Abstract
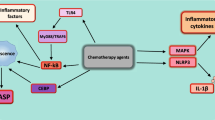
Chronic low-grade inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of several cancer forms including breast cancer. The pleiotropic cytokine IL-6 is a key player in systemic inflammation, regulating both the inflammatory response and tissue metabolism during acute stimulations. Here, we review the associations between IL-6 and breast cancer ranging from in vitro cell culture studies to clinical studies, covering the role of IL-6 in controlling breast cancer cell growth, regulation of cancer stem cell renewal, as well as breast cancer cell migration. Moreover, associations between circulating IL-6 and risk of breast cancer, prognosis for patients with prevalent disease, adverse effects and interventions to control systemic IL-6 levels in patients are discussed. In summary, direct application of IL-6 on breast cancer cells inhibits proliferation in estrogen receptor positive cells, while high circulating IL-6 levels are correlated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. This discrepancy reflects distinct roles of IL-6, with elevated systemic levels being a biomarker for tumor burden, physical inactivity, and impaired metabolism, while local intratumoral IL-6 signaling is important for controlling breast cancer cell growth, metastasis, and self renewal of cancer stem cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pedersen B (2009) The diseasome of physical inactivity—and the role of myokines in muscle—fat cross talk. J Physiol 587:5559–5568
Pedersen B (2006) The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise: its role in diabetes and cardiovascular disease control. Essays Biochem 42:105–117
Starkie R, Ostrowski SR, Jauffred S, Febbraio M, Pedersen B (2003) Exercise and IL-6 infusion inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-alpha production in humans. FASEB J 17:884–886
Pedersen B, Febbraio M (2008) Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol Rev 88:1379–1406
Pedersen B, Febbraio M (2012) Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:457–465
Scheele C, Nielsen S, Kelly M, Broholm C, Nielsen AR, Taudorf S, Pedersen M, Fischer CP, Pedersen BK (2012) Satellite cells derived from obese humans with type 2 diabetes and differentiated into myocytes in vitro exhibit abnormal response to IL-6. Plos One 76:e39657
Fischer CP, Berntsen A, Perstrup LB, Eskildsen P, Pedersen B (2007) Plasma levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein are associated with physical inactivity independent of obesity. Scand J Med Sci Sports 17(5):580–587
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490:61–70
Chiu JJ, Sgagias MK, Cowan KH (1996) Interleukin 6 acts as a paracrine growth factor in human mammary carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 2:215–221
Danforth DN Jr, Sgagias MK (1993) Interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-6 act additively to inhibit growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Res 53:1538–1545
Douglas AM, Goss GA, Sutherland RL, Hilton DJ, Berndt MC, Nicola NA, Begley CG (1997) Expression and function of members of the cytokine receptor superfamily on breast cancer cells. Oncogene 14:661–669
Morinaga Y, Suzuki H, Takatsuki F, Akiyama Y, Taniyama T, Matsushima K, Onozaki K (1989) Contribution of IL-6 to the antiproliferative effect of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor on tumor cell lines. J Immunol 143:3538–3542
Shen Z, Wen XF, Lan F, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM (2002) The tumor suppressor gene LKB1 is associated with prognosis in human breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 8:2085–2090
Asgeirsson KS, Olafsdottir K, Jonasson JG, Ogmundsdottir HM (1998) The effects of IL-6 on cell adhesion and e-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Cytokine 10:720–728
Badache A, Hynes NE (2001) Interleukin 6 inhibits proliferation and, in cooperation with an epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine loop, increases migration of T47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:383–391
Tamm I, Cardinale I, Krueger J, Murphy JS, May LT, Sehgal PB (1989) Interleukin 6 decreases cell–cell association and increases motility of ductal breast carcinoma cells. J Exp Med 170:1649–1669
