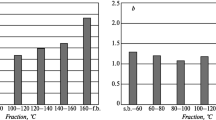
A destructive process of hydroisomerization of straight-run 85–185°C gasoline fraction followed by close fractionation of the products into a high-octane low-boiling (–85°C) isocomponent and a fraction with a final BP of 85°C is proposed. The latter is free of benzene-forming hydrocarbons and is submitted to catalytic reforming under mild conditions. Gasoline with octane number 86 (MM) and containing ~51 wt. % of aromatic hydrocarbons, including less than 0.5 wt. % of benzene, is obtained by compounding the isocomponent and the reformate in 25:75 ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. I. Levinbuk, E. F. Kaminskii, and O. F. Glagoleva, Khim. Tekhnol. Topl. Masel, No. 2, 6-11 (2000).
B. K. Nefedov, Neftekhim., 39, No. 5, 343-352 (1999).
USSR Author’s Certificate 727213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 2, pp. 31 – 33, March – April, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abad-Zade, K.I., Gasymova, Z.A., Mukhtarova, G.S. et al. Destructive hydroisomerization – A new method of reducing benzine content in commercial gasoline. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 48, 130–134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-012-0348-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-012-0348-x