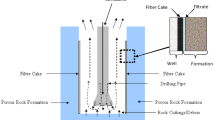
We have developed a flush fluid for alkaline oxidation degradation of the mud cake for inhibited drilling fluid. The permeability of the smeary core when treated with the flush fluid increases by 125.6%. The mechanism of the washing process was studied by IR spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive x-ray spectrometry. The polymer backbone is broken down by the strong oxidant; the oligomers or even lower molecular weight fragments formed in this case are easily washed out.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. H. Li et al., Oilfield Chemistry, 22, 381-383 (2005) .
C. X. Su et al., Drilling & Production Technology, 24, 53-54 (2001).
J. H. Yang et al., Oil & Gas Recovery Technology, 7, 52-53 (2000).
B. Jonathan et al., Changing Environments, No. 1, 323-330 (2012).
M. B. Dusseault et al., in: International Symposium on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette USA, 23-24 February 2000; pp. 89-102.
R. C. Burton et al., in: European Formation Damage Control Conference, Lafayette USA, 23-24 February 2000; pp. 1-13.
Y. Chen. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 33, 51-53 (2005).
L. Yu et al., Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 40, 33-37 (2012).
Q. Lan et al., Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 27, 11-13 (2011).
J. Miller, in: International Symposium on Oil Chemistry, Houston USA, 28 February-2 March, 2007; SPE 106506.
S. Cobianco et al., in: European Formation Damage Control Conference, Scheveningen, The Netherlands, 30 May-1 June, 2007; SPE 107756.
Z. Y. Lian et al., Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 34, 107-109 (2012).
SY/T 5273-2000, “Evaluation method for behavior of corrosion inhibitor for produced water of oil field.”
G. Gonzalez et al., Energy & Fuels, 17, 879-886 (2003).
H. A. Nasr-El-Din et al., in: International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette USA, 15-17 February 2006; SPE 98300.
Y. T. Bai et al., Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 34, 263-271 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 37 – 41, November – December, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, Z., Chen, D., Wei, W. et al. Washing Technology for the Mud Cake of Inhibited Drilling Fluid. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 50, 501–507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0556-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0556-2