Jiang XP, Yang DC, Elliott RL, Head JF (2011) Down-regulation of expression of interleukin-6 and its receptor results in growth inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res 31:2899–2906
Studebaker AW, Storci G, Werbeck JL, Sansone P, Sasser AK, Tavolari S, Huang T, Chan MW, Marini FC, Rosol TJ, Bonafe M, Hall BM (2008) Fibroblasts isolated from common sites of breast cancer metastasis enhance cancer cell growth rates and invasiveness in an interleukin-6-dependent manner. Cancer Res 68:9087–9095
Johnston PG, Rondinone CM, Voeller D, Allegra CJ (1992) Identification of a protein factor secreted by 3T3-L1 preadipocytes inhibitory for the human MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res 52:6860–6865
Lee J, Hahm ER, Singh SV (2010) Withaferin A inhibits activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 31:1991–1998
Barbieri I, Pensa S, Pannellini T, Quaglino E, Maritano D, Demaria M, Voster A, Turkson J, Cavallo F, Watson CJ, Provero P, Musiani P, Poli V (2010) Constitutively active Stat3 enhances neu-mediated migration and metastasis in mammary tumors via upregulation of Cten. Cancer Res 70:2558–2567
Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D (2007) Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 7:41–51
Leslie K, Gao SP, Berishaj M, Podsypanina K, Ho H, Ivashkiv L, Bromberg J (2010) Differential interleukin-6/Stat3 signaling as a function of cellular context mediates Ras-induced transformation. Breast Cancer Res 12(5):R80
Liao D, Liu Z, Wrasidlo WJ, Luo Y, Nguyen G, Chen T, Xiang R, Reisfeld RA (2011) Targeted therapeutic remodeling of the tumor microenvironment improves an HER-2 DNA vaccine and prevents recurrence in a murine breast cancer model. Cancer Res 71:5688–5696
Lieblein JC, Ball S, Hutzen B, Sasser AK, Lin HJ, Huang TH, Hall BM, Lin J (2008) STAT3 can be activated through paracrine signaling in breast epithelial cells. BMC Cancer 8:302
Snyder M, Huang XY, Zhang JJ (2011) Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) directly regulates cytokine-induced fascin expression and is required for breast cancer cell migration. J Biol Chem 286:38886–38893
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K (2009) An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 139:693–706
Chavey C, Bibeau F, Gourgou-Bourgade S, Burlinchon S, Boissiere F, Laune D, Roques S, Lazennec G (2007) Oestrogen receptor negative breast cancers exhibit high cytokine content. Breast Cancer Res 9:R15
Fontanini G, Campani D, Roncella M, Cecchetti D, Calvo S, Toniolo A, Basolo F (1999) Expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) correlates with oestrogen receptor in human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 80:579–584
Faggioli L, Costanzo C, Merola M, Bianchini E, Furia A, Carsana A, Palmieri M (1996) Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B), nuclear factor interleukin-6 (NFIL-6 or C/EBP beta) and nuclear factor interleukin-6 beta (NFIL6-beta or C/EBP delta) are not sufficient to activate the endogenous interleukin-6 gene in the human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7. Comparative analysis with MDA-MB-231 cells, an interleukin-6-expressing human breast carcinoma cell line. Eur J Biochem 239:624–631
Robinson EK, Sneige N, Grimm EA (1998) Correlation of interleukin 6 with interleukin 1alpha in human mammary tumours, but not with oestrogen receptor expression. Cytokine 10:970–976
Selander KS, Li L, Watson L, Merrell M, Dahmen H, Heinrich PC, Muller-Newen G, Harris KW (2004) Inhibition of gp130 signaling in breast cancer blocks constitutive activation of Stat3 and inhibits in vivo malignancy. Cancer Res 64:6924–6933
Singh A, Purohit A, Ghilchik MW, Reed MJ (1999) The regulation of aromatase activity in breast fibroblasts: the role of interleukin-6 and prostaglandin E2. Endocr Relat Cancer 6:139–147
Purohit A, Newman SP, Reed MJ (2002) The role of cytokines in regulating estrogen synthesis: implications for the etiology of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 4:65–69
