Abstract
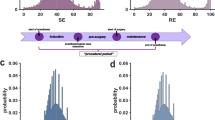
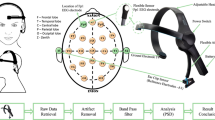
Conventional methods for positioning electroencephalography electrodes according to the international 10/20 system are based on the manual identification of the principal 10/20 landmarks via visual inspection and palpation, inducing intersession variations in their determined locations due to structural ambiguity or poor visibility. To address the variation issue, we propose an image guidance system for precision electrode placement. Following the electrode placement according to the 10/20 system, affixed electrodes are laser-scanned together with the facial surface. For subsequent procedures, the laser scan is conducted likewise after positioning the electrodes in an arbitrary manner, and following the measurement of fiducial electrode locations, frame matching is performed to determine a transformation from the coordinate frame of the position tracker to that of the laser-scanned image. Finally, by registering the intra-procedural scan of the facial surface to the reference scan, the current tracking data of the electrodes can be visualized relative to the reference goal positions without manually measuring the four principal landmarks for each trial. The experimental results confirmed that use of the electrode navigation system significantly improved the electrode placement precision compared to the conventional 10/20 system (p < 0.005). The proposed system showed the possibility of precise image-guided electrode placement as an alternative to the conventional manual 10/20 system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arata J, Kozuka H, Kim HW et al (2010) Open core control software for surgical robots. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 5:211–220
Arun KS, Huang TS, Blostein SD (1987) Least-squares fitting of two 3-D point sets. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 9:698–700
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D et al (2007) Comparison of different cortical connectivity estimators for high-resolution EEG recordings. Hum Brain Mapp 28:143–157
Atcherson SR, Gould HJ, Pousson MA, Prout TM (2007) Variability of electrode positions using electrode caps. Brain Topogr 20:105–111
Baysal U, Şengül G (2010) Single camera photogrammetry system for EEG electrode identification and localization. Ann Biomed Eng 38:1539–1547
Besl PJ, McKay ND (1992) Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In: Robotics-DL tentative. pp 586–606
Böcker KBE, van Avermaete JAG, van den Berg-Lenssen MMC (1994) The international 10–20 system revisited: Cartesian and spherical co-ordinates. Brain Topogr 6:231–235
Bradski G, Kaehler A (2008) Learning OpenCV: Computer vision with the OpenCV library. O’Reilly Media, Inc., Farnham
Bulea TC, Kim J, Damiano DL et al (2015) Prefrontal, posterior parietal and sensorimotor network activity underlying speed control during walking. Front Hum Neurosci 9:247
Chatrian GE, Lettich E, Nelson PL (1985) Ten percent electrode system for topographic studies of spontaneous and evoked EEG activities. Am J EEG Technol 25:83–92
Chatrian GE, Lettich E, Nelson PL (1988) Modified Nomenclature for the “10%” Electrode System1. J Clin Neurophysiol 5:183–186
Chen Y, Medioni G (1992) Object modelling by registration of multiple range images. Image Vis Comput 10:145–155
Cho B, Oka M, Matsumoto N et al (2013) Warning navigation system using real-time safe region monitoring for otologic surgery. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8:395–405
Coben LA, Danziger W, Storandt M (1985) A longitudinal EEG study of mild senile dementia of Alzheimer type: changes at 1 year and at 2.5 years. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 61:101–112
Committee EPN others (1994) Guideline thirteen: guidelines for standard electrode position nomenclature. J Clin Neurophysiol 11:111–113
Cutini S, Scatturin P, Zorzi M (2011) A new method based on ICBM152 head surface for probe placement in multichannel fNIRS. Neuroimage 54:919–927
De Munck JC, Vijn PCM, Spekreijse H (1991) A practical method for determining electrode positions on the head. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 78:85–87
Deonna T, Zesiger P, Davidoff V et al (2000) Benign partial epilepsy of childhood: a longitudinal neuropsychological and EEG study of cognitive function. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:595–603
