Abstract
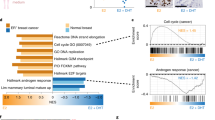
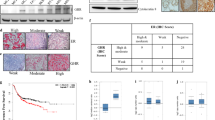
Tamoxifen (Tam) resistance represents a significant clinical problem in estrogen receptor (ER) α-positive breast cancer. We previously showed that decreased expression of Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (Rho GDI) α, a negative regulator of the Rho GTPase pathway, is associated with Tam resistance. We now discover that androgen receptor (AR) is overexpressed in cells with decreased Rho GDIα and seek to determine AR’s contribution to resistance. We engineered ERα-positive cell lines with stable knockdown (KD) of Rho GDIα (KD cells). Resistance mechanisms were examined using microarray profiling, protein-interaction studies, growth and reporter gene assays, and Western blot analysis combined with a specific AR antagonist and other signaling inhibitors. Tam-resistant tumors and cell lines with low Rho GDIα levels exhibited upregulated AR expression. Microarray of Rho GDIα KD cells indicated that activation of EGFR and ERα was associated with Tam treatment. When AR levels were elevated, interaction between AR and EGFR was detected. Constitutive and Tam-induced phosphorylation of EGFR and ERK1/2 was blocked by the AR antagonist Enzalutamide, suggesting that AR-mediated EGFR activation was a mechanism of resistance in these cells. Constitutive ERα phosphorylation and transcriptional activity was inhibited by Enzalutamide and the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib, demonstrating that AR-mediated EGFR signaling activated ERα. Tam exhibited agonist activity in AR overexpressing cells, stimulating ERα transcriptional activity and proliferation, which was blocked by Enzalutamide and gefitinib. We describe a novel model of AR-mediated Tam resistance through activation of EGFR signaling leading to ER activation in ERα-positive cells with low expression of Rho GDIα.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66544-0
Jensen EV, Jordan VC (2003) The estrogen receptor: a model for molecular medicine. Clin Cancer Res 9:1980–1989
Giuliano M, Schifp R, Osborne CK, Trivedi MV (2011) Biological mechanisms and clinical implications of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Breast 20(Suppl 3):S42–S49. doi:10.1016/S0960-9776(11)70293-4
Johnston SR (2015) Enhancing endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: cotargeting signaling pathways. J Natl Cancer Inst. doi:10.1093/jnci/djv212
Barone I, Brusco L, Gu G, Selever J, Beyer A, Covington KR, Tsimelzon A, Wang T, Hilsenbeck SG, Chamness GC, Ando S, Fuqua SA (2011) Loss of Rho GDIalpha and resistance to tamoxifen via effects on estrogen receptor alpha. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:538–552. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr058
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–635. doi:10.1038/nature01148
Jiang WG, Watkins G, Lane J, Cunnick GH, Douglas-Jones A, Mokbel K, Mansel RE (2003) Prognostic value of rho GTPases and rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors in human breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res 9:6432–6440
De Amicis F, Thirugnansampanthan J, Cui Y, Selever J, Beyer A, Parra I, Weigel NL, Herynk MH, Tsimelzon A, Lewis MT, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Ando S, Fuqua SA (2010) Androgen receptor overexpression induces tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:1–11. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0436-8
Rechoum Y, Rovito D, Iacopetta D, Barone I, Ando S, Weigel NL, O’Malley BW, Brown PH, Fuqua SA (2014) AR collaborates with ERalpha in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 147:473–485. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-3082-8
Heinlein CA, Chang C (2002) The roles of androgen receptors and androgen-binding proteins in nongenomic androgen actions. Mol Endocrinol 16:2181–2187. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0070
Lea OA, Kvinnsland S, Thorsen T (1989) Improved measurement of androgen receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:7162–7167
Cochrane DR, Bernales S, Jacobsen BM, Cittelly DM, Howe EN, D’Amato NC, Spoelstra NS, Edgerton SM, Jean A, Guerrero J, Gomez F, Medicherla S, Alfaro IE, McCullagh E, Jedlicka P, Torkko KC, Thor AD, Elias AD, Protter AA, Richer JK (2014) Role of the androgen receptor in breast cancer and preclinical analysis of enzalutamide. Breast Cancer Res 16:R7. doi:10.1186/bcr3599
Fujii R, Hanamura T, Suzuki T, Gohno T, Shibahara Y, Niwa T, Yamaguchi Y, Ohnuki K, Kakugawa Y, Hirakawa H, Ishida T, Sasano H, Ohuchi N, Hayashi S (2014) Increased androgen receptor activity and cell proliferation in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast carcinoma. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 144(Pt B):513–522. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.08.019
Cui Y, Parra I, Zhang M, Hilsenbeck SG, Tsimelzon A, Furukawa T, Horii A, Zhang ZY, Nicholson RI, Fuqua SA (2006) Elevated expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 in breast tumors: a mechanism of tamoxifen resistance. Cancer Res 66:5950–5959. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3243
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:926–935
Thrane S, Lykkesfeldt AE, Larsen MS, Sorensen BS, Yde CW (2013) Estrogen receptor alpha is the major driving factor for growth in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and supported by HER/ERK signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139:71–80. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2485-2
Zhang Y, Moerkens M, Ramaiahgari S, de Bont H, Price L, Meerman J, van de Water B (2011) Elevated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling induces antiestrogen resistance through the MAPK/ERK and PI3 K/Akt signaling routes. Breast Cancer Res 13:R52. doi:10.1186/bcr2883
Migliaccio A, Di Domenico M, Castoria G, Nanayakkara M, Lombardi M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Varricchio L, Ciociola A, Auricchio F (2005) Steroid receptor regulation of epidermal growth factor signaling through Src in breast and prostate cancer cells: steroid antagonist action. Cancer Res 65:10585–10593. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0912
Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Barone MV, Ametrano D, Zannini MS, Abbondanza C, Auricchio F (2000) Steroid-induced androgen receptor-oestradiol receptor beta-Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 19:5406–5417. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.20.5406
Zhu X, Li H, Liu JP, Funder JW (1999) Androgen stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 152:199–206
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME, Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, Armstrong AJ, Flaig TW, Flechon A, Mainwaring P, Fleming M, Hainsworth JD, Hirmand M, Selby B, Seely L, de Bono JS (2012) Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 367:1187–1197. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1207506
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Gutteridge E, Ellis IO, Pinder SE, Rubini M, Nicholson RI (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2/insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling and oestrogen receptor activity in clinical breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 12(Suppl 1):S99–S111. doi:10.1677/erc.1.01005
Massarweh S, Schiff R (2006) Resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: exploiting estrogen receptor/growth factor signaling crosstalk. Endocr Relat Cancer 13(Suppl 1):S15–S24. doi:10.1677/erc.1.01273
Bunone G, Briand PA, Miksicek RJ, Picard D (1996) Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J 15:2174–2183
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, Giles M, McClelland RA, Gee JM, Nicholson RI (2006) Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 96:131–146. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-9070-2
Rayala SK, Talukder AH, Balasenthil S, Tharakan R, Barnes CJ, Wang RA, Aldaz CM, Khan S, Kumar R (2006) P21-activated kinase 1 regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha activation involves serine 305 activation linked with serine 118 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 66:1694–1701. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2922
Guix M, Granja Nde M, Meszoely I, Adkins TB, Wieman BM, Frierson KE, Sanchez V, Sanders ME, Grau AM, Mayer IA, Pestano G, Shyr Y, Muthuswamy S, Calvo B, Krontiras H, Krop IE, Kelley MC, Arteaga CL (2008) Short preoperative treatment with erlotinib inhibits tumor cell proliferation in hormone receptor-positive breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 26:897–906. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.13.5939
Reddy KB, Mangold GL, Tandon AK, Yoneda T, Mundy GR, Zilberstein A, Osborne CK (1992) Inhibition of breast cancer cell growth in vitro by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res 52:3636–3641
Song RX, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Bao Y, Santen RJ (2007) Estrogen signaling via a linear pathway involving insulin-like growth factor I receptor, matrix metalloproteinases, and epidermal growth factor receptor to activate mitogen-activated protein kinase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 148:4091–4101. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0240
Fritz G, Just I, Kaina B (1999) Rho GTPases are over-expressed in human tumors. Int J Cancer 81:682–687
Cops EJ, Bianco-Miotto T, Moore NL, Clarke CL, Birrell SN, Butler LM, Tilley WD (2008) Antiproliferative actions of the synthetic androgen, mibolerone, in breast cancer cells are mediated by both androgen and progesterone receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 110:236–243. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.10.014
Peters AA, Buchanan G, Ricciardelli C, Bianco-Miotto T, Centenera MM, Harris JM, Jindal S, Segara D, Jia L, Moore NL, Henshall SM, Birrell SN, Coetzee GA, Sutherland RL, Butler LM, Tilley WD (2009) Androgen receptor inhibits estrogen receptor-alpha activity and is prognostic in breast cancer. Cancer Res 69:6131–6140. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0452
Yardley DA, Awada A, Cortes J, Burris HA, Peterson A, Tudor IC, Stopatschinskaja S, Gianni L, Miller K, Winer E (2013) A Phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of enzalutamide in combination with exemestane in estrogen or progesterone receptor-positive and HER2-normal advanced breast cancer. Cancer Res 73:OT3-2-01. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.SABCS13-OT3-2-01
Ma Y, Croxton R, Moorer RL Jr, Cress WD (2002) Identification of novel E2F1-regulated genes by microarray. Arch Biochem Biophys 399:212–224. doi:10.1006/abbi.2002.2761
Hu R, Dawood S, Holmes MD, Collins LC, Schnitt SJ, Cole K, Marotti JD, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Tamimi RM (2011) Androgen receptor expression and breast cancer survival in postmenopausal women. Clin Cancer Res 17:1867–1874. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2021
Cristofanilli M, Valero V, Mangalik A, Royce M, Rabinowitz I, Arena FP, Kroener JF, Curcio E, Watkins C, Bacus S, Cora EM, Anderson E, Magill PJ (2010) Phase II, randomized trial to compare anastrozole combined with gefitinib or placebo in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:1904–1914. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2282
Johnston SRD, Basik M, Hegg R, Lausoontornsiri W, Grzeda L, Clemons M, Dreosti ML, Ghiorghiu S, Mann H, Landers D, Stuart M, Cristofanilli M (2013) Phase II randomized study of the EGFR, HER2, HER3 signaling inhibitor AZD8931 in combination with anastrozole (A) in women with endocrine therapy (ET) naive advanced breast cancer (MINT). J Clin Oncol 31(15 Suppl):531(abstract)
Creighton CJ, Hilger AM, Murthy S, Rae JM, Chinnaiyan AM, El-Ashry D (2006) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer cells in vitro induces an in vivo molecular phenotype of estrogen receptor alpha-negative human breast tumors. Cancer Res 66:3903–3911. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4363
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute R01 CA72038, Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas RP120732, and Susan G. Komen for the Cure PG12221410 to SAWF. The project described was supported in part by Award Number T32GM088129 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciupek, A., Rechoum, Y., Gu, G. et al. Androgen receptor promotes tamoxifen agonist activity by activation of EGFR in ERα-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 154, 225–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3609-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3609-7