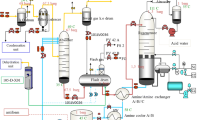
We use the Aspen HYSYS software to simulate the process of amine sweetening of natural gas with high acid gas content. We analyze the effect of the lean amine (absorbent) temperature on the acid gas content in the sweetened gas and saturated amine solution (the rich amine). We found that the optimal temperature for the regenerated amine solution (lean amine), at which the maximum sweetening of the gas is achieved with minimum amine circulation rate, is within the range 38°C-45°C.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Stewart and K. Arnold, Gas Sweetening and Processing Field Manual, Gulf Professional Publishing, Waltham (2011).
J. Kidnay and R. William, Fundamentals of Natural Gas Processing, CRC Press, Texas. (2006)
R. Maddox, R. Gas Conditioning and Processing: Gas and Liquid Sweetening: Volume 4, Campbell Petroleum, Oklahoma (1982).
K. Abdel-Aal and M. Aggour, Petroleum and Gas Field Processing, CRC Press, New York (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 4, pp. 10 – 12, July – August, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulrahman, R., Sebastine, I. Effect of lean amine temperature on amine gas sweetening: case study and simulation. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 49, 293–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-013-0444-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-013-0444-6