Echallier JF, Perrin F, Pernier J (1992) Computer-assisted placement of electrodes on the human head. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:160–163
Eddelbuettel D, Sanderson C (2014) RcppArmadillo: accelerating R with high-performance C + + linear algebra. Comput Stat Data Anal 71:1054–1063
Egger J, Tokuda J, Chauvin L et al (2012) Integration of the OpenIGTLink Network Protocol for image-guided therapy with the medical platform MeVisLab. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 8:282–290
Elhawary H, Liu H, Patel P et al (2011) Intra-operative real-time querying of white matter tracts during frameless stereotactic neuronavigation. Neurosurgery 68:506
Figueiredo CP, Dias NS, Hoffmann K-P, Mendes PM (2008) 3D electrode localization on wireless sensor networks for wearable BCI. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2008. EMBS 2008. 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE. pp 2365–2368
Giacometti P, Diamond SG (2013) Compliant head probe for positioning electroencephalography electrodes and near-infrared spectroscopy optodes. J Biomed Opt 18:27005
He P, Estepp JR (2013) A practical method for quickly determining electrode positions in high-density EEG studies. Neurosci Lett 541:73–76
Herwig U, Satrapi P, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C (2003) Using the international 10–20 EEG system for positioning of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr 16:95–99
Hong J, Hashizume M (2010) An effective point-based registration tool for surgical navigation. Surg Endosc 24:944–948
Horn BKP (1987) Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions. JOSA A 4:629–642
Jasper H (1958) Report of the committee on methods of clinical examination in electroencephalography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 10:370–375
Jeon S, Lee GW, Jeon YD et al (2015) A preliminary study on surgical navigation for epiduroscopic laser neural decompression. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 229:693–v702
Jurcak V, Okamoto M, Singh A, Dan I (2005) Virtual 10–20 measurement on MR images for inter-modal linking of transcranial and tomographic neuroimaging methods. Neuroimage 26:1184–1192
Jurcak V, Tsuzuki D, Dan I (2007) 10/20, 10/10, and 10/5 systems revisited: their validity as relative head-surface-based positioning systems. Neuroimage 34:1600–1611
Kähkönen S, Kesäniemi M, Nikouline VV et al (2001) Ethanol modulates cortical activity: direct evidence with combined TMS and EEG. Neuroimage 14:322–328
Kavanagh KT, Clark ST (1989) Comparison of the mastoid to vertex and mastoid to high forehead electrode arrays in recording auditory evoked potentials. Ear Hear 10:259–261
Kim S, Hong J, Joung S et al (2011) Dual surgical navigation using augmented and virtual environment techniques. Int J Optomechatronics 5:155–169
Klem GH, Luders HO, Jasper HH et al (1999) The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52:3–6
Koessler L, Maillard L, Benhadid A et al (2007) Spatial localization of EEG electrodes. Neurophysiol Clin Neurophysiol 37:97–102
Koessler L, Benhadid A, Maillard L et al (2008) Automatic localization and labeling of EEG sensors (ALLES) in MRI volume. Neuroimage 41:914–923
Koessler L, Cecchin T, Ternisien E, Maillard L (2010) 3D handheld laser scanner based approach for automatic identification and localization of EEG sensors. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE. pp 3707–3710
Lagerlund TD, Sharbrough FW, Jack CR et al (1993) Determination of 10–20 system electrode locations using magnetic resonance image scanning with markers. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 86:7–14
Le J, Lu M, Pellouchoud E, Gevins A (1998) A rapid method for determining standard 10/10 electrode positions for high resolution EEG studies. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106:554–558
Lepetit V, Moreno-Noguer F, Fua P (2009) Epnp: an accurate o (n) solution to the pnp problem. Int J Comput Vis 81:155
Matsumoto N, Oka M, Cho B et al (2012) Cochlear implantation assisted by noninvasive image guidance. Otol Neurotol 33:1333–1338
Munoz-Salinas R (2012) ARUCO: a minimal library for Augmented Reality applications based on OpenCv
Myslobodsky MS, Coppola R, Bar-Ziv J, Weinberger DR (1990) Adequacy of the International 10–20 electrode system for computed neurophysiologic topography. J Clin Neurophysiol 7:507–518
Nuwer MR, Comi G, Emerson R et al (1998) IFCN standards for digital recording of clinical EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106:259–261
