Abstract
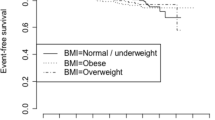
The association between obesity and prognosis in early breast cancer (EBC) is unclear, especially when aggressive phenotypes are considered. We evaluated the influence of BMI on the prognosis of women with high-risk EBC enrolled in a phase III trial of adjuvant chemotherapy (CT). The association was assessed in 1066 patients with rapidly proliferating tumors, randomized to receive adjuvant CT with or without anthracyclines. Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated by Kaplan–Meier; multivariate analysis was performed according to age, tumor size, nodal, estrogen receptor (ER), and HER2 status and type of CT. Information on BMI was available for 959 women. Of these, 529 (55.2 %) were overweight or obese. Median age was 52 years. A total of 457 (47.7 %) patients had nodal involvement. Centralized pathology was performed in 850 cases: 522 (61.4 %) were ER positive, and 194 (22.8 %) were HER-2 positive. At a median follow-up of 103 months (range 1–188), 5-year DFS was 81 % (95 % CI 77–85), 82 % (95 % CI 77–86), and 76 % (95 % CI 70–83), in normal, overweight, and obese women, respectively (p = 0.44). Five-year OS was 92 % (95 % CI 89–95), 94 % (95 % CI 91–96), and 89 % (95 % CI 84–93), respectively (p = 0.60). BMI was not associated by multivariate analysis with differences in DFS or OS. Higher BMI had no influence on prognosis in high-risk EBC patients treated with CT. These data are consistent with prior observations and suggest that in aggressive biological subtypes, the impact of host factors on patient prognosis is minor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303:235–241
Finkelstein EA, Trogdon JG, Cohen JW, Dietz W (2009) Annual medical spending attributable to obesity: payer-and-service-specific estimates. Health Aff (Millwod) 28:w22–w831
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M (2008) Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 371:569–578
Calle E, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun M (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med 348:1625–1638
Bergstrom A, Pisani P, Tenet V, Wolk A, Adami HO (2001) Overweight as an avoidable cause of cancer in Europe. Int J Cancer 91:421–430
Arnold M, Leitzmann M, Freisling H, Bray F, Romieu I, Renehan A, Soerjomataram I (2016) Obesity and cancer: an update of the global impact. Cancer Epidemiol 41:8–15
Protani M, Coory M, Martin JH (2010) Effect of obesity on survival of women with breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:627–635
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, Moore SC, Tobias GS, Anton-Culver H, Freeman LB, Beeson WL, Clipp SL, English DR, Folsom AR, Freedman DM, Giles G, Hakansson N, Henderson KD, Hoffman-Bolton J, Hoppin JA, Koenig KL, Lee IM, Linet MS, Park Y, Pocobelli G, Schatzkin A, Sesso HD, Weiderpass E, Willcox BJ, Wolk A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Willett WC, Thun MJ (2010) Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N Engl J Med 363:2211–2219
Reeves GK, Pirie K, Beral V, Green J, Spencer E, Bull D. Million Women Study Collaboration (2007) Cancer incidence and mortality in relation to body mass index in the Million women study: cohort study. BMJ 335:1134
Fedele P, Orlando L, Schiavone P, Quaranta A, Lapolla AM, De Pasquale M, Ardizzone A, Bria E, Sperduti I, Calvani N, Marino A, Caliolo C, Mazzoni E, Cinieri S (2014) BMI variation increases recurrence risk in women with early-stage breast cancer. Future Oncol 10:2459–2468
Sparano JA, Wang M, Zhao F, Stearns V, Martino S, Ligibel JA, Perez EA, Saphner T, Wolff AC, Sledge GW Jr, Wood WC, Fetting J, Davidson NE (2012) Obesity at diagnosis is associated with inferior outcomes in hormone receptor-positive operable breast cancer. Cancer 118:5937–5946
Pfeiler G, Königsberg R, Fesl C, Mlineritsch B, Stoeger H, Singer CF, Pöstlberger S, Steger GG, Seifert M, Dubsky P, Taucher S, Samonigg H, Bjelic-Radisic V, Greil R, Marth C, Gnant M (2011) Impact of body mass index on the efficacy of endocrine therapy in premenopausal patients with breast cancer: an analysis of the prospective ABCSG-12 trial. J Clin Oncol 29:2653–2659
Ewertz M, Gray KP, Regan MM, Ejlertsen B, Price KN, Thürlimann B, Bonnefoi H, Forbes JF, Paridaens RJ, Rabaglio M, Gelber RD, Colleoni M, Láng I, Smith IE, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A, Mouridsen HT (2012) Obesity and risk of recurrence or death after adjuvant endocrine therapy with letrozole or tamoxifen in the breast international group 1-98 trial. J Clin Oncol 30:3967–3975
