Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the prevalence of and factors associated with internal mammary node (IMN) adenopathy on MRI and PET/CT used for initial staging in patients with operable breast cancer.
Methods
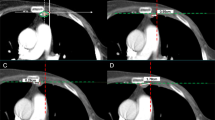
A total of 1320 patients diagnosed with invasive breast carcinoma between January 2011 and December 2015 underwent MRI and PET/CT for initial staging. The patients were considered to have IMN adenopathy when MRI revealed IMNs with the longest diameter of 5 mm or greater and a standardized uptake value greater than that of the mediastinal blood pool/contralateral parasternal area on PET/CT. The prevalence was determined as overall percentage of patients with IMN adenopathy, as well as percentages among patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and those who did not. The association of IMN adenopathy with factors was evaluated using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
Of the 1320 patients, 35 patients [2.7 %; 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.8–3.6 %] had IMN adenopathy, with a total of 49 IMNs. Among patients without and with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (n = 1092 and n = 228, respectively), IMN adenopathy was identified in 13 (1.2 %; 95 % CI 0.6–2.0 %) and 22 patients (9.6 %; 95 % CI 6.0–14.6 %), respectively. Inner tumor location [odds ratio (OR) 5.9; P = .002] and positive axillary lymph node status (OR 4.4; P < .0001) were associated with IMN adenopathy.
Conclusions
IMN adenopathy was identified at initial staging with PET/CT and MRI with a prevalence of 2.7 %. Inner tumor location and positive axillary lymph node status were associated with IMN adenopathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark G, Edge SB, Hayes DF, Hughes LL, Hutter RV, Morrow M, Page DL, Recht A, Theriault RL, Thor A, Weaver DL, Wieand HS, Greene FL (2002) Revision of the American joint committee on cancer staging system for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 20(17):3628–3636
Veronesi U, Arnone P, Veronesi P, Galimberti V, Luini A, Rotmensz N, Botteri E, Ivaldi GB, Leonardi MC, Viale G, Sagona A, Paganelli G, Panzeri R, Orecchia R (2008) The value of radiotherapy on metastatic internal mammary nodes in breast cancer. Results on a large series. Ann Oncol 19(9):1553–1560. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn183
Stemmer SM, Rizel S, Hardan I, Adamo A, Neumann A, Goffman J, Brenner HJ, Pfeffer MR (2003) The role of irradiation of the internal mammary lymph nodes in high-risk stage II to IIIA breast cancer patients after high-dose chemotherapy: a prospective sequential nonrandomized study. J Clin Oncol 21(14):2713–2718. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.09.096
Thorsen LB, Offersen BV, Dano H, Berg M, Jensen I, Pedersen AN, Zimmermann SJ, Brodersen HJ, Overgaard M, Overgaard J (2015) DBCG-IMN: a population-based cohort study on the effect of internal mammary node irradiation in early node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.63.6456
Poortmans PM, Collette S, Kirkove C, Van Limbergen E, Budach V, Struikmans H, Collette L, Fourquet A, Maingon P, Valli M, De Winter K, Marnitz S, Barillot I, Scandolaro L, Vonk E, Rodenhuis C, Marsiglia H, Weidner N, van Tienhoven G, Glanzmann C, Kuten A, Arriagada R, Bartelink H, Van den Bogaert W, Oncology ER, Breast Cancer G (2015) Internal mammary and medial supraclavicular irradiation in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 373(4):317–327. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415369
Chen RC, Lin NU, Golshan M, Harris JR, Bellon JR (2008) Internal mammary nodes in breast cancer: diagnosis and implications for patient management—A systematic review. J Clin Oncol 26(30):4981–4989. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.4862
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, Bennet AM, Blom-Goldman U, Bronnum D, Correa C, Cutter D, Gagliardi G, Gigante B, Jensen MB, Nisbet A, Peto R, Rahimi K, Taylor C, Hall P (2013) Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 368(11):987–998. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1209825
Byrd DR, Dunnwald LK, Mankoff DA, Anderson BO, Moe RE, Yeung RS, Schubert EK, Eary JF (2001) Internal mammary lymph node drainage patterns in patients with breast cancer documented by breast lymphoscintigraphy. Ann Surg Oncol 8(3):234–240
Carcoforo P, Sortini D, Feggi L, Feo CV, Soliani G, Panareo S, Corcione S, Querzoli P, Maravegias K, Lanzara S, Liboni A (2006) Clinical and therapeutic importance of sentinel node biopsy of the internal mammary chain in patients with breast cancer: a single-center study with long-term follow-up. Ann Surg Oncol 13(10):1338–1343. doi:10.1245/s10434-006-9062-4
Madsen E, Gobardhan P, Bongers V, Albregts M, Burgmans J, De Hooge P, Van Gorp J, van Dalen T (2007) The impact on post-surgical treatment of sentinel lymph node biopsy of internal mammary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 14(4):1486–1492. doi:10.1245/s10434-006-9230-6
Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS, Carter WB, Bhargavan M, Lewis RS, Ioffe OB (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology 233(3):830–849. doi:10.1148/radiol.2333031484
Plana MN, Carreira C, Muriel A, Chiva M, Abraira V, Emparanza JI, Bonfill X, Zamora J (2012) Magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative assessment of patients with primary breast cancer: systematic review of diagnostic accuracy and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 22(1):26–38. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2238-8