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A, Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ, Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, Wu Z, Gonen M, Mulvey LA, Bessarabova MO, Huh SJ, Silver SJ, Kim SY, Park SY, Lee HE, Anderson KS, Richardson AL, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Liu XS, Root DE, Hahn WC, Frank DA, Polyak K (2011) The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44(+) CD24(−) stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest 121:2723–2735
Korkaya H, Liu S, Wicha MS (2011) Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest 121:3804–3809
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G, Struhl K (2011) Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1397–1402
Qiu M, Peng Q, Jiang I, Carroll C, Han G, Rymer I, Lippincott J, Zachwieja J, Gajiwala K, Kraynov E, Thibault S, Stone D, Gao Y, Sofia S, Gallo J, Li G, Yang J, Li K, Wei P (2013) Specific inhibition of Notch1 signaling enhances the antitumor efficacy of chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer through reduction of cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett 328(2):261–270
Kelleher FC, Fennelly D, Rafferty M (2006) Common critical pathways in embryogenesis and cancer. Acta Oncol 45:375–388
Liu CC, Prior J, Piwnica-Worms D, Bu G (2010) LRP6 overexpression defines a class of breast cancer subtype and is a target for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:5136–5141
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P, Marcu KB, Chieco P, Bonafe M (2007) IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland. J Clin Invest 117:3988–4002
Guo S, Liu M, Gonzalez-Perez RR (2011) Role of Notch and its oncogenic signaling crosstalk in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815:197–213
Heller E, Hurchla MA, Xiang J, Su X, Chen S, Schneider J, Joeng KS, Vidal M, Goldberg L, Deng H, Hornick MC, Prior JL, Piwnica-Worms D, Long F, Cagan R, Weilbaecher KN (2012) Hedgehog signaling inhibition blocks growth of resistant tumors through effects on tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 72:897–907
Madden KS, Szpunar MJ, Brown EB (2011) Beta-adrenergic receptors (beta-AR) regulate VEGF and IL-6 production by divergent pathways in high beta-AR-expressing breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130:747–758
Korkaya H, Kim GI, Davis A, Malik F, Henry NL, Ithimakin S, Quraishi AA, Tawakkol N, D’Angelo R, Paulson AK, Chung S, Luther T, Paholak HJ, Liu S, Hassan KA, Zen Q, Clouthier SG, Wicha MS (2012) Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2+ breast cancer by expanding the cancer stem cell population. Mol Cell 47:570–584
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F, Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM, Hall BM (2009) Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28:2940–2947
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Tamm I, Kikuchi T, Cardinale I, Krueger JG (1994) Cell-adhesion-disrupting action of interleukin 6 in human ductal breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3329–3333
Liu S, Ginestier C, Ou SJ, Clouthier SG, Patel SH, Monville F, Korkaya H, Heath A, Dutcher J, Kleer CG, Jung Y, Dontu G, Taichman R, Wicha MS (2011) Breast cancer stem cells are regulated by mesenchymal stem cells through cytokine networks. Cancer Res 71:614–624
Rattigan Y, Hsu JM, Mishra PJ, Glod J, Banerjee D (2010) Interleukin 6 mediated recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to the hypoxic tumor milieu. Exp Cell Res 316:3417–3424
De LA, Lamura L, Gallo M, Maffia V, Normanno N (2012) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor promote breast cancer cell migration. J Cell Biochem 113:3363–3370
Knupfer H, Preiss R (2007) Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res Treat 102:129–135
Karczewska A, Nawrocki S, Breborowicz D, Filas V, Mackiewicz A (2000) Expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor, and glycoprotein 130 correlates with good prognoses for patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 88:2061–2071
Garcia-Tunon I, Ricote M, Ruiz A, Fraile B, Paniagua R, Royuela M (2005) IL-6, its receptors and its relationship with bcl-2 and bax proteins in infiltrating and in situ human breast carcinoma. Histopathology 47:82–89
