes it necessary to run sucker-rod pumps to great depths, which increases the load on the polished rod and creates pumping problems in deep wells. This study examines two rod-load-reduction techniques for deep wells, one using composite fiberglass-steel rods and the other using load reducers for the rods. The effects of these techniques on polished-rod load reduction are evaluated by calculation based on well operation data and comparison of the two techniques. Energy efficiency is analyzed by calculating the torque based on the difference between the maximum and minimum loads on the polished rod. The study results show that composite fiberglass-steel rods reduce the maximum load by 35.7% and that the load reducer decreases the load by an average of 22.8%, which is a significant outcome. The composite fiberglass-steel rod is more energy efficient than the load reducer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qi Zhang, Theory and Design of Oil Production Engineering. China University of Petroleum Press, Beijing (2006).
Luan Guohua, Well Testing, 22, 71–74 (2013).
Qiu Jun and Gong Hengxin, Ibid., 11, 49–50 (2002).
Chan Can, Chen Feng, Zha, Zhang Yao, et al., Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 3, 54–57 (2013).
Xiadong Wu, Ming Zhu, Guoqing Han, et al., Advances in Information Sciences and Service Sciences, 4, 149–157 (2012).
Cen Xueqi et al., Oil Field Equipment, 41 28–32 (2012).
Jianxin Shen, Xiaodong Wu, and Jiexiang Wang, SPE ATCE 2010, Sept. 19–22, 2010. SPE 134068.
Du Yong, Jia Yaoqin, Zou Qun, et al., Oil Field Equipment, 40, 74–76 (2011).
Tang Zhouhuai, Lin Weimin, Lou Yongchang, et al., Drilling & Production Technology, 25, 58–62 (2002).
Xue Qi Cen et al., Advanced Materials Research, 772, 808 (2013).
D. McCannell and D. Holden, 2001 SPE Western Regional Meeting. Bakersfield, California, March 26–30, 2001. SPE 68791.
T. O. Allen and A. P. Roberts, Production Operations. Vols. 1 and 2. Oil and Gas Consultants International. Tulsa, Oklahoma (1978).
M. A. Naguib, S. E. Shahen, A. E. Bayoumi, et al., 2000 SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference, Cybernetics and Management Science. Brisbane, Australia, October 16–18, 2000. SPE 64508.
Wu Xiaodong, Shi Junfeng, Chen Fujun, et al., The International Journal of Systems, Cybernetics, and Management Science, 38, 1684–1692 (2009).
Z. Yufeng, W. Xiaodong, T. Shouceng, et al., Petroleum Science and Technology, 28, 1884–1894 (2010).
This research was conducted with the support of the Chinese National Program of Research and Development in the Area of High Technologies: “Key Technologies for Optimizing the Design and Control of Wells of Complex Configuration (Grant No. 2011ZX05009-005).”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 4, pp. 25 – 28, July – August, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cen, X., Wu, X. & Gao, Se. Two Techniques for Reducing Sucker-Rod Loads in Deep Wells. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 51, 371–378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0614-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0614-9