Abstract
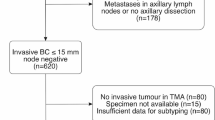
Knowledge is limited about prognostic significance of breast cancer subtypes among women with small invasive node-negative breast tumours. We explored patterns of recurrence in 1691 women with pT1mic/T1a/T1b, pN0 and M0 breast cancer according to four immunohistochemically defined tumour subtypes: (i) Luminal A (ER-positive, PgR-positive, HER2-negative and Ki-67 < 14%); (ii) Luminal B (ER-positive and/or PgR-positive, HER2-positive and/or Ki-67 ≥ 14%); (iii) HER2-positive, both endocrine receptors absent; and (iv) Triple Negative. At multivariate analysis, women with the Triple Negative breast cancer subtype had an increased risk of loco-regional relapse (LRR) (Hazards Ratio (HR) 3.58; 95%CI: 1.40–9.13) and breast cancer related events (HR 2.18; 95%CI: 1.04–4.57). Overall, Luminal B subtype was not associated with a statistically significant increased risk of recurrence compared with Luminal A, while patients with Luminal B subtype tumours overexpressing HER2 had a 2 fold risk of reduced breast cancer related survival (BCS), but not an increased risk of LRR and distant metastases. Women with HER2 breast cancer subtype had a statistically significant increased risk of LRR (HR 4.53; 95%CI: 1.56–13.1), distant metastases and reduced BCS (HR 3.22; 95%CI: 1.44–7.18) and overall survival (HR 2.87; 95%CI: 1.05–7.89) when compared with the Luminal A subtype, at multivariate analysis. In conclusion, women with small size, node-negative, breast cancer are at higher risk of relapse if with HER2-positive endocrine receptor absent or Triple Negative disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK et al (2005) Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:1784–1792
Fracheboud J, Otto SJ, van Dijck JA et al (2004) National Evaluation Team for Breast Cancer Screening (NETB): decreased rates of advanced breast cancer due to mammography screening in the Netherlands. Br J Cancer 91:861–867
Hanrahan EO, Valero V, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hortobagyi GN (2006) Prognosis and management of patients with node-negative invasive breast carcinoma that is 1 cm or smaller in size (stage 1; T1a, bN0M0): a review of the literature. J Clin Oncol 24:2113–2122
Quiet CA, Ferguson DJ, Weichselbaum RR, Hellman S (1995) Natural history of node-negative breast cancer: a study of 826 patients with long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol 13:1144–1151
Rosner D, Lane W (1993) Predicting recurrence in axillary-node negative breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 25:127–139
Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Peruzzotti G et al (2004) Minimal and small size invasive breast cancer with no axillary lymph node involvement: the need for tailored adjuvant therapies. Ann Oncol 15:1633–1639
Hanrahan EO, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Giordano SH et al (2007) Overall survival and cause-specific mortality of patients with stage T1a, bN0M0 breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 25:4952–4960
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Litton JK, Broglio KR et al (2009) High risk of recurrence for patients with breast cancer who have human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive, node-negative tumors 1 cm or smaller. J Clin Oncol 27:5700–5706
Curigliano G, Viale G, Bagnardi V et al (2009) Clinical relevance of HER2 overexpression/amplification in patients with small tumor size and node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:5693–5699
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J et al (2003) Repeated observation of breast tumour subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8418–8423
Oh DS, Troester MA, Usary J et al (2006) Estrogen-regulated genes predict survival in hormone receptor-positive breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 24:1656–1664
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF et al (2005) Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 11:5678–5685
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10869–10874
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D et al (2009) Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal b breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:736–750
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC et al (2009) Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol 27:1168–1176
Cancello G, Maisonneuve P, Rotmensz N et al (2010) Prognosis and adjuvant treatment effects in selected breast cancer subtypes of very young women (<35 years) with operable breast cancer. Ann Oncol 21:1974–1981
Rosen PP, Oberman H (1993) Tumors of the mammary gland. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Viale G, Regan MM, Mastropasqua MG et al (2008) Predictive value of tumor Ki-67 expression in two randomized trials of adjuvant chemoendocrine therapy for node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:207–212
Kwon JH, Kim YJ, Lee KW et al (2010) Triple negativity and young age as prognostic factors in lymph node-negative invasive ductal carcinoma of 1 cm or less. BMC Cancer 10:557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cancello, G., Maisonneuve, P., Rotmensz, N. et al. Prognosis in women with small (T1mic,T1a,T1b) node-negative operable breast cancer by immunohistochemically selected subtypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat 127, 713–720 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1465-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1465-7