Abstract
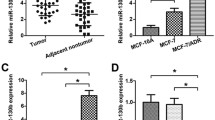
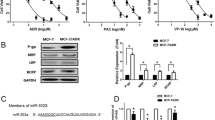
Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)/ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2) mediates multidrug resistance (MDR) in breast cancers. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of microRNAs in regulation of BCRP expression and BCRP-mediated drug resistance in breast cancer cells. Microarray analysis was performed to determine the differential expression patterns of miRNAs that target BCRP between the MX-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF-7/MX and its parental MX-sensitive cell line MCF-7. MiR-181a was found to be the most significantly down-regulated miRNA in MCF-7/MX cells. Luciferase activity assay showed that miR-181a mimics inhibited BCRP expression by targeting the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the BCRP mRNA. Overexpression of miR-181a down-regulated BCRP expression, and sensitized MX-resistant MCF-7/MX cells to MX. In a nude mouse xenograft model, intratumoral injection of miR-181a mimics inhibited BCRP expression, and enhanced the antitumor activity of MX. In addition, miR-181a inhibitors up-regulated BCRP expression, and rendered MX-sensitive MCF-7 cells resistant to MX. These findings suggest that miR-181a regulates BCRP expression via binding to the 3′-UTR of BCRP mRNA. MiR-181a is critical for regulation of BCRP-mediated resistance to MX. MiR-181a may be a potential target for preventing and reversing drug resistance in breast cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002, CA. Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Kuo MT (2007) Roles of multidrug resistance genes in breast cancer chemoresistance. Adv Exp Med Biol 608:23–30
Knutsen T, Rao VK, Ried T, Mickley L, Schneider E, Miyake K, Ghadimi BM, Padilla-Nash H, Pack S, Greenberger L, Cowan K, Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S (2000) Amplification of 4q21–q22 and the MXR gene in independently derived mitoxantrone-resistant cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 27(1):110–116
Ni Z, Bikadi Z, Rosenberg MF, Mao Q (2010) Structure and function of the human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Curr Drug Metab 11(7):603–617
Nakanishi T, Ross DD (2012) Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2): its role in multidrug resistance and regulation of its gene expression. Chin J Cancer 31(2):73–99. doi:10.5732/cjc.011.10320
Shiozawa K, Oka M, Soda H, Yoshikawa M, Ikegami Y, Tsurutani J, Nakatomi K, Nakamura Y, Doi S, Kitazaki T, Mizuta Y, Murase K, Yoshida H, Ross DD, Kohno S (2004) Reversal of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2)-mediated drug resistance by novobiocin, a coumermycin antibiotic. Int J Cancer 108(1):146–151. doi:10.1002/ijc.11528
Selever J, Gu G, Lewis MT, Beyer A, Herynk MH, Covington KR, Tsimelzon A, Dontu G, Provost P, Di Pietro A, Boumendjel A, Albain K, Miele L, Weiss H, Barone I, Ando S, Fuqua SA (2011) Dicer-mediated upregulation of BCRP confers tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 17(20):6510–6521. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1403
Hou X, Huang F, Carboni JM, Flatten K, Asmann YW, Ten Eyck C, Nakanishi T, Tibodeau JD, Ross DD, Gottardis MM, Erlichman C, Kaufmann SH, Haluska P (2011) Drug efflux by breast cancer resistance protein is a mechanism of resistance to the benzimidazole insulin-like growth factor receptor/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-536924. Mol Cancer Ther 10(1):117–125. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-10-0438
Burger H, Foekens JA, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Klijn JG, Wiemer EA, Stoter G, Nooter K (2003) RNA expression of breast cancer resistance protein, lung resistance-related protein, multidrug resistance-associated proteins 1 and 2, and multidrug resistance gene 1 in breast cancer: correlation with chemotherapeutic response. Clin Cancer Res 9(2):827–836
Nguyen NP, Almeida FS, Chi A, Nguyen LM, Cohen D, Karlsson U, Vinh-Hung V (2010) Molecular biology of breast cancer stem cells: potential clinical applications. Cancer Treat Rev 36(6):485–491. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.02.016
Fiorucci G, Chiantore MV, Mangino G, Percario ZA, Affabris E, Romeo G (2012) Cancer regulator microRNA: potential relevance in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer. Curr Med Chem 19(4):461–474
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B et al (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409(6822):860–921. doi:10.1038/35057062
Jensen LE, Whitehead AS (2004) The 3′ untranslated region of the membrane-bound IL-1R accessory protein mRNA confers tissue-specific destabilization. J Immunol 173(10):6248–6258
To KK, Robey RW, Knutsen T, Zhan Z, Ried T, Bates SE (2009) Escape from hsa-miR-519c enables drug-resistant cells to maintain high expression of ABCG2. Mol Cancer Ther 8(10):2959–2968. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-09-0292
To KK, Zhan Z, Litman T, Bates SE (2008) Regulation of ABCG2 expression at the 3′ untranslated region of its mRNA through modulation of transcript stability and protein translation by a putative microRNA in the S1 colon cancer cell line. Mol Cell Biol 28(17):5147–5161. doi:10.1128/mcb.00331-08