Hudis CA, Subbaramaiah K, Morris PG, Dannenberg AJ (2012) Breast cancer risk reduction: no pain, no gain? J Clin Oncol 30:3434–3438
Heikkilä K, Harris R, Lowe G, Rumley A, Yarnell J, Gallacher J, Ben-shlomo Y, Ebrahim S, Lawlor DA (2009) Associations of circulating C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 with cancer risk: findings from two prospective cohorts and a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 20:15–26
Il’yasova D, Colbert LH, Harris TB, Newman AB, Bauer DC, Satterfield S, Kritchecsky SB (2005) Circulating levels of inflammatory markers and cancer risk in the health, aging and body composition cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:2413–2418
Yu KD, Di GH, Fan L, Chen AX, Yang C, Shao ZM (2012) Lack of an association between a functional polymorphism in the interleukin-6 gene promoter and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis involving 25703 subjects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122:483–488
Taudorf S, Krabbe KS, Berg RM, Møller K, Pedersen B, Bruunsgaard H (2008) Common studied polymorphisms do not affect plasma cytokine levels upon endotoxin exposure in humans. Clin Exp Immunol 152:147–152
DeMichele A, Gray R, Horn M, Chen J, Aplenc R, Vaughan WP, Tallman MS (2009) Host genetic variants in the interleukin-6 promoter predict poor outcome in patients with estrogen receptor-positive, node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 69:4184–4191
Fuksiewics M, Kowalska M, Kotowics B, Rubach M, Chechlinska M, Pienkowski T, Kaminska J (2010) Serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor type 1 concentrations independently predict prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Clin Chem Lab Med 48:1481–1486
Salgado R, Junius S, Benoy I, Van Dam P, Vermeulen P, Van Marck E, Huget P, Dirix LY (2003) Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer 103:642–646
Mills PJ, Ancoli-Israel S, Parker B, Natarajan L, Hong S, Jain S, Sadler GR, von Känel R (2008) Predictors of inflammation in response to antracycline-based chemotherapy for breast cancer. Brain Behav Immun 22:98–104
Kang DH, Weaver MT, Park NJ, Smith B, McArdle T, Carpenter J (2009) Significant impairment in immune recovery after cancer treatment. Nurs Res 58:105–114
Pusztai L, Mendoza TR, Reuben JM, Martinez MM, Willey JS, Lara J, Syed A, Fritsche HA, Bruera E, Booser D, Valero V, Arun B, Ibrahim N, Rivera E, Royce M, Cleeland CS, Hortobagyi GN (2004) Changes in plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines in response tp paclitaxel chemotherapy. 25(3):94–102
Tsavaris N, Kosmas C, Vadiaka M, Kanelopoulos P, Boulamatsis D (2002) Immune changes in patients with advanced breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy with taxanes. Br J Cancer 87:21–27
Oner-Iyidogan Y, Oner P, Kocak H, Lama A, Gurdol F, Bekpihar S, Unur N, Ozbek-Kir Z (2005) Evaluation of leukocyte arylsulphatase a, serum interleukin-6 and urinary heparan sulphate following tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Pharmacol Res 52:340–345
Saligan LN, Kim HS (2012) A systematic review of the association between immunogenic markers and cancer-related fatigue. Brain Behav Immun 26:830–848
Bower JE, Ganz PA, Tao ML, Hu W, Belin TR, Sepah S, Cole S, Aziz N (2009) Inflammatory biomarkers and fatigue during radiation therapy for breast and prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:5534–5540
Cameron BA, Bennett B, Li H, Boyle F, Desouza P, Wilcken N, Friedlander M, Goldstein D, Lloyd AR (2012) Post-cancer fatigue is not associated with immune activation or altered cytokine production. Ann Oncol 23(11):2890–2895
Orre IJ, Reinertsen KV, Aukrust P, Dahl AA, Fosså SD, Ueland T, Murison R (2011) Higher levels of fatigue are associated with higher CRP levels in disease-free breast cancer survivors. J Psychosom Res 71:136–141
Raison CL, Capuron L, Miller AH (2006) Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol 27:24–31
Anisman H, Merali Z (2002) Cytokines, stress, and depressive illness. Brain Behav Immun 16:513–524
Soygur H, Palaoglu O, Akarsu ES, Cankurtaran ES, Ozalp E, Turhan L, Ayhan IH (2007) Interleukin-6 levels and HPA axis activation in breast cancer patients with major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:1242–1247
