Summary
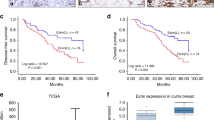
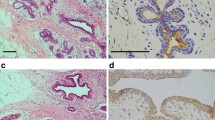
The membrane-cytoskeleton crosslinker ezrin is associated with malignant progression and metastasis in human neoplasias. To study the role of ezrin in breast cancer, we first assessed ezrin expression in a panel of breast cancer cell lines by western blot and confocal microscopy. Western blot revealed no differences in total ezrin levels among these breast cell lines. However, immunofluorescence staining revealed that Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, noninvasive and nontumorigenic cell lines concentrated ezrin at the apical surface, whereas invasive cell lines localized ezrin in motile structures (membrane ruffles and filopodia) but also had more diffuse cytoplasmic staining. We next studied ezrin expression in 509 breast carcinomas using tissue microarrays. Immunohistochemical staining for ezrin, p53, Ki-67, phospho-Akt, HER2, and hormonal receptors was performed. Ezrin staining in normal breast epithelium localized at the apical, but not lateral, cell surface, whereas, in most breast tumor cases (331, 70.3%), it localized in the cytoplasm. Complete membranous staining occurred in 89 (18.9%) samples, and apical staining was seen in 51 (10.8%) cases. There were significant positive associations between cytoplasmic ezrin localization and adverse tumor characteristics such as high grade, high level of Ki-67 expression, hormonal-receptor negativity, and lymph-node metastases. Apical ezrin staining was associated with favorable clinicopathological features and node-negative tumors. Membranous ezrin staining was associated with high grade, strong HER2 and p-Akt expression. In conclusion, the switch of ezrin localization from the apical membrane to either the complete membrane or to the cytoplasm is correlated with dedifferentiation and adverse features in invasive breast tumors and cancer cell lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bretscher A, Regulation of cortical structure by the ezrin–radixin–moesin protein family Curr Opin Cell Biol 11: 109–116, 1999
Tsukita S, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) family: from cytoskeleton to signal transduction Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 70–75, 1997
Crepaldi T, Gautreau A, Comoglio PM, Louvard D, Arpin M, Ezrin is an effector of hepatocyte growth factor-mediated migration and morphogenesis in epithelial cells J Cell Biol 138: 423–434, 1997
Mackay DJ, Esch F, Furthmayr H, Hall A, Rho- and rac-dependent assembly of focal adhesion complexes and actin filaments in permeabilized fibroblasts: an essential role for ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins J Cell Biol 138: 927–938, 1997
Mangeat P, Roy C, Martin M, ERM proteins in cell adhesion and membrane dynamics Trends Cell Biol 9: 187–192, 1999
Pujuguet P, Del Maestro L, Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M, Ezrin regulates E-cadherin-dependent adherens junction assembly through Rac1 activation Mol Biol Cell 14: 2181–2191, 2003
Hiscox S, Jiang WG, Ezrin regulates cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, a possible role with E-cadherin/beta-catenin J Cell Sci 112: 3081–3090, 1999
Berryman M, Franck Z, Bretscher A, Ezrin is concentrated in the apical microvilli of a wide variety of epithelial cells whereas moesin is found primarily in endothelial cells J Cell Sci 105: 1025–1043, 1993
Gautreau A, Poullet P, Louvard D, Arpin M, Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96:7300–7305, 1999
Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M, Morphogenic effects of ezrin require a phosphorylation-induced transition from oligomers to monomers at the plasma membrane J Cell Biol 150: 193–203, 2000
Martin TA, Harrison G, Mansel RE, Jiang WG, The role of the CD44/ezrin complex in cancer metastasis Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 46: 165–186, 2003
Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M, ERM proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical actin organization and cell growth signaling Curr Opin Cell Biol 14: 104–109, 2002
McClatchey AI, Merlin and ERM proteins: unappreciated roles in cancer development? Nat Rev Cancer 3: 877–883, 2003
Kaul SC, Mitsui Y, Komatsu Y, Reddel RR, Wadhwa R, A highly expressed 81 kDa protein in immortalized mouse fibroblast: its proliferative function and identity with ezrin Oncogene 13: 1231–1237, 1996
Shen ZY, Xu LY, Chen MH, Li EM, Li JT, Wu XY, Zeng Y, Upregulated expression of Ezrin and invasive phenotype in malignantly transformed esophageal epithelial cells World J Gastroenterol 9: 1182–1186, 2003
Ohtani K, Sakamoto H, Rutherford T, Chen Z, Satoh K, Naftolin F, Ezrin, a membrane-cytoskeletal linking protein, is involved in the process of invasion of endometrial cancer cells Cancer Lett 147: 31–38, 1999
Khanna C, Khan J, Nguyen P, Prehn J, Caylor J, Yeung C, Trepel J, Meltzer P, Helman L, Metastasis-associated differences in gene expression in a murine model of osteosarcoma Cancer Res 61: 3750–3759, 2001
Khanna C, Wan X, Bose S, Cassaday R, Olomu O, Mendoza A, Yeung C, Gorlick R, Hewitt SM, Helman LJ, The membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma metastasis Nat Med 10: 182–186, 2004
Yu Y, Khan J, Khanna C, Helman L, Meltzer PS, Merlino G, Expression profiling identifies the cytoskeletal organizer ezrin and the developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key metastatic regulators Nat Med 10: 175–181, 2004
