Abstract
Purpose
Despite robust antitumor activity in diverse preclinical models, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor agonists have not demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, underscoring the need to identify agents that enhance their activity. We postulated that the metabolic stress induced by the diabetes drug metformin would sensitize breast cancer cells to TRAIL receptor agonists.
Methods
Human triple (estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2)-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines were treated with TRAIL receptor agonists (monoclonal antibodies or TRAIL peptide), metformin, or the combination. The effects on cell survival, caspase activation, and expression of TRAIL receptors and the antiapoptotic protein XIAP were determined. In addition, XIAP was silenced by RNAi in TNBC cells and the effects on sensitivity to TRAIL were determined. The antitumor effects of metformin, TRAIL, or the combination were evaluated in an orthotopic model of metastatic TNBC.
Results
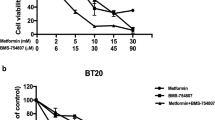
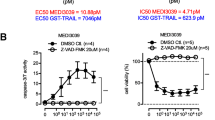
Metformin sensitized diverse TNBC cells to TRAIL receptor agonists. Metformin selectively enhanced the sensitivity of transformed breast epithelial cells to TRAIL receptor agonist-induced caspase activation and apoptosis with little effect on untransformed breast epithelial cells. These effects of metformin were accompanied by robust reductions in the protein levels of XIAP, a negative regulator of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Silencing XIAP in TNBC cells mimicked the TRAIL-sensitizing effects of metformin. Metformin also enhanced the antitumor effects of TRAIL in a metastatic murine TNBC model.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that metformin enhances the activity of TRAIL receptor agonists, thereby supporting the rationale for additional translational studies combining these agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi A (2015) Targeting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in cancer: lessons learned and future directions. J Clin Invest 125(2):487–489
de Miguel D, Lemke J, Anel A, Walczak H, Martinez-Lostao L (2016) Onto better TRAILs for cancer treatment. Cell Death Differ 23(5):733–747
Plummer R, Attard G, Pacey S, Li L, Razak A, Perrett R, Barrett M, Judson I, Kaye S, Fox NL et al (2007) Phase 1 and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res 13(20):6187–6194
Soria JC, Smit E, Khayat D, Besse B, Yang X, Hsu CP, Reese D, Wiezorek J, Blackhall F (2010) Phase 1b study of dulanermin (recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL) in combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(9):1527–1533
Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG, Kurzrock R, Ebbinghaus S, O’Dwyer PJ, Gordon MS, Novotny W, Goldwasser MA, Tohnya TM, Lum BL et al (2010) Phase I dose-escalation study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(17):2839–2846
Leong S, Cohen RB, Gustafson DL, Langer CJ, Camidge DR, Padavic K, Gore L, Smith M, Chow LQ, von Mehren M et al (2009) Mapatumumab, an antibody targeting TRAIL-R1, in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid malignancies: results of a phase I and pharmacokinetic study. J Clin Oncol 27(26):4413–4421
Merchant MS, Geller JI, Baird K, Chou AJ, Galli S, Charles A, Amaoko M, Rhee EH, Price A, Wexler LH et al (2012) Phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in pediatric patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 30(33):4141–4147
Fuchs CS, Fakih M, Schwartzberg L, Cohn AL, Yee L, Dreisbach L, Kozloff MF, Hei YJ, Galimi F, Pan Y et al (2013) TRAIL receptor agonist conatumumab with modified FOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase 1b/2 trial. Cancer 119(24):4290–4298
Inoue S, Mai A, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2006) Inhibition of histone deacetylase class I but not class II is critical for the sensitization of leukemic cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 66(13):6785–6792
Lu M, Strohecker A, Chen F, Kwan T, Bosman J, Jordan VC, Cryns VL (2008) Aspirin sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by reducing survivin levels. Clin Cancer Res 14(10):3168–3176
Lu M, Kwan T, Yu C, Chen F, Freedman B, Schafer JM, Lee EJ, Jameson JL, Jordan VC, Cryns VL (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists promote TRAIL-induced apoptosis by reducing survivin levels via cyclin D3 repression and cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem 280(8):6742–6751
Zhao L, Yue P, Khuri FR, Sun SY (2013) mTOR complex 2 is involved in regulation of Cbl-dependent c-FLIP degradation and sensitivity of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 73(6):1946–1957
Abdulghani J, Allen JE, Dicker DT, Liu YY, Goldenberg D, Smith CD, Humphreys R, El-Deiry WS (2013) Sorafenib sensitizes solid tumors to Apo2L/TRAIL and Apo2L/TRAIL receptor agonist antibodies by the Jak2-Stat3-Mcl1 axis. PLoS ONE 8(9):e75414
Strekalova E, Malin D, Good DM, Cryns VL (2015) Methionine deprivation induces a targetable vulnerability in triple-negative breast cancer cells by enhancing TRAIL receptor-2 expression. Clin Cancer Res 21(12):2780–2791
Corominas-Faja B, Quirantes-Pine R, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A, Cufi S, Martin-Castillo B, Micol V, Joven J, Segura-Carretero A, Menendez JA (2012) Metabolomic fingerprint reveals that metformin impairs one-carbon metabolism in a manner similar to the antifolate class of chemotherapy drugs. Aging (Albany NY) 4(7):480–498
Cabreiro F, Au C, Leung KY, Vergara-Irigaray N, Cocheme HM, Noori T, Weinkove D, Schuster E, Greene ND, Gems D (2013) Metformin retards aging in C. elegans by altering microbial folate and methionine metabolism. Cell 153(1):228–239