Wang F, Xue X, Wei J, An Y, Yao J, Cai H, Wu J, Dai C, Qian Z, Xu Z, Miao Y (2010) hsa-miR-520h downregulates ABCG2 in pancreatic cancer cells to inhibit migration, invasion, and side populations. Br J Cancer 103(4):567–574. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605724
Pan YZ, Morris ME, Yu AM (2009) MicroRNA-328 negatively regulates the expression of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in human cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 75(6):1374–1379. doi:10.1124/mol.108.054163
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334(4):1351–1358. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.030
Neilson JR, Zheng GX, Burge CB, Sharp PA (2007) Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development. Genes Dev 21(5):578–589. doi:10.1101/gad.1522907
Maillot G, Lacroix-Triki M, Pierredon S, Gratadou L, Schmidt S, Benes V, Roche H, Dalenc F, Auboeuf D, Millevoi S, Vagner S (2009) Widespread estrogen-dependent repression of micrornas involved in breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 69(21):8332–8340. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-2206
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, Liu LY, Tian T, Ni L, Zhang WG, Nan KJ, Song TS, Huang C (2009) MicroRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol Med Report 2(6):963–970. doi:10.3892/mmr_00000199
Nurul-Syakima AM, Yoke-Kqueen C, Sabariah AR, Shiran MS, Singh A, Learn-Han L (2011) Differential microRNA expression and identification of putative miRNA targets and pathways in head and neck cancers. Int J Mol Med 28(3):327–336. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2011.714
Marton S, Garcia MR, Robello C, Persson H, Trajtenberg F, Pritsch O, Rovira C, Naya H, Dighiero G, Cayota A (2008) Small RNAs analysis in CLL reveals a deregulation of miRNA expression and novel miRNA candidates of putative relevance in CLL pathogenesis. Leukemia 22(2):330–338. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2405022
Fei J, Li Y, Zhu X, Luo X (2012) miR-181a post-transcriptionally downregulates oncogenic RalA and contributes to growth inhibition and apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). PLoS ONE 7(3):e32834. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032834
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Vitale I, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Criollo A, Servant N, Paccard C, Hupe P, Robert T, Ripoche H, Lazar V, Harel-Bellan A, Dessen P, Barillot E, Kroemer G (2010) miR-181a and miR-630 regulate cisplatin-induced cancer cell death. Cancer Res 70(5):1793–1803. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-3112
Ke G, Liang L, Yang JM, Huang X, Han D, Huang S, Zhao Y, Zha R, He X, Wu X (2012) MiR-181a confers resistance of cervical cancer to radiation therapy through targeting the pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.323
Li H, Hui L, Xu W (2012) miR-181a sensitizes a multidrug-resistant leukemia cell line K562/A02 to daunorubicin by targeting BCL-2. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 44(3):269–277. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmr128
Bai H, Cao Z, Deng C, Zhou L, Wang C (2012) miR-181a sensitizes resistant leukaemia HL-60/Ara-C cells to Ara-C by inducing apoptosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138(4):595–602. doi:10.1007/s00432-011-1137-3
Guo LJ, Zhang QY (2012) Decreased serum miR-181a is a potential new tool for breast cancer screening. Int J Mol Med 30(3):680–686. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2012.1021
Taylor MA, Sossey-Alaoui K, Thompson CL, Danielpour D, Schiemann WP (2013) TGF-beta upregulates miR-181a expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest 123(1):150–163. doi:10.1172/jci64946
Li S, Yang C, Zhai L, Zhang W, Yu J, Gu F, Lang R, Fan Y, Gong M, Zhang X, Fu L (2012) Deep sequencing reveals small RNA characterization of invasive micropapillary carcinomas of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136(1):77–87. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2166-6
Tekirdag KA, Korkmaz G, Ozturk DG, Agami R, Gozuacik D (2013) MIR181A regulates starvation- and rapamycin-induced autophagy through targeting of ATG5. Autophagy 9(3):374–385
de Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J, Miyano S (2004) Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 20(9):1453–1454. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth078
Saldanha AJ (2004) Java treeview–extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 20(17):3246–3248. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth349
Liang Z, Wu H, Xia J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Huang K, Wagar N, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Scala S, Shim H (2010) Involvement of miR-326 in chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer through modulating expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. Biochem Pharmacol 79(6):817–824. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.10.017
Peng H, Dong Z, Qi J, Yang Y, Liu Y, Li Z, Xu J, Zhang JT (2009) A novel two mode-acting inhibitor of ABCG2-mediated multidrug transport and resistance in cancer chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 4(5):e5676. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005676