Cermik TF, Mavi A, Basu S, Alavi A (2008) Impact of FDG PET on the preoperative staging of newly diagnosed breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35(3):475–483. doi:10.1007/s00259-007-0580-5
Groheux D, Espie M, Giacchetti S, Hindie E (2013) Performance of FDG PET/CT in the clinical management of breast cancer. Radiology 266(2):388–405. doi:10.1148/radiol.12110853
Aukema TS, Straver ME, Peeters MJ, Russell NS, Gilhuijs KG, Vogel WV, Rutgers EJ, Olmos RA (2010) Detection of extra-axillary lymph node involvement with FDG PET/CT in patients with stage II-III breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 46(18):3205–3210. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.034
Kinoshita T, Odagiri K, Andoh K, Doiuchi T, Sugimura K, Shiotani S, Asaga T (1999) Evaluation of small internal mammary lymph node metastases in breast cancer by MRI. Radiat Med 17(3):189–193
Jochelson MS, Lebron L, Jacobs SS, Zheng J, Moskowitz CS, Powell SN, Sacchini V, Ulaner GA, Morris EA, Dershaw DD (2015) Detection of internal mammary adenopathy in patients with breast cancer by PET/CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 205(4):899–904. doi:10.2214/AJR.14.13804
An YY, Kim SH, Kang BJ, Lee AW (2015) Comparisons of positron emission tomography/computed tomography and ultrasound imaging for detection of internal mammary lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer and pathologic correlation by ultrasound-guided biopsy procedures. J Ultrasound Med 34(8):1385–1394. doi:10.7863/ultra.34.8.1385
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM (1998) Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol 11(2):155–168
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M, Fitzgibbons P, Hanna W, Jenkins RB, Mangu PB, Paik S, Perez EA, Press MF, Spears PA, Vance GH, Viale G, Hayes DF, American Society of Clinical O, College of American P (2013) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: american society of clinical oncology/college of American pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31(31):3997–4013. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984
Caceres E (1963) Incidence of metastasis in the internal mammary chain in operable carcinoma of the breast and 5 year results. Acta Unio Int Contra Cancrum 19:1566–1569
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Greco M, Bufalino R, Morabito A, Galluzzo D, Conti R, De Lellis R, Delle Donne V, Piotti P et al (1985) Prognosis of breast cancer patients after mastectomy and dissection of internal mammary nodes. Ann Surg 202(6):702–707
Sardanelli F, Boetes C, Borisch B, Decker T, Federico M, Gilbert FJ, Helbich T, Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Kaiser WA, Kerin MJ, Mansel RE, Marotti L, Martincich L, Mauriac L, Meijers-Heijboer H, Orecchia R, Panizza P, Ponti A, Purushotham AD, Regitnig P, Del Turco MR, Thibault F, Wilson R (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: recommendations from the EUSOMA working group. Eur J Cancer 46(8):1296–1316. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.015
Sardanelli F (2010) Additional findings at preoperative MRI: a simple golden rule for a complex problem? Breast Cancer Res Treat 124(3):717–721. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1144-0
Orel S (2008) Who should have breast magnetic resonance imaging evaluation? J Clin Oncol 26(5):703–711. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.3594
Wang CL, Eissa MJ, Rogers JV, Aravkin AY, Porter BA, Beatty JD (2013) 18F-FDG PET/CT-positive internal mammary lymph nodes: pathologic correlation by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and assessment of associated risk factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200(5):1138–1144. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.8754
Huang O, Wang L, Shen K, Lin H, Hu Z, Liu G, Wu J, Lu J, Shao Z, Han Q, Shen Z (2008) Breast cancer subpopulation with high risk of internal mammary lymph nodes metastasis: analysis of 2269 Chinese breast cancer patients treated with extended radical mastectomy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 107(3):379–387. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9561-4
Eubank WB, Mankoff DA, Takasugi J, Vesselle H, Eary JF, Shanley TJ, Gralow JR, Charlop A, Ellis GK, Lindsley KL, Austin-Seymour MM, Funkhouser CP, Livingston RB (2001) 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to detect mediastinal or internal mammary metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 19(15):3516–3523
Mack M, Chetlen A, Liao J (2015) Incidental internal mammary lymph nodes visualized on screening breast MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 205(1):209–214. doi:10.2214/AJR.14.13586
Ray KM, Munir R, Wisner DJ, Azziz A, Holland BC, Kornak J, Joe BN (2015) Internal mammary lymph nodes as incidental findings at screening breast MRI. Clin Imaging 39(5):791–793. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.05.011
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Biomedical Research Institute Grant, Kyungpook National University Hospital (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheon, H., Kim, H.J., Lee, SW. et al. Internal mammary node adenopathy on breast MRI and PET/CT for initial staging in patients with operable breast cancer: prevalence and associated factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 160, 523–530 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-4022-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-4022-6