Martin-Montalvo A, Mercken EM, Mitchell SJ, Palacios HH, Mote PL, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Gomes AP, Ward TM, Minor RK, Blouin MJ et al (2013) Metformin improves healthspan and lifespan in mice. Nat Commun 4:2192
Foretz M, Guigas B, Bertrand L, Pollak M, Viollet B (2014) Metformin: from mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab 20(6):953–966
Chae YK, Arya A, Malecek MK, Shin DS, Carneiro B, Chandra S, Kaplan J, Kalyan A, Altman JK, Platanias L et al (2016) Repurposing metformin for cancer treatment: current clinical studies. Oncotarget 7(26):40767–40780
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM (2009) New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(9):1620–1625
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Jenkins-Jones S, Gale EA, Johnson JA, Morgan CL (2012) Mortality after incident cancer in people with and without type 2 diabetes: impact of metformin on survival. Diabetes Care 35(2):299–304
Zhang P, Li H, Tan X, Chen L, Wang S (2013) Association of metformin use with cancer incidence and mortality: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol 37(3):207–218
Niraula S, Dowling RJ, Ennis M, Chang MC, Done SJ, Hood N, Escallon J, Leong WL, McCready DR, Reedijk M et al (2012) Metformin in early breast cancer: a prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135(3):821–830
Malin D, Strekalova E, Petrovic V, Deal AM, Al Ahmad A, Adamo B, Miller CR, Ugolkov A, Livasy C, Fritchie K et al (2014) αB-crystallin: a novel regulator of breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Clin Cancer Res 20(1):56–67
Moyano JV, Evans JR, Chen F, Lu M, Werner ME, Yehiely F, Diaz LK, Turbin D, Karaca G, Wiley E et al (2006) αB-crystallin is a novel oncoprotein that predicts poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. J Clin Invest 116(1):261–270
Malin D, Chen F, Schiller C, Koblinski J, Cryns VL (2011) Enhanced metastasis suppression by targeting TRAIL receptor 2 in a murine model of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17(15):5005–5015
Cummins JM, Kohli M, Rago C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Bunz F (2004) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is a nonredundant modulator of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 64(9):3006–3008
Deng Y, Lin Y, Wu X (2002) TRAIL-induced apoptosis requires Bax-dependent mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO. Genes Dev 16(1):33–45
Do MT, Kim HG, Choi JH, Jeong HG (2014) Metformin induces microRNA-34a to downregulate the Sirt1/Pgc-1alpha/Nrf2 pathway, leading to increased susceptibility of wild-type p53 cancer cells to oxidative stress and therapeutic agents. Free Radic Biol Med 74:21–34
Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee JH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Eo SK, Lee JH, Park SY (2016) Activation of autophagy flux by metformin downregulates cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein and enhances TRAIL- induced apoptosis. Oncotarget 7(17):23468–23481
Tanaka R, Tomosugi M, Horinaka M, Sowa Y, Sakai T (2015) Metformin causes G1-phase arrest via down-regulation of MiR-221 and enhances TRAIL sensitivity through DR5 Up-regulation in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0125779
Zhang T, Wang X, He D, Jin X, Guo P (2014) Metformin sensitizes human bladder cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through mTOR/S6K1-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP. Anticancer Drugs 25(8):887–897
Chandel NS, Avizonis D, Reczek CR, Weinberg SE, Menz S, Neuhaus R, Christian S, Haegebarth A, Algire C, Pollak M (2016) Are metformin doses used in murine cancer models clinically relevant? Cell Metab 23(4):569–570
Wahdan-Alaswad R, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Liu B, Deng XS, Arnadottir SS, Richer JK, Anderson SM, Thor AD (2013) Glucose promotes breast cancer aggression and reduces metformin efficacy. Cell Cycle 12(24):3759–3769
Herold CI, Anders CK (2013) New targets for triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 27(9):846–854
Yan H, Frost P, Shi Y, Hoang B, Sharma S, Fisher M, Gera J, Lichtenstein A (2006) Mechanism by which mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors sensitize multiple myeloma cells to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 66(4):2305–2313
Allensworth JL, Aird KM, Aldrich AJ, Batinic-Haberle I, Devi GR (2012) XIAP inhibition and generation of reactive oxygen species enhances TRAIL sensitivity in inflammatory breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 11(7):1518–1527
Tseng HY, Chen LH, Ye Y, Tay KH, Jiang CC, Guo ST, Jin L, Hersey P, Zhang XD (2012) The melanoma-associated antigen MAGE-D2 suppresses TRAIL receptor 2 and protects against TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Carcinogenesis 33(10):1871–1881
Panner A, James CD, Berger MS, Pieper RO (2005) mTOR controls FLIPS translation and TRAIL sensitivity in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Mol Cell Biol 25(20):8809–8823
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr. Robin Humphreys for providing mapatumumab and lexatumumab.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (VLC), the Department of Defense PC150221P1 (VLC), and P30CA14520 University of Wisconsin Comprehensive Cancer Center core facility support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strekalova, E., Malin, D., Rajanala, H. et al. Metformin sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to proapoptotic TRAIL receptor agonists by suppressing XIAP expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 163, 435–447 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4201-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4201-0