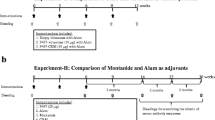
Abstract
Passive immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies is a routinely performed but cost intensive treatment against certain cancers. Induction of humoral anti-tumor responses by active peptide immunization has therefore become a favorable treatment concept. We have recently identified three peptides representing B-cell epitopes of the extracellular domain of Her-2/neu each of them inducing Her-2/neu specific immune responses with anti-tumor activity in vitro. The present study was performed to evaluate the in vivo protective capacity of a combined vaccination with these three peptides in FVB/N transgenic mice spontaneously developing c-neu overexpressing breast cancers. The three Her-2/neu peptides coupled to tetanus toxoid were administered with or without addition of recombinant IL-12. At the time all untreated mice had developed tumors about 40% of peptide-immunized mice and nearly 60% of mice immunized with the peptide vaccine co-applied with IL-12 remained tumor free. Moreover, co-administration of IL-12 had a significant impact on the retardation of tumor progression. The enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of the vaccine by IL-12 was associated with a Th1 biased immune response as demonstrated by an increased IFN-γ production in vitro and elevated Her-2-specific IgG levels. Our findings clearly demonstrate that this multi-peptide vaccine is effective in tumor prevention and support its use against minimal disease, drug-resistant tumors or even for prophylaxis against cancers overexpressing Her-2/neu.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dougall WC, Qian X, Peterson NC, Miller MJ, Samanta A, Greene MI (1994) The neu-oncogene: signal transduction pathways, transformation mechanisms and evolving therapies. Oncogene 9:2109–2123
Masood S, Bui MM (2002) Prognostic and predictive value of HER2/neu oncogene in breast cancer. Microsc Res Tech 59:102–108
Disis ML, Gralow JR, Bernhard H, Hand SL, Rubin WD, Cheever MA (1996) Peptide-based, but not whole protein, vaccines elicit immunity to HER-2/neu, oncogenic self-protein. J Immunol 156:3151–3158
Dakappagari NK, Douglas DB, Triozzi PL, Stevens VC, Kaumaya PT (2000) Prevention of mammary tumors with a chimeric HER-2 B-cell epitope peptide vaccine. Cancer Res 60:3782–3789
Dakappagari NK, Pyles J, Parihar R, Carson WE, Young DC, Kaumaya PT (2003) A chimeric multi-human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 B cell epitope peptide vaccine mediates superior antitumor responses. J Immunol 170:4242–4253
Jasinska J, Wagner S, Radauer C, Sedivy R, Brodowicz T, Wiltschke C, Breiteneder H, Pehamberger H, Scheiner O, Wiedermann U, Zielinski CC (2003) Inhibition of tumor cell growth by antibodies induced after vaccination with peptides derived from the extracellular domain of Her-2/neu. Int J Cancer 107:976–983
Spiridon CI, Ghetie MA, Uhr J, Marches R, Li JL, Shen GL, Vitetta ES (2002) Targeting multiple Her-2 epitopes with monoclonal antibodies results in improved antigrowth activity of a human breast cancer cell line in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 8:1720–1730
Nanni P, Nicoletti G, De Giovanni C, Landuzzi L, Di Carlo E, Cavallo F, Pupa SM, Rossi I, Colombo MP, Ricci C, Astolfi A, Musiani P, Forni G, Lollini PL (2001) Combined allogeneic tumor cell vaccination and systemic interleukin 12 prevents mammary carcinogenesis in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. J Exp Med 194:1195–1205
De Giovanni C, Nicoletti G, Landuzzi L, Astolfi A, Croci S, Comes A, Ferrini S, Meazza R, Iezzi M, Di Carlo E, Musiani P, Cavallo F, Nanni P, Lollini PL (2004) Immunoprevention of HER-2/neu transgenic mammary carcinoma through an interleukin 12-engineered allogeneic cell vaccine. Cancer Res 64:4001–4009
Reilly RT, Gottlieb MB, Ercolini AM, Machiels JP, Kane CE, Okoye FI, Muller WJ, Dixon KH, Jaffee EM (2000) HER-2/neu is a tumor rejection target in tolerized HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Cancer Res 60:3569–3576
Disis ML, Shiota FM, Cheever MA (1998) Human HER-2/neu protein immunization circumvents tolerance to rat neu: a vaccine strategy for ‘self’ tumour antigens. Immunology 93:192–199
Guy CT, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ (1996) Activated neu induces rapid tumor progression. J Biol Chem 271:7673–7678
Wiedermann U, Jahn-Schmid B, Fritsch R, Bauer L, Renz H, Kraft D, Ebner C (1998) Effects of adjuvants on the immune response to allergens in a murine model of allergen inhalation: cholera toxin induces a Th1-like response to Bet v 1, the major birch pollen allergen. Clin Exp Immunol 111:144–151
Winkler B, Baier K, Wagner S, Repa A, Eichler HG, Scheiner O, Kraft D, Wiedermann U (2002) Mucosal tolerance as therapy of type I allergy: intranasal application of recombinant Bet v 1, the major birch pollen allergen, leads to the suppression of allergic immune responses and airway inflammation in sensitized mice. Clin Exp Allergy 32:30–36
Yip YL, Smith G, Koch J, Dubel S, Ward RL (2001) Identification of epitope regions recognized by tumor inhibitory and stimulatory anti-ErbB-2 monoclonal antibodies: implications for vaccine design. J Immunol 166:5271–5278
Kim KM, Shin EY, Moon JH, Heo TH, Lee JY, Chung Y, Lee YJ, Cho HM, Shin SU, Kang CY (2002) Both the epitope specificity and isotype are important in the antitumor effect of monoclonal antibodies against Her-2/neu antigen. Int J Cancer 102:428–434
Boggio K, Nicoletti G, Di Carlo E, Cavallo F, Landuzzi L, Melani C, Giovarelli M, Rossi I, Nanni P, De Giovanni C, Bouchard P, Wolf S, Modesti A, Musiani P, Lollini PL, Colombo MP, Forni G (1998) Interleukin 12-mediated prevention of spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in two lines of Her-2/neu transgenic mice. J Exp Med 188:589–596
Wagner S, Hafner C, Allwardt D, Jasinska J, Ferrone S, Zielinski CC, Scheiner O, Wiedermann U, Pehamberger H, Breiteneder H (2005) Vaccination with a human high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen mimotope induces a humoral response inhibiting melanoma cell growth in vitro. J Immunol 174:976–982
Snapper CM, Paul WE (1987) Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science 236:944–947
Pedersen KB, Andersen K, Fodstad O, Maelandsmo GM (2004) Sensitization of interferon-gamma induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by extracellular S100A4. BMC Cancer 4:52
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from BioLife Science GmbH and by the research grant GZ 200.062/2-VI/1/2002 of the Austrian Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stefan Wagner and Joanna Jasinska contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, S., Jasinska, J., Breiteneder, H. et al. Delayed tumor onset and reduced tumor growth progression after immunization with a Her-2/neu multi-peptide vaccine and IL-12 in c-neu transgenic mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106, 29–38 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9469-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9469-4