Abstract
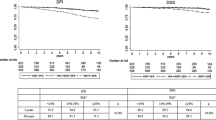
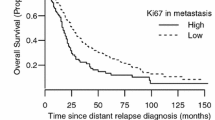
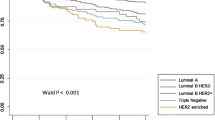
Combined B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2) and Ki67 expression for breast cancer prognostication has been proposed recently. However, the combinatorial relationship with patient outcome, clinico-pathologic features, and various biomarkers has not been fully explored. Bcl2 and Ki67 expression were examined in a large cohort of breast cancers. Differential Bcl2 and Ki67 combinatorial analysis, particularly in luminal cancers, were evaluated with respect to the clinico-pathologic features, biomarkers profile and outcome. Combined Bcl2/Ki67 phenotypes classified by Bcl2 and Ki67 cutoffs showed a better correlation with outcome. Multivariate analysis revealed this to be an independent prognostic factor in luminal cancers. Both Ki67 and Bcl2 contributed to the prognostic implications of different subgroups defined by Bcl2/Ki67 combination phenotypes with clinico-pathologic features and biomarkers profile. Ki67low/Bcl2high cases showed better DFS (HR = 2.17, P = 0.015) and OS (HR = 3.217, P = 0.015) compared to Ki67high/Bcl2low cases. Interestingly, Ki67low/Bcl2high cases also showed better outcome than other phenotypes in grade 2 cancers (log-rank = 4.844, P = 0.028) and TNM stage 2 cancers (log-rank = 8.161, P = 0.004). This classification by Bcl2/Ki67 combination phenotypes, together with PR expression, can also refine luminal A cancers prognostication. Not all PR low luminal A cases had poorer outcome compared to the PR high luminal A cases; poor prognosis was only limited to those with also low Bcl2 (log-rank = 23.568, P < 0.001 compared to PR high Bcl2 high cases). The combined Ki67/Bcl2 phenotyping was useful in luminal cancers prognostication. It also refined prognostication in intermediate groups (grade 2 and stage 2 cancers) of luminal cancers; and aided in further classification of luminal A cancers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rakha EA, Martin S, Lee AH, Morgan D, Pharoah PD, Hodi Z, Macmillan D, Ellis IO (2012) The prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer 118(15):3670–3680. doi:10.1002/cncr.26711
Mujtaba SS, Ni YB, Tsang JY, Chan SK, Yamaguchi R, Tanaka M, Tan PH, Tse GM (2013) Fibrotic focus in breast carcinomas: relationship with prognostic parameters and biomarkers. Ann Surg Oncol 20(9):2842–2849. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-2955-0
Wazer DE, Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Ruthazer R, DiPetrillo T, Boyle T, Kanski J, Safaii H (1999) The influence of age and extensive intraductal component histology upon breast lumpectomy margin assessment as a predictor of residual tumor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45(4):885–891
Gilchrist KW, Gray R, Fowble B, Tormey DC, Taylor SGt (1993) Tumor necrosis is a prognostic predictor for early recurrence and death in lymph node-positive breast cancer: a 10-year follow-up study of 728 Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group patients. J Clin Oncol 11(10):1929–1935
Weigelt B, Horlings HM, Kreike B, Hayes MM, Hauptmann M, Wessels LF, de Jong D, Van de Vijver MJ, Van’t Veer LJ, Peterse JL (2008) Refinement of breast cancer classification by molecular characterization of histological special types. J Pathol 216(2):141–150. doi:10.1002/path.2407
Thike AA, Cheok PY, Jara-Lazaro AR, Tan B, Tan P, Tan PH (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinicopathological characteristics and relationship with basal-like breast cancer. Mod Pathol 23(1):123–133. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.145
Tsang JY, Au SK, Ni YB, Shao MM, Siu WM, Hui SW, Chan SK, Chan KW, Kwok YK, Chan KF, Tse GM (2013) P-cadherin and vimentin are useful basal markers in breast cancers. Hum Pathol 44(12):2782–2791. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2013.07.029
Huang YH, Luo MH, Ni YB, Tsang JY, Chan SK, Lui PC, Yu AM, Tan PH, Tse GM (2014) Increased SOX2 expression in less differentiated breast carcinomas and their lymph node metastases. Histopathology 64(4):494–503. doi:10.1111/his.12257
Tsang JY, Ni YB, Chan SK, Shao MM, Law BK, Tan PH, Tse GM (2014) Androgen receptor expression shows distinctive significance in ER positive and negative breast cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 21(7):2218–2228. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3629-2
Galea MH, Blamey RW, Elston CE, Ellis IO (1992) The Nottingham Prognostic Index in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22(3):207–219
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2011) Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22(8):1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM (2004) Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10(16):5367–5374. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0220
Ni YB, Tsang JY, Chan SK, Tse GM (2014) A novel morphologic-molecular recurrence predictive model refines traditional prognostic tools for invasive breast carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 21(9):2928–2933. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3691-9
Ali HR, Dawson SJ, Blows FM, Provenzano E, Leung S, Nielsen T, Pharoah PD, Caldas C (2012) A Ki67/BCL2 index based on immunohistochemistry is highly prognostic in ER-positive breast cancer. J Pathol 226(1):97–107. doi:10.1002/path.2976