Akisawa N, Nishimori I, Iwamura T, Onishi S, Hollingsworth MA, High levels of ezrin expressed by human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines with high metastatic potential Biochem Biophys Res Comm 258: 395–400, 1999
Chen Z, Fadiel A, Feng Y, Ohtani K, Rutherford T, Naftolin F, Ovarian epithelial carcinoma tyrosine phosphorylation, cell proliferation, and ezrin translocation are stimulated by interleukin 1alpha and epidermal growth factor Cancer 92: 3068–3075, 2001
Ohtani K, Sakamoto H, Rutherford T, Chen Z, Kikuchi A, Yamamoto T, Satoh K, Naftolin F, Ezrin, a membrane-cytoskeletal linking protein, is highly expressed in atypical endometrial hyperplasia and uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma Cancer Lett 179: 79–86, 2002
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP, Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens Nat Med 4: 844–847, 1998
Moilanen J, Lassus H, Leminen A, Vaheri A, Butzow R, Carpen O, Ezrin immunoreactivity in relation to survival in serous ovarian carcinoma patients Gynecol Oncol 90: 273–281, 2003
Pang ST, Fang X, Valdman A, Norstedt G, Pousette A, Egevad L, Ekman P, Expression of ezrin in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia Urology 63: 609–612, 2004
Geiger KD, Stoldt P, Schlote W, Derouiche A, Ezrin immunoreactivity is associated with increasing malignancy of astrocytic tumors but is absent in oligodendrogliomas Am J Pathol 157: 1785–1793, 2000
Ilmonen S, Vaheri A, Asko-Seljavaara S, Carpén O, Ezrin in primary cutaneous melanoma Mod Pathol 2: 1–8, 2004
Palacios J, Honrado E, Osorio A, Cazorla A, Sarrio D, Barroso A, Rodriguez S, Cigudosa JC, Diez O, Alonso C, Lerma E, Sanchez L, Rivas C, Benitez J, Immunohistochemical characteristics defined by tissue microarray of hereditary breast cancer not attributable to BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations: differences from breast carcinomas arising in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers Clin Cancer Res 9: 3606–3614, 2003
Zajchowski DA, Bartholdi MF, Gong Y, Webster L, Liu HL, Munishkin A, Beauheim C, Harvey S, Ethier SP, Johnson PH, Identification of gene expression profiles that predict the aggressive behavior of breast cancer cells Cancer Res 61: 5168–5178, 2001
Ziche M, Gullino PM, Angiogenesis and neoplastic progression in vitro J Natl Cancer Inst 69: 483–487, 1982
Elliott BE, Meens JA, SenGupta SK, Louvard D, Arpin M, The membrane cytoskeletal crosslinker ezrin is required for metastasis of breast carcinoma cells Breast Cancer Res 7: R365–373, 2005
Tokunou M, Niki T, Saitoh Y, Imamura H, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S: Altered expression of the ERM proteins in lung adenocarcinoma Lab Invest 80: 1643–1650, 2000
Smith PM, Cowan A, Milgram SL, White BA, Tissue-specific regulation by estrogen of ezrin and ezrin/radixin/moesin-binding protein 50 Endocrine 22: 119–126, 2003
Song J, Fadiel A, Edusa V, Chen Z, So J, Sakamoto H, Fishman DA, Naftolin F, Estradiol-induced ezrin overexpression in ovarian cancer: a new signaling domain for estrogen Cancer Lett 220: 57–65, 2005
Carmeci C, Thompson DA, Kuang WW, Lightdale N, Furthmayr H, Weigel RJ, Moesin expression is associated with the estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer phenotype Surgery 124: 211–217, 1998
Bretscher A, Edwards K, Fehon RG, ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 586–599, 2002
Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M, Morphogenic effects of ezrin require a phosphorylation-induced transition from oligomers to monomers at the plasma membrane J Cell Biol 150: 193–203, 2000
Bretscher A, Rapid phosphorylation and reorganization of ezrin and spectrin accompany morphological changes induced in A-431 cells by epidermal growth factor J Cell Biol 108: 921–931, 1989
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Singhrao SK, Puntis MC, Nakamura T, Mansel RE, Hallett MB, Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation and translocation of ezrin by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217: 1062–1069, 1995
Ghatak S, Misra S, Toole BP, Hyaluronan constitutively regulates ErbB2 phosphorylation and signaling complex formation in carcinoma cells J Biol Chem 280: 8875–8883, 2005
Tokunaga E, Kimura Y, Oki E, Ueda N, Futatsugi M, Mashino K, Yamamoto M, Ikebe M, Kakeji Y, Baba H, Maehara Y, Akt is frequently activated in HER2/neu-positive breast cancers and associated with poor prognosis among hormone-treated patients Int J Cancer 118: 284–289, 2006
Panigrahi AR, Pinder SE, Chan SY, Paish EC, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, The role of PTEN and its signalling pathways, including AKT, in breast cancer; an assessment of relationships with other prognostic factors and with outcome J Pathol 204: 93–100, 2004
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Diego Megías (Biotechnology Programme, CNIO) and Ester Martín-Villar (CSIC, Madrid, Spain) for helping with confocal microscopy experiments. We are also grateful to Amancio Carnero (Experimental Therapeutics Programme, CNIO) for providing cell lines, and the CNIO Immunohistochemical Unit for expert technical assistance. David Sarrió (BEFI, 01/9132), and S. María Rodriguez-Pinilla are recipients of research grants from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria, Spain. Partially supported by grant SAF2004-08258-C02-01 to José Palacios.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarrió, D., Rodríguez-Pinilla, S.M., Dotor, A. et al. Abnormal ezrin localization is associated with clinicopathological features in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 98, 71–79 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9133-4