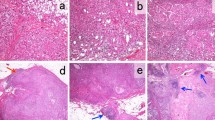
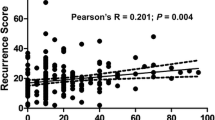
Abstract
Purpose
The present study evaluated whether morphological-measured stromal and intra-tumour tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) levels were associated with gene expression profiles, and whether TILs-associated genomic signature (GS) could be used to predict clinical outcomes and response to therapies in several breast cancer subtypes.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated haematoxylin eosin (HE)-TILs levels and gene expression profiling data from 40 patients with primary breast cancer and extracted the 22 overexpressed genes in cases with high TILs scores as the TILs-GS. The TILs-GS were compared with breast cancer subtype and were evaluated predictive values for prognosis and response to therapies.
Results
Higher TILs-GS expressions were observed for triple-negative and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive (+) breast cancers, compared to the luminal types (P < 0.001). With the exception of HER2+, the TILs-GS had no prognostic value in subtypes of breast cancers. The Wilcoxon test revealed significantly different TILs-GS levels between the cases with pathological complete response (pCR) and residual disease after anthracycline and taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, with the exception of the luminal-low proliferation subtype. In the multivariate analysis, pCR was independently associated with smaller tumour size, higher histological grade, ER negativity, HER2 positivity and higher TILs-GS scores (OR 2.02, 95% CI 1.30–3.14, P = 0.025).
Conclusions
TILs-GS was associated with stromal and intra-tumour TILs levels, as evaluated using HE, which predicted prognosis and chemotherapy response in several breast cancer subtypes. Further studies are needed to perform stratification according to TILs-GS levels and the conventional breast cancer subtypes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HR:
-
Hormone receptor
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- TILs:
-
Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin eosin
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- NAC:
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- TN:
-
ER−/HER2−
- DEFS:
-
Distant event-free survival
- pCR:
-
Pathological complete response
- RD:
-
Residual disease
References
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, Baehner FL, Walker MG, Watson D, Park T, Hiller W, Fisher ER, Wickerham DL, Bryant J, Wolmark N (2004) A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 351(27):2817–2826. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa041588
Sotiriou C, Pusztai L (2009) Gene-expression signatures in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 360(8):790–800. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0801289
Sparano JA, Gray RJ, Makower DF, Pritchard KI, Albain KS, Hayes DF, Geyer CE Jr, Dees EC, Perez EA, Olson JA Jr, Zujewski J, Lively T, Badve SS, Saphner TJ, Wagner LI, Whelan TJ, Ellis MJ, Paik S, Wood WC, Ravdin P, Keane MM, Gomez Moreno HL, Reddy PS, Goggins TF, Mayer IA, Brufsky AM, Toppmeyer DL, Kaklamani VG, Atkins JN, Berenberg JL, Sledge GW (2015) Prospective validation of a 21-gene expression assay in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 373(21):2005–2014. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1510764
Cardoso F, van’t Veer LJ, Bogaerts J, Slaets L, Viale G, Delaloge S, Pierga JY, Brain E, Causeret S, DeLorenzi M, Glas AM, Golfinopoulos V, Goulioti T, Knox S, Matos E, Meulemans B, Neijenhuis PA, Nitz U, Passalacqua R, Ravdin P, Rubio IT, Saghatchian M, Smilde TJ, Sotiriou C, Stork L, Straehle C, Thomas G, Thompson AM, van der Hoeven JM, Vuylsteke P, Bernards R, Tryfonidis K, Rutgers E, Piccart M, Investigators M (2016) 70-Gene signature as an aid to treatment decisions in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med 375(8):717–729. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1602253
Kondo M, Hoshi SL, Ishiguro H, Yoshibayashi H, Toi M (2008) Economic evaluation of 21-gene reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay in lymph-node-negative, estrogen-receptor-positive, early-stage breast cancer in Japan. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112(1):175–187. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9842-y
Tsoi DT, Inoue M, Kelly CM, Verma S, Pritchard KI (2010) Cost-effectiveness analysis of recurrence score-guided treatment using a 21-gene assay in early breast cancer. Oncologist 15(5):457–465. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0275
Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, Martino S, Wang M, Jones VE, Saphner TJ, Wolff AC, Wood WC, Davidson NE, Sledge GW, Sparano JA, Badve SS (2014) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol 32(27):2959–2966. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.55.0491