Abdel-Fatah TM, Powe DG, Ball G, Lopez-Garcia MA, Habashy HO, Green AR, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO (2010) Proposal for a modified grading system based on mitotic index and Bcl2 provides objective determination of clinical outcome for patients with breast cancer. J Pathol 222(4):388–399. doi:10.1002/path.2775
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC, Croce CM (1984) Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science 226(4678):1097–1099
Aizawa K, Ueki K, Suzuki S, Yabusaki H, Kanda T, Nishimaki T, Suzuki T, Hatakeyama K (1999) Apoptosis and Bbcl-2 expression in gastric carcinomas: correlation withclinicopathological variables, p53 expression, cell proliferation and prognosis. Int J Oncol 14(1):85–91
Saleh HA, Jackson H, Khatib G, Banerjee M (1999) Correlation of bcl-2 oncoprotein immunohistochemical expression with proliferation index and histopathologic parameters in colorectal neoplasia. Pathol Oncol Res 5(4):273–279
Laudanski J, Chyczewski L, Niklinska WE, Kretowska M, Furman M, Sawicki B, Niklinski J (1999) Expression of bcl-2 protein in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival. Neoplasma 46(1):25–30
Hwang KT, Woo JW, Shin HC, Kim HS, Ahn SK, Moon HG, Han W, Park IA, Noh DY (2012) Prognostic influence of BCL2 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 131(7):E1109–E1119. doi:10.1002/ijc.27539
Larsen MS, Bjerre K, Giobbie-Hurder A, Laenkholm AV, Henriksen KL, Ejlertsen B, Lykkesfeldt AE, Rasmussen BB (2012) Prognostic value of Bcl-2 in two independent populations of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy. Acta Oncol 51(6):781–789. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2011.653009
Dawson SJ, Makretsov N, Blows FM, Driver KE, Provenzano E, Le Quesne J, Baglietto L, Severi G, Giles GG, McLean CA, Callagy G, Green AR, Ellis I, Gelmon K, Turashvili G, Leung S, Aparicio S, Huntsman D, Caldas C, Pharoah P (2010) BCL2 in breast cancer: a favourable prognostic marker across molecular subtypes and independent of adjuvant therapy received. Br J Cancer 103(5):668–675. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605736
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 133(4):1710–1715
Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A’Hern R, Bartlett J, Coombes RC, Cuzick J, Ellis M, Henry NL, Hugh JC, Lively T, McShane L, Paik S, Penault-Llorca F, Prudkin L, Regan M, Salter J, Sotiriou C, Smith IE, Viale G, Zujewski JA, Hayes DF (2011) Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(22):1656–1664. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr393
Stuart-Harris R, Caldas C, Pinder SE, Pharoah P (2008) Proliferation markers and survival in early breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 85 studies in 32,825 patients. Breast 17(4):323–334. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2008.02.002
Urruticoechea A, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2005) Proliferation marker Ki-67 in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(28):7212–7220. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.07.501
Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA (2010) Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol 11(2):174–183. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70262-1
Harbeck N, Sotlar K, Wuerstlein R, Doisneau-Sixou S (2014) Molecular and protein markers for clinical decision making in breast cancer: today and tomorrow. Cancer Treat Rev 40(3):434–444. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.09.014
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9242-8
Carlson RW, Allred DC, Anderson BO, Burstein HJ, Carter WB, Edge SB, Erban JK, Farrar WB, Goldstein LJ, Gradishar WJ, Hayes DF, Hudis CA, Jahanzeb M, Kiel K, Ljung BM, Marcom PK, Mayer IA, McCormick B, Nabell LM, Pierce LJ, Reed EC, Smith ML, Somlo G, Theriault RL, Topham NS, Ward JH, Winer EP, Wolff AC (2009) Breast cancer. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 7(2):122–192
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M, Hicks DG, Lester S, Love R, Mangu PB, McShane L, Miller K, Osborne CK, Paik S, Perlmutter J, Rhodes A, Sasano H, Schwartz JN, Sweep FC, Taube S, Torlakovic EE, Valenstein P, Viale G, Visscher D, Wheeler T, Williams RB, Wittliff JL, Wolff AC (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(16):2784–2795. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M, Fitzgibbons P, Hanna W, Jenkins RB, Mangu PB, Paik S, Perez EA, Press MF, Spears PA, Vance GH, Viale G, Hayes DF (2013) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31(31):3997–4013. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, Perou CM, Ellis MJ, Nielsen TO (2009) Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(10):736–750. doi:10.1093/jnci/djp082
Prat A, Cheang MC, Martin M, Parker JS, Carrasco E, Caballero R, Tyldesley S, Gelmon K, Bernard PS, Nielsen TO, Perou CM (2013) Prognostic significance of progesterone receptor-positive tumor cells within immunohistochemically defined luminal A breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 31(2):203–209. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.43.4134
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, LY., Tsang, J.Y.S., Ni, YB. et al. Bcl2 and Ki67 refine prognostication in luminal breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 149, 631–643 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3288-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3288-4