Abstract
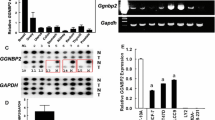
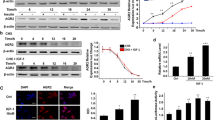
Although estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling are important for normal mammary development and breast cancer, cross-talk between these pathways, particularly at the level of transcription, remains poorly understood. We performed microarray analysis on MCF-7 breast cancer cells treated with estradiol (E2) or IGF-I for 3 or 24 h. IGF-I regulated mRNA of five to tenfold more genes than E2, and many genes were co-regulated by both ligands. Importantly, expression of these co-regulated genes correlated with poor prognosis of human breast cancer. Closer examination revealed enrichment of repressed transcripts. Interestingly, a number of potential tumor suppressors, for example, B-cell linker (BLNK), were down-regulated by IGF-I and E2. Analysis of three down-regulated genes showed that E2-mediated repression occurred independently of IGF-IR, and IGF-I-mediated repression occurred independently of ERα. However, repression by IGF-I or E2 required common kinases, such as PI3K and MEK, suggesting downstream convergence of the two pathways. In conclusion, E2 and IGF-I co-regulate a set of genes that affect breast cancer outcome. There is enrichment of repressed transcripts, and, for some genes, the down-regulation is independent at the receptor level. This may be important clinically, as tumors with active ERα and IGF-IR signaling may require co-targeting of both pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Hall JM, Couse JF, Korach KS (2001) The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 276:36869–36872
Casa AJ, Dearth RK, Litzenburger BC, Lee AV, Cui X (2008) The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway: a key player in cancer therapeutic resistance. Front Biosci 13:3273–3287
Sachdev D, Yee D (2001) The IGF system and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 8:197–209
Richards RG, DiAugustine RP, Petrusz P, Clark GC, Sebastian J (1996) Estradiol stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 in the uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12002–12007
Richards RG, Walker MP, Sebastian J, DiAugustine RP (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor-insulin receptor substrate complexes in the uterus. Altered signaling response to estradiol in the IGF-1(m/m) mouse. J Biol Chem 273:11962–11969
Klotz DM, Hewitt SC, Ciana P, Raviscioni M, Lindzey JK, Foley J, Maggi A, DiAugustine RP, Korach KS (2002) Requirement of estrogen receptor-alpha in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)-induced uterine responses and in vivo evidence for IGF-1/estrogen receptor cross-talk. J Biol Chem 277:8531–8537
Hewitt SC, Collins J, Grissom S, Deroo B, Korach KS (2005) Global uterine genomics in vivo: microarray evaluation of the estrogen receptor alpha-growth factor cross-talk mechanism. Mol Endocrinol 19:657–668
Bocchinfuso WP, Korach KS (1997) Mammary gland development and tumorigenesis in estrogen receptor knockout mice. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2:323–334
Ruan W, Kleinberg DL (1999) Insulin-like growth factor I is essential for terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis during mammary development. Endocrinology 140:5075–5081
Ruan W, Catanese V, Wieczorek R, Feldman M, Kleinberg DL (1995) Estradiol enhances the stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on mammary development and growth hormone-induced IGF-I messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 136:1296–1302
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK, Yee D (1999) Enhancement of insulin-like growth factor signaling in human breast cancer: estrogen regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol Endocrinol 13:787–796
Molloy CA, May FE, Westley BR (2000) Insulin receptor substrate-1 expression is regulated by estrogen in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. J Biol Chem 275:12565–12571
Cui X, Zhang P, Deng W, Oesterreich S, Lu Y, Mills GB, Lee AV (2003) Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits progesterone receptor expression in breast cancer cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway: progesterone receptor as a potential indicator of growth factor activity in breast cancer. Mol Endocrinol 17:575–588
Pollak M (1998) IGF-I physiology and breast cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res 152:63–70
Pollak M (2000) Insulin-like growth factor physiology and cancer risk. Eur J Cancer 36:1224–1228
Flemming A, Brummer T, Reth M, Jumaa H (2003) The adaptor protein SLP-65 acts as a tumor suppressor that limits pre-B cell expansion. Nat Immunol 4:38–43
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Huang S, Podsypanina K, Chen Y, Cai W, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck S, Li Y (2006) Wnt-1 is dominant over Neu in specifying mammary tumor expression profiles. Technol Cancer Res Treat 5:565–571
Li C, Wong WH (2001) Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:31–36
Simon RM, Korn EL, McShane LM, Radmacher MD, Wright GW, Zhao Y (2004) Design and analysis of DNA microarray investigations. Springer, New York