Musselman DL, Miller AH, Porter MR, Manatunga A, Gao F, Penna S, Pearce B, Landry J, Glover S, McDaniel JS, Nemeroff CB (2001) Higher than normal plasma interleukin-6 concentrations in cancer patients with depression: preliminary findings. Am J Psychiatry 158:1252–1257
Jehn CF, Flath B, Strux A, Krebs M, Possinger K, Pezzutto A, Lüftner D (2012) Influence of age, performance status, cancer activity, and IL-6 on anxiety and depression in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136(3):789–794
Janelsins M, Mustian K, Palesh O, Mohile SG, Peppone LJ, Sprod LK, Heckler CE, Roscoe JA, Katz AW, Williams JP, Morrow G (2012) Differential expression of cytokines in breast cancer patients receiving different chemotherapies: implications for cognitive impairment research. Support Care Cancer 20:831–839
Kesler S, Janelsins M, Koovakkattu D, Palesh O, Mustian K, Morrow G, Dhabhar FS (2012) Reduced hippocampal volume and verbal memory performance associated with interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in chemotherapy-treated breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 13(9):1184–1190
Pedersen B (2000) Exercise and cytokines. Immunol Cell Biol 78:532–535
Friedenreich CM, Neilson HK, Woolcott CG, Wang Q, Stanczyk FZ, McTiernan A, Jones CA, Irwin ML, Yasui Y, Courneya KS (2012) Inflammatory marker changes in a yearlong randomized exercise intervention trial among postmenopausal women. Cancer Prev Res 5:98–108
Rogers LQ, Fogleman A, Trammell R, Hopkins-Price P, Vicari S, Rao K, Edson B, Verhulst S, Courneya KS, Hoelzer K (2012) Effects of a physical activity behavior change intervention on inflammation and related health outcomes in breast cancer survivors: pilot randomized trial. Integr Cancer Ther (in press)
Gomez AM, Martinez C, Liuza-Luces C, Herrero F, Perez M, Madero L, Ruiz JR, Lucia A, Ramirez M (2011) Exercise training and cytokines in breast cancer survivors. Int J Sports Med 32:461–467
Fairey AS, Courneya KS, Field CJ, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Mackey JR (2005) Randomized controlled trial of exercise and blood immune function in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors. J Appl Physiol 98:1534–1540
Hutnick NA, Williams NI, Kraemer WJ, Orsega-Smith E, Dixon RH, Bleznak AD, Mastro AM (2005) Exercise and lymphocyte activation following chemotherapy for breast cancer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:1827–1835
Pakiz B, Flatt SW, Bardwell WA, Rock CL, Mills PJ (2011) Effects of a weight loss intervention on body mass, fitness, and inflammatory biomarkers in overweight or obese breast cancer survivors. Int J Behav Med 18:333–341
Janelsins M, Davis PG, Wideman L, Katula JA, Sprod LK, Peppone LJ, Palesh O, Heckler CE, Williams JP, Morrow G, Mustian K (2011) Effects of Tai Chi Chuan on insulin and cytokine levels in a randomized controlled pilot study on breast cancer survivors. Clin Breast Cancer 11:161–170
Kang DH, McArdle T, Park NJ, Weaver MT, Smith B, Carpenter J (2011) Dose effects of relaxation practice on immune responses in women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: an exploratory study. Oncol Nurs Forum 38:E240–E252
Witek-Janusek L, Albuquerque K, Chroniak KR, Chroniak C, Durazo-Arvizu R, Mathews HL (2008) Effect of mindfulness based stress reduction on immune function, quality of life and coping in women newly diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. Brain Behav Immun 22:969–981
Acknowledgments
The Centre of Inflammation and Metabolism (CIM) is supported by a grant from the Danish National Research Foundation (# 02-512-55). This study was further supported by the Danish Medical Research Council, and Rigshospitalets Research Funds. CIM is part of the UNIK Project: Food, Fitness & Pharma for Health and Disease, supported by the Danish Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Disclosure
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Christine Dethlefsen and Grith Højfeldt contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dethlefsen, C., Højfeldt, G. & Hojman, P. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 657–664 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2488-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2488-z