Abstract
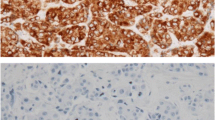
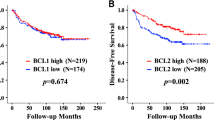
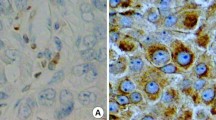
B‐cell lymphoma‐2 (Bcl‐2) is one of the most important anti‐apoptotic genes. Although Bcl-2 promotes tumor cell survival in vitro, previous studies have shown conflicting results regarding the association between Bcl-2 and breast cancer survival. The aim of this study was to assess the prognostic significance of Bcl-2 according to the molecular tumor subtype in primary invasive breast cancer patients. The relationship between immunohistochemical Bcl-2 expression and overall survival was analyzed in 2399 primary invasive breast cancer patients treated by curative surgery. Patients were classified into four subtypes based on hormone receptor (HR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor‐2 (HER2) status: HR+/HER2−, HR+/HER2+, HR−/HER2+, and HR−/HER2−. A total of 1304 patients (54.4 %) had Bcl‐2 positive (+) tumors by immunohistochemistry. Bcl‐2 (+) tumors were significantly associated with a younger age (<50 years), early stage, lower grade, positive expression of HR, and negative expression of HER2. In the HR+/HER2− group, patients with Bcl‐2 (+) tumors showed a significantly better prognosis (p < 0.001). In contrast, there was no significant prognostic effect of Bcl‐2 expression in other subtypes. In multivariate analysis, Bcl‐2 positivity remained an independent, favorable prognostic factor in the HR+/HER2− subtype (hazard ratio, 0.609; 95 % confidence interval, 0.424–0.874; p < 0.007). The prognostic significance of Bcl‐2 expression differed according to the molecular subtype of breast cancer. The expression of Bcl‐2 was an independent, favorable prognostic factor in breast cancer patients with the HR+/HER2− subtype.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE (1989) Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer 63:181–187. doi:10.1001/jama.1964.03060170107050
Nemoto T, Vana J, Bedwani RN, Baker HW, McGregor FH, Murphy GP (1980) Management and survival of female breast cancer: results of a national survey by the American College of Surgeons. Cancer 45:2917–2924. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19800615)45:12<2917:aid-cncr2820451203>3.0.co;2-m
Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Linette GP, Stec J, Clark E, Ayers M, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Bloom KJ (2003) The Her-2/neu gene and protein in breast cancer 2003: biomarker and target of therapy. Oncologist 8:307–325. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.8-4-307
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182:311–322. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-4652(200003)182:3<311:aid-jcp1>3.0.co;2-9
van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536. doi:10.1038/415530a
Sparano JA, Paik S (2008) Development of the 21-gene assay and its application in clinical practice and clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 26:721–728. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.15.1068
Cardoso F, Van’t Veer L, Rutgers E, Loi S, Mook S, Piccart-Gebhart MJ (2008) Clinical application of the 70-gene profile: the MINDACT trial. J Clin Oncol 26:729–735. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.14.3222
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–1326. doi:10.1126/science.281.5381.1322
Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM (2003) The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22:8590–8607. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207102
Tzifi F, Economopoulou C, Gourgiotis D, Ardavanis A, Papageorgiou S, Scorilas A (2012) The role of Bcl2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins in acute and chronic leukemias. Adv Hematol 2012:524308. doi:10.1155/2012/524308
Hellemans P, van Dam PA, Weyler J, van Oosterom AT, Buytaert P, Van Marck E (1995) Prognostic value of bcl-2 expression in invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer 72:354–360. doi:10.1038/bjc.1995.338
Callagy GM, Pharoah PD, Pinder SE, Hsu FD, Nielsen TO, Ragaz J, Ellis IO, Huntsman D, Caldas C (2006) Bcl-2 is a prognostic marker in breast cancer independently of the Nottingham prognostic index. Clin Cancer Res 12:2468–2475. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-05-2719
Dawson SJ, Makretsov N, Blows FM, Driver KE, Provenzano E, Le Quesne J, Baglietto L, Severi G, Giles GG, McLean CA, Callagy G, Green AR, Ellis I, Gelmon K, Turashvili G, Leung S, Aparicio S, Huntsman D, Caldas C, Pharoah P (2010) BCL2 in breast cancer: a favourable prognostic marker across molecular subtypes and independent of adjuvant therapy. Br J Cancer 103:668–675. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605736
Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U (1994) The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer 86:499–504. doi:10.1093/jnci/86.7.499
Lipponen P, Pietilainen T, Kosma VM, Aaltomaa S, Eskelinen M, Syrjanen K (1995) Apoptosis suppressing protein bcl-2 is expressed in well-differentiated breast carcinomas with favourable prognosis. J Pathol 177:49–55. doi:10.1002/path.1711770109
Yu B, Sun X, Shen HY, Gao F, Fan YM, Sun ZJ (2010) Expression of the apoptosis-related genes Bcl-2 and BAD in human breast carcinoma and their associated relationship with chemosensitivity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:1–7. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-29-107
Yang Q, Moran MS, Haffty BG (2009) Bcl-2 expression predicts local relapse for early stage breast cancer receiving conserving surgery and radiotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 115:343–348. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-0068-4
Martinez-Arribas F, Alvarez T, Del Val G, Martin-Garabato E, Nunez-Villar MJ, Lucas R, Sánchez J, Tejerina A, Schneider J (2007) Bcl-2 expression in breast cancer: a comparative study at the mRNA and protein level. Anticancer Res 27:219–222
Amundson SA, Myers TG, Scudiero D, Kitada S, Reed JC, Fornace AJ Jr (2000) An informatics approach identifying markers of chemosensitivity in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 60:6101–6110
Kang MH, Reynolds CP (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:1126–1132. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0144
O’Brien S, Moore JO, Boyd TE et al (2009) 5-year survival in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a randomized, phase III trial of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide with or without oblimersen. J Clin Oncol 27:5208–5212. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.5748
Pezzella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar MF, Dunnill MS, Pierce CB, Harris A, Gatter KC, Mason DY (1993) Bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 329:690–694. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309023291003
Manne U, Myers RB, Moron C, Poczatek RB, Dillard S, Weiss H, Brown D, Srivastava S, Grizzle WE (1997) Prognostic significance of Bcl-2 expression and p53 nuclear accumulation in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 74:346–358. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19970620)74:3<346::AID-IJC19>3.0.CO;2-9
Del Bufalo D, Biroccio A, Leonetti C, Zupi G (1997) Bcl-2 overexpression enhances the metastatic potential of a human breast cancer line. FASEB J 11:947–953
DiVito KA, Berger AJ, Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL, Kluger HM (2004) Automated quantitative analysis of tissue microarrays reveals an association between high Bcl-2 expression and improved outcome in melanoma. Cancer Res 64:8773–8777. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1387
Knowlton K, Mancini M, Creason S, Morales C, Hockenberry D, Anderson BO (1998) Bcl-2 slows in vitro breast cancer growth despite its antiapoptotic effect. J Surg Res 76:22–26. doi:10.1006/jsre.1998.5277
Pietenpol JA, Papadopoulos N, Markowitz S, Willson JK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1994) Paradoxicial inhibition of solid tumor cell growth by bcl2. Cancer Res 54:3714–3717
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752. doi:10.1038/35021093
Cuzick J, Dowsett M, Pineda S, Wale C, Salter J, Quinn E, Zabaglo L, Mallon E, Green AR, Ellis IO, Howell A, Buzdar AU, Forbes JF (2011) Prognostic value of a combined estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, Ki-67, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 immunohistochemical score and comparison with the Genomic Health recurrence score in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29:4273–4278. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.2835
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC (2006) Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina breast cancer study. JAMA 295:2492–2502. doi:10.1001/jama.295.21.2492
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Radiological Translational Research Program (50451-2013).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This study complies with the current laws of South Korea inclusive ethics approval.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min-Ki Seong and Ju-Young Lee have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seong, MK., Lee, JY., Byeon, J. et al. Bcl-2 is a highly significant prognostic marker of hormone-receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150, 141–148 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3305-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3305-7