Dieci MV, Mathieu MC, Guarneri V, Conte P, Delaloge S, Andre F, Goubar A (2015) Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials. Ann Oncol 26(8):1698–1704. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv239
West NR, Milne K, Truong PT, Macpherson N, Nelson BH, Watson PH (2011) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes predict response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13(6):R126. doi:10.1186/bcr3072
Ibrahim EM, Al-Foheidi ME, Al-Mansour MM, Kazkaz GA (2014) The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 148(3):467–476. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-3185-2
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, Panel M (2015) Tailoring therapies–improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol 26(8):1533–1546. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv221
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, Wienert S, Van den Eynden G, Baehner FL, Penault-Llorca F, Perez EA, Thompson EA, Symmans WF, Richardson AL, Brock J, Criscitiello C, Bailey H, Ignatiadis M, Floris G, Sparano J, Kos Z, Nielsen T, Rimm DL, Allison KH, Reis-Filho JS, Loibl S, Sotiriou C, Viale G, Badve S, Adams S, Willard-Gallo K, Loi S, International TWG (2015) The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol 26(2):259–271. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu450
Varga Z, Diebold J, Dommann-Scherrer C, Frick H, Kaup D, Noske A, Obermann E, Ohlschlegel C, Padberg B, Rakozy C, Sancho Oliver S, Schobinger-Clement S, Schreiber-Facklam H, Singer G, Tapia C, Wagner U, Mastropasqua MG, Viale G, Lehr HA (2012) How reliable is Ki-67 immunohistochemistry in grade 2 breast carcinomas? A QA study of the Swiss Working Group of Breast- and Gynecopathologists. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37379. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037379
Polley MY, Leung SC, McShane LM, Gao D, Hugh JC, Mastropasqua MG, Viale G, Zabaglo LA, Penault-Llorca F, Bartlett JM, Gown AM, Symmans WF, Piper T, Mehl E, Enos RA, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group of the Breast International G, North American Breast Cancer G (2013) An international Ki67 reproducibility study. J Natl Cancer Inst 105(24):1897–1906. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt306
Swisher SK, Wu Y, Castaneda CA, Lyons GR, Yang F, Tapia C, Wang X, Casavilca SA, Bassett R, Castillo M, Sahin A, Mittendorf EA (2016) Interobserver agreement between pathologists assessing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer using methodology proposed by the International TILs Working Group. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-016-5173-8
Hida AI, Ohi Y (2015) Evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer; proposal of a simpler method. Ann Oncol 26(11):2351. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv363
Symmans WF, Ayers M, Clark EA, Stec J, Hess KR, Sneige N, Buchholz TA, Krishnamurthy S, Ibrahim NK, Buzdar AU, Theriault RL, Rosales MF, Thomas ES, Gwyn KM, Green MC, Syed AR, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2003) Total RNA yield and microarray gene expression profiles from fine-needle aspiration biopsy and core-needle biopsy samples of breast carcinoma. Cancer 97(12):2960–2971. doi:10.1002/cncr.11435
Pusztai L, Ayers M, Stec J, Clark E, Hess K, Stivers D, Damokosh A, Sneige N, Buchholz TA, Esteva FJ, Arun B, Cristofanilli M, Booser D, Rosales M, Valero V, Adams C, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF (2003) Gene expression profiles obtained from fine-needle aspirations of breast cancer reliably identify routine prognostic markers and reveal large-scale molecular differences between estrogen-negative and estrogen-positive tumors. Clin Cancer Res 9(7):2406–2415
Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, Van Eenoo F, Rouas G, Francis P, Crown JP, Hitre E, de Azambuja E, Quinaux E, Di Leo A, Michiels S, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2013) Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J Clin Oncol 31(7):860–867. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0902
Gong Y, Yan K, Lin F, Anderson K, Sotiriou C, Andre F, Holmes FA, Valero V, Booser D, Pippen JE Jr, Vukelja S, Gomez H, Mejia J, Barajas LJ, Hess KR, Sneige N, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L, Symmans WF (2007) Determination of oestrogen-receptor status and ERBB2 status of breast carcinoma: a gene-expression profiling study. Lancet Oncol 8(3):203–211. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70042-6
Iwamoto T, Bianchini G, Booser D, Qi Y, Coutant C, Shiang CY, Santarpia L, Matsuoka J, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Holmes FA, O’Shaughnessy J, Hellerstedt B, Pippen J, Andre F, Simon R, Pusztai L (2011) Gene pathways associated with prognosis and chemotherapy sensitivity in molecular subtypes of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(3):264–272. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq524