Sendur MA, Aksoy S, Zengin N, Altundag K (2012) Efficacy of adjuvant aromatase inhibitor in hormone receptor-positive postmenopausal breast cancer patients according to the body mass index. Br J Cancer 107:1815–1819
Colleoni M, Li S, Gelber RD, Price KN, Coates AS, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Goldhirsch A (2005) International Breast Cancer Study Group. Relation between chemotherapy dose, oestrogen receptor expression, and body-mass index. Lancet 366:1108–1110
Ademuyiwa FO, Groman A, O’Connor T, Ambrosone C, Watroba N, Edge SB (2011) Impact of body mass index on clinical outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 117:4132–4140
Dawood S, Lei X, Litton JK, Buchholz TA, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2012) Impact of body mass index on survival outcome among women with early stage triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 12:364–372
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Madarnas Y, Hartwick W, Hoffman B, Hood N (2002) Fasting insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol 20:42–51
Decensi A, Gennari A (2011) Insulin breast cancer connection: confirmatory data set the stage for better care. J Clin Oncol 29:7–10
Amadori D, Silvestrini R, De Lena M, Boccardo F, Rocca A, Scarpi E, Schittulli F, Brandi M, Maltoni R, Serra P, Ponzone R, Biglia N, Gianni L, Tienghi A, Valerio MR, Bonginelli P, Amaducci L, Faedi M, Baldini E, Paradiso A (2011) Randomized phase III trial of adjuvant epirubicin followed by cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil (CMF) versus CMF followed by epirubicin in patients with node-negative or 1-3 node-positive rapidly proliferating breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 125:775–784
Rocca A, Bravaccini S, Scarpi E, Mangia A, Petroni S, Puccetti M, Medri L, Serra L, Ricci M, Cerasoli S, Biglia N, Maltoni R, Giunchi DC, Gianni L, Tienghi A, Brandi M, Faedi M, Sismondi P, Paradiso A, Silvestrini R, Amadori D (2014) Benefit from anthracyclines in relation to biological profiles in early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144:307–318
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (1998) Polychemotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 352:930–942
Park J, Morley TS, Kim M, Clegg DJ, Scherer PE (2014) Obesity and cancer-mechanisms underlying tumor progression and recurrence. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:455–465
Sestak I, Distler W, Forbes JF, Dowsett M, Howell A, Cuzick J (2010) Effect of body mass index on recurrences in tamoxifen and anastrozole treated women: an exploratory analysis from the ATAC trial. J Clin Oncol 28:3411–3415
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ; Panel Members (2015) Tailoring therapies-improving the management of early breast cancer: st Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol 26:1533–1546
Griggs JJ, Mangu PB, Anderson H, Balaban EP, Dignam JJ, Hryniuk WM, Morrison VA, Pini TM, Runowicz CD, Rosner GL, Shayne M, Sparreboom A, Sucheston LE, Lyman GH (2012) Appropriate chemotherapy dosing for obese adult patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol 30:1553–1561
Bucholz EM, Rathore SS, Reid KJ, Jones PG, Chan PS, Rich MW, Spertus JA, Krumholz HM (2012) Body mass index and mortality in acute myocardial infarction patients. Am J Med 125:796–803
Ashwell M, Gunn P, Gibson S (2012) Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 13:275–286
Gami AS, Witt BJ, Howard DE, Erwin PJ, Gami LA, Somers VK, Montori VM (2007) Metabolic syndrome and risk of incident cardiovascular events and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:403–414
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the following contributors. Patrizia Serra, Ilaria Massa, Monia Dall’Agata, Britt Rudnas, Alessandra Piancastelli, Emanuela Montanari, Bernadette Vertogen, Federica Zumaglini: IRCCS IRST, Meldola, Italy; Davide Tassinari, Barbara Venturini: Department of Oncology, Infermi Hospital, Rimini, Italy; Riccardo Roagna: Mauriziano Hospital “Umberto I,”Turin, Italy.
Funding
AIRC Italian Association for Cancer Research IG 9239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gennari, A., Amadori, D., Scarpi, E. et al. Impact of body mass index (BMI) on the prognosis of high-risk early breast cancer (EBC) patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 159, 79–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3923-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3923-8