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP, Golubov A, Shpyleva SI, Kovalchuk O (2010) Alterations of microRNAs and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer 127(8):1785–1794. doi:10.1002/ijc.25191
Ward A, Balwierz A, Zhang JD, Kublbeck M, Pawitan Y, Hielscher T, Wiemann S, Sahin O (2012) Re-expression of microRNA-375 reverses both tamoxifen resistance and accompanying EMT-like properties in breast cancer. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.128
Cuesta R, Martinez-Sanchez A, Gebauer F (2009) miR-181a regulates cap-dependent translation of p27(kip1) mRNA in myeloid cells. Mol Cell Biol 29(10):2841–2851. doi:10.1128/mcb.01971-08
Zhang X, Nie Y, Du Y, Cao J, Shen B, Li Y (2012) MicroRNA-181a promotes gastric cancer by negatively regulating tumor suppressor KLF6. Tumour Biol 33(5):1589–1597. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0414-3
Shin KH, Bae SD, Hong HS, Kim RH, Kang MK, Park NH (2011) miR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404(4):896–902. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.055
Brangi M, Litman T, Ciotti M, Nishiyama K, Kohlhagen G, Takimoto C, Robey R, Pommier Y, Fojo T, Bates SE (1999) Camptothecin resistance: role of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC), mitoxantrone-resistance half-transporter (MXR), and potential for glucuronidation in MXR-expressing cells. Cancer Res 59(23):5938–5946
Wander SA, Zhao D, Besser AH, Hong F, Wei J, Ince TA, Milikowski C, Bishopric NH, Minn AJ, Creighton CJ, Slingerland JM (2013) PI3K/mTOR inhibition can impair tumor invasion and metastasis in vivo despite a lack of antiproliferative action in vitro: implications for targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138(2):369–381. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2389-6
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F, Costantini A, Guadagnoli M, Bonanno E, Muto G, Frajese GV, De Maria R, Spagnoli LG, Farace MG, Ciafre SA (2008) The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in mice. PLoS ONE 3(12):e4029. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004029
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, Wang Z, Ding G, Dong Q, Qin L, Wu X, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Tian W, Zhang Q, Wang C, Zhuang SM, Zheng L, Liang A, Tao W, Cao X (2011) Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 19(2):232–243. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.001
Fedier A, Schwarz VA, Walt H, Carpini RD, Haller U, Fink D (2001) Resistance to topoisomerase poisons due to loss of DNA mismatch repair. Int J Cancer 93(4):571–576
Lu H, Hallstrom TC (2012) Sensitivity to TOP2 targeting chemotherapeutics is regulated by Oct1 and FILIP1L. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42921. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042921
Goler-Baron V, Sladkevich I, Assaraf YG (2012) Inhibition of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway disrupts ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles and overcomes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 83(10):1340–1348. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.033
Ji J, Yamashita T, Wang XW (2011) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activates microRNA-181 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biosci 1(1):4. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-1-4
Bisso A, Faleschini M, Zampa F, Capaci V, De Santa J, Santarpia L, Piazza S, Cappelletti V, Daidone M, Agami R, Del Sal G (2013) Oncogenic miR-181a/b affect the DNA damage response in aggressive breast cancer. Cell Cycle 12(11):251–266
Zhu DX, Zhu W, Fang C, Fan L, Zou ZJ, Wang YH, Liu P, Hong M, Miao KR, Xu W, Li JY (2012) miR-181a/b significantly enhances drug sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via targeting multiple anti-apoptosis genes. Carcinogenesis 33(7):1294–1301. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs179
Su SF, Chang YW, Andreu-Vieyra C, Fang JY, Yang Z, Han B, Lee AS, Liang G (2012) miR-30d, miR-181a and miR-199a-5p cooperatively suppress the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78 in cancer. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.483
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr Zhirong Zhan (Molecular Therapeutics Section, Medical Oncology Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) for providing the MCF-7/MX cell. We also greatly appreciate the generous help from Qinghuan Xiao for typing and editing this manuscript. This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30973559, No. 81173092), and this study was also supported by Liaoning S&T Projects (No. 2011415052), and Shenyang Technology Projects (No. F11-264-1-19).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xuyang Jiao and Lin Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, X., Zhao, L., Ma, M. et al. MiR-181a enhances drug sensitivity in mitoxantone-resistant breast cancer cells by targeting breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Breast Cancer Res Treat 139, 717–730 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2607-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2607-x