Bianchini G, Iwamoto T, Qi Y, Coutant C, Shiang CY, Wang B, Santarpia L, Valero V, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Gianni L, Pusztai L (2010) Prognostic and therapeutic implications of distinct kinase expression patterns in different subtypes of breast cancer. Cancer Res 70(21):8852–8862. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1039
Altman DG, Lausen B, Sauerbrei W, Schumacher M (1994) Dangers of using “optimal” cutpoints in the evaluation of prognostic factors. J Natl Cancer Inst 86(11):829–835
Gu-Trantien C, Loi S, Garaud S, Equeter C, Libin M, de Wind A, Ravoet M, Le Buanec H, Sibille C, Manfouo-Foutsop G, Veys I, Haibe-Kains B, Singhal SK, Michiels S, Rothe F, Salgado R, Duvillier H, Ignatiadis M, Desmedt C, Bron D, Larsimont D, Piccart M, Sotiriou C, Willard-Gallo K (2013) CD4(+) follicular helper T cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival. J Clin Invest 123(7):2873–2892. doi:10.1172/JCI67428
Bianchini G, Qi Y, Alvarez RH, Iwamoto T, Coutant C, Ibrahim NK, Valero V, Cristofanilli M, Green MC, Radvanyi L, Hatzis C, Hortobagyi GN, Andre F, Gianni L, Symmans WF, Pusztai L (2010) Molecular anatomy of breast cancer stroma and its prognostic value in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative cancers. J Clin Oncol 28(28):4316–4323. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.27.2419
Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Bono P, Kataja V, Desmedt C, Piccart MJ, Loibl S, Denkert C, Smyth MJ, Joensuu H, Sotiriou C (2014) Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol 25(8):1544–1550. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu112
Vinayak S, Gray R, Adams S (2014) Association of increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) with immunomodulatory (IM) triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtype and response to neoadjuvant platinum-based therapy in PrECOG0105. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.65.6595
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, Pfitzner BM, Salat C, Loi S, Schmitt WD, Schem C, Fisch K, Darb-Esfahani S, Mehta K, Sotiriou C, Wienert S, Klare P, Andre F, Klauschen F, Blohmer JU, Krappmann K, Schmidt M, Tesch H, Kummel S, Sinn P, Jackisch C, Dietel M, Reimer T, Untch M, Loibl S (2015) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 33(9):983–991. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.58.1967
Callari M, Cappelletti V, D’Aiuto F, Musella V, Lembo A, Petel F, Karn T, Iwamoto T, Provero P, Daidone MG, Gianni L, Bianchini G (2016) Subtype-specific metagene-based prediction of outcome after neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 22(2):337–345. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0757
Hayes DF, Thor AD, Dressler LG, Weaver D, Edgerton S, Cowan D, Broadwater G, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, Ingle JN, Henderson IC, Norton L, Winer EP, Hudis CA, Ellis MJ, Berry DA, Cancer, Leukemia Group BI (2007) HER2 and response to paclitaxel in node-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 357(15):1496–1506. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa071167
Penault-Llorca F, Andre F, Sagan C, Lacroix-Triki M, Denoux Y, Verriele V, Jacquemier J, Baranzelli MC, Bibeau F, Antoine M, Lagarde N, Martin AL, Asselain B, Roche H (2009) Ki67 expression and docetaxel efficacy in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(17):2809–2815. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.18.2808
Nitz U, Gluz O, Huober J, Kreipe HH, Kates RE, Hartmann A, Erber R, Scholz M, Lisboa B, Mohrmann S, Mobus V, Augustin D, Hoffmann G, Weiss E, Bohmer S, Kreienberg R, Du Bois A, Sattler D, Thomssen C, Kiechle M, Janicke F, Wallwiener D, Harbeck N, Kuhn W (2014) Final analysis of the prospective WSG-AGO EC-Doc versus FEC phase III trial in intermediate-risk (pN1) early breast cancer: efficacy and predictive value of Ki67 expression. Ann Oncol 25(8):1551–1557. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu186
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K, Costantino JP, Wolmark N, Bonnefoi H, Cameron D, Gianni L, Valagussa P, Swain SM, Prowell T, Loibl S, Wickerham DL, Bogaerts J, Baselga J, Perou C, Blumenthal G, Blohmer J, Mamounas EP, Bergh J, Semiglazov V, Justice R, Eidtmann H, Paik S, Piccart M, Sridhara R, Fasching PA, Slaets L, Tang S, Gerber B, Geyer CE Jr, Pazdur R, Ditsch N, Rastogi P, Eiermann W, von Minckwitz G (2014) Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 384(9938):164–172. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62422-8