Oostenveld R, Praamstra P (2001) The five percent electrode system for high-resolution EEG and ERP measurements. Clin Neurophysiol 112:713–719
Otten P, Kim J, Son SH (2015) A framework to automate assessment of upper-limb motor function impairment: A feasibility study. Sensors 15:20097–20114
Qian S, Sheng Y (2011) A single camera photogrammetry system for multi-angle fast localization of EEG electrodes. Ann Biomed Eng 39:2844
Reis PMR, Lochmann M (2015) Using a motion capture system for spatial localization of EEG electrodes. Front Neurosci 9:130
Richards JE, Boswell C, Stevens M, Vendemia JMC (2015) Evaluating methods for constructing average high-density electrode positions. Brain Topogr 28:70–86
Sanderson C et al (2010) Armadillo: an open source C + + linear algebra library for fast prototyping and computationally intensive experiments
Schwartz D, Lemoine D, Poiseau E, Barillot C (1996) Registration of MEG/EEG data with 3D MRI: methodology and precision issues. Brain Topogr 9:101–116
Sitaram R, Zhang H, Guan C et al (2007) Temporal classification of multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy signals of motor imagery for developing a brain–computer interface. Neuroimage 34:1416–1427
Souzaki R, Kinoshita Y, Matsuura T et al (2011) Successful resection of an undifferentiated sarcoma in a child using a real-time surgical navigation system in an open magnetic resonance imaging operation room. J Pediatr Surg 46:608–611
Tauscher S, Tokuda J, Schreiber G et al (2015) OpenIGTLink interface for state control and visualisation of a robot for image-guided therapy systems. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10:285–292
Tokuda J, Fischer GS, Papademetris X et al (2009) OpenIGTLink: an open network protocol for image-guided therapy environment. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 5:423–434
Tokuda J, Fischer GS, DiMaio SP et al (2010) Integrated navigation and control software system for MRI-guided robotic prostate interventions. Comput Med Imaging Graph 34:3–8
Towle VL, Bolanos J, Suarez D et al (1993) The spatial location of EEG electrodes: locating the best-fitting sphere relative to cortical anatomy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 86:1–6
Tsutsumi N, Tomikawa M, Uemura M et al (2013) Image-guided laparoscopic surgery in an open MRI operating theater. Surg Endosc 27:2178–2184
Tsuzuki D, Watanabe H, Dan I, Taga G (2016) Minr 10/20 system: Quantitative and reproducible cranial landmark setting method for mri based on minimum initial reference points. J Neurosci Methods 264:86–93
Van Olphen AF, Rodenburg M, Verwey C (1978) Distribution of brain stem responses to acoustic stimuli over the human scalp. Audiology 17:511–518
Vaughan HG, Ritter W (1970) The sources of auditory evoked responses recorded from the human scalp. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 28:360–367
Wilm J (2010) Iterative Closest Point. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/27804-iterative-closest-point. Accessed 27 Jun 2017
Wood CC, Allison T (1981) Interpretation of evoked potentials: A neurophysiological perspective. Can J Psychol Can Psychol 35:113
Yoo S-S, Guttmann CRG, Ives JR et al (1997) 3D localization of surface 10–20 EEG electrodes on high resolution anatomical MR images. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 102:335–339
Zhang Z (2000) A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22:1330–1334
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BD-0401). Part of this study was reported at the Asian Conference on Computer Aided Surgery held in Singapore in 2015, at the International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering held in Montpellier France in 2015 and at the 30th International Congress of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery held in Heidelberg Germany in 2016, respectively. The authors thank Hyunseok Choi, a PhD candidate from DGIST, for his valuable help on software programming.
Funding
This study was funded by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BD-0401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
For this type of study, formal approval is not required.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, S., Chien, J., Song, C. et al. A Preliminary Study on Precision Image Guidance for Electrode Placement in an EEG Study. Brain Topogr 31, 174–185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0610-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0610-y