Creighton CJ, Casa A, Lazard Z, Huang S, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck SG, Osborne CK, Lee AV (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-I activates gene transcription programs strongly associated with poor breast cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 26:4078–4085
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucl Acids Res 30:207–210
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, Schreiber GJ, Peterse JL, Roberts C, Marton MJ, Parrish M, Atsma D, Witteveen A, Glas A, Delahaye L, van der Velde T, Bartelink H, Rodenhuis S, Rutgers ET, Friend SH, Bernards R (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1999–2009
Whitfield ML, Sherlock G, Saldanha AJ, Murray JI, Ball CA, Alexander KE, Matese JC, Perou CM, Hurt MM, Brown PO, Botstein D (2002) Identification of genes periodically expressed in the human cell cycle and their expression in tumors. Mol Biol Cell 13:1977–2000
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, Borresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10869–10874
Pacher M, Seewald MJ, Mikula M, Oehler S, Mogg M, Vinatzer U, Eger A, Schweifer N, Varecka R, Sommergruber W, Mikulits W, Schreiber M (2007) Impact of constitutive IGF1/IGF2 stimulation on the transcriptional program of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 28:49–59
Dupont J, Khan J, Qu BH, Metzler P, Helman L, LeRoith D (2001) Insulin and IGF-1 induce different patterns of gene expression in mouse fibroblast NIH-3T3 cells: identification by cDNA microarray analysis. Endocrinology 142:4969–4975
Mulligan C, Rochford J, Denyer G, Stephens R, Yeo G, Freeman T, Siddle K, O’Rahilly S (2002) Microarray analysis of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor signaling reveals the selective up-regulation of the mitogen heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by IGF-1. J Biol Chem 277:42480–42487
Cicatiello L, Scafoglio C, Altucci L, Cancemi M, Natoli G, Facchiano A, Iazzetti G, Calogero R, Biglia N, De Bortoli M, Sfiligoi C, Sismondi P, Bresciani F, Weisz A (2004) A genomic view of estrogen actions in human breast cancer cells by expression profiling of the hormone-responsive transcriptome. J Mol Endocrinol 32:719–775
Cunliffe HE, Ringner M, Bilke S, Walker RL, Cheung JM, Chen Y, Meltzer PS (2003) The gene expression response of breast cancer to growth regulators: patterns and correlation with tumor expression profiles. Cancer Res 63:7158–7166
Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS (2003) Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology 144:4562–4574
Lin CY, Strom A, Vega VB, Kong SL, Yeo AL, Thomsen JS, Chan WC, Doray B, Bangarusamy DK, Ramasamy A, Vergara LA, Tang S, Chong A, Bajic VB, Miller LD, Gustafsson JA, Liu ET (2004) Discovery of estrogen receptor alpha target genes and response elements in breast tumor cells. Genome Biol 5:R66
Watanabe H, Suzuki A, Mizutani T, Khono S, Lubahn DB, Handa H, Iguchi T (2002) Genome-wide analysis of changes in early gene expression induced by oestrogen. Genes Cells 7:497–507
Malik S, Jiang S, Garee JP, Verdin E, Lee AV, O’Malley BW, Zhang M, Belaguli NS, Oesterreich S (2010) Histone deacetylase 7 and FoxA1 in estrogen-mediated repression of RPRM. Mol Cell Biol 30:399–412
Katzenellenbogen BS, Norman MJ (1990) Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: interrelationships among insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I, serum, and estrogen. Endocrinology 126:891–898
Zhang S, Li X, Burghardt R, Smith R III, Safe SH (2005) Role of estrogen receptor (ER) alpha in insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I-induced responses in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol 35:433–447
Cascio S, Bartella V, Garofalo C, Russo A, Giordano A, Surmacz E (2007) Insulin-like growth factor 1 differentially regulates estrogen receptor-dependent transcription at estrogen response element and AP-1 sites in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 282:3498–3506
Jumaa H, Bossaller L, Portugal K, Storch B, Lotz M, Flemming A, Schrappe M, Postila V, Riikonen P, Pelkonen J, Niemeyer CM, Reth M (2003) Deficiency of the adaptor SLP-65 in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 423:452–456
Fu C, Turck CW, Kurosaki T, Chan AC (1998) BLNK: a central linker protein in B cell activation. Immunity 9:93–103
Nakayama J, Yamamoto M, Hayashi K, Satoh H, Bundo K, Kubo M, Goitsuka R, Farrar MA, Kitamura D (2009) BLNK suppresses pre-B-cell leukemogenesis through inhibition of JAK3. Blood 113:1483–1492
Grabbe A, Wienands J (2006) Human SLP-65 isoforms contribute differently to activation and apoptosis of B lymphocytes. Blood 108:3761–3768
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program W81XWH-06-1-0714 (AJC) and BC043880 (SM), and by grants from the National Institutes of Health P01CA30195 (AVL), P30CA58183 (AVL), and R01CA097213 (SO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casa, A.J., Potter, A.S., Malik, S. et al. Estrogen and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) independently down-regulate critical repressors of breast cancer growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132, 61–73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1540-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1540-0