Perez EA, Thompson EA, Ballman KV, Anderson SK, Asmann YW, Kalari KR, Eckel-Passow JE, Dueck AC, Tenner KS, Jen J, Fan JB, Geiger XJ, McCullough AE, Chen B, Jenkins RB, Sledge GW, Winer EP, Gralow JR, Reinholz MM (2015) Genomic analysis reveals that immune function genes are strongly linked to clinical outcome in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group n9831 Adjuvant Trastuzumab Trial. J Clin Oncol 33(7):701–708. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.57.6298
Salgado R, Denkert C, Campbell C, Savas P, Nuciforo P, Aura C, de Azambuja E, Eidtmann H, Ellis CE, Baselga J, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Michiels S, Bradbury I, Sotiriou C, Loi S (2015) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and associations with pathological complete response and event-free survival in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer treated with lapatinib and trastuzumab: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO TRIAL. JAMA Oncol 1(4):448–454. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0830
Dushyanthen S, Beavis PA, Savas P, Teo ZL, Zhou C, Mansour M, Darcy PK, Loi S (2015) Relevance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. BMC Med 13:202. doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0431-3
Perez EA, Ballman KV, Tenner KS, Thompson EA, Badve SS, Bailey H, Baehner FL (2016) Association of stromal tumor-Infiltrating lymphocytes with recurrence-free survival in the N9831 adjuvant trial in patients with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer. JAMA Oncol 2(1):56–64. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.3239
Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A, Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C, Vermaelen K, Panaretakis T, Mignot G, Ullrich E, Perfettini JL, Schlemmer F, Tasdemir E, Uhl M, Genin P, Civas A, Ryffel B, Kanellopoulos J, Tschopp J, Andre F, Lidereau R, McLaughlin NM, Haynes NM, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L (2009) Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat Med 15(10):1170–1178. doi:10.1038/nm.2028
Umansky V, Sevko A (2012) Overcoming immunosuppression in the melanoma microenvironment induced by chronic inflammation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61(2):275–282. doi:10.1007/s00262-011-1164-6
Ma Y, Adjemian S, Mattarollo SR, Yamazaki T, Aymeric L, Yang H, Portela Catani JP, Hannani D, Duret H, Steegh K, Martins I, Schlemmer F, Michaud M, Kepp O, Sukkurwala AQ, Menger L, Vacchelli E, Droin N, Galluzzi L, Krzysiek R, Gordon S, Taylor PR, Van Endert P, Solary E, Smyth MJ, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2013) Anticancer chemotherapy-induced intratumoral recruitment and differentiation of antigen-presenting cells. Immunity 38(4):729–741. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.03.003
Dunbier AK, Ghazoui Z, Anderson H, Salter J, Nerurkar A, Osin P, A’Hern R, Miller WR, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2013) Molecular profiling of aromatase inhibitor-treated postmenopausal breast tumors identifies immune-related correlates of resistance. Clin Cancer Res 19(10):2775–2786. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1000
Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ (2011) Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 331(6024):1565–1570. doi:10.1126/science.1203486
Fan C, Oh DS, Wessels L, Weigelt B, Nuyten DS, Nobel AB, van’t Veer LJ, Perou CM (2006) Concordance among gene-expression-based predictors for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 355(6):560–569. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052933
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10549_2017_4502_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementry Fig. 1. Kaplan-Meier curves according to tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes gene signatures in the tamoxifen-treated data set. Kaplan-Meier curves for (a) luminal-low and (b) luminal-high breast cancer were compared using the log-rank test. Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for distant event-free survival were estimated using Cox regression analysis. Supplementry Fig. 2. Neoadjuvant therapy responses and tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes gene signatures among HER2 + cases in the trastuzumab-treated data set. The boxplots show the associations between tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes gene signatures (TILs-GS) and neoadjuvant therapy response. P-values were calculated using Wilcoxon’s test. pCR pathological complete response, RD residual disease. Supplementary material 1 (PPTX 86 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kochi, M., Iwamoto, T., Niikura, N. et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)-related genomic signature predicts chemotherapy response in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 167, 39–47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4502-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4502-3