Abstract
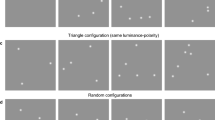
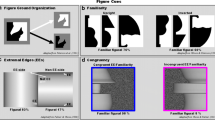
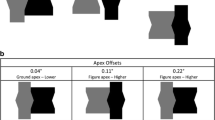
Figure recognition process: From the coarse configuration standing from the background to the closure of a meaningful shape, was investigated by ERP technique. ERP components at different latencies from stimulus onset allowed to tap into the figure recognition process at discrete time-points when different cognitive operations take place. In this study, we present two experiments where the support-ratio (SR) of illusory figures was manipulated to vary continuously the recognition of geometrical figures. In the first experiment three shapes were used to vary the SR and the P1 component (80–130 ms) was modulated by the configuration-effect explained, in part for the first time, with the unbalanced physical stimulation between upper and lower visual field. In the second experiment, we used one shape and varied systematically the SR in a discrimination task. The N1 (130–180 ms) and the N2 (230–270 ms) were modulated by two effects: The Ic-effect, represented by the N1, and the closure-effect, represented by the N2, being larger when the SR was small and the discrimination more difficult with respect to large SRs and easier discrimination. These results showed that figure recognition proceeded from the coarse parsing of the visual scene (configuration-effect), through the completion of a set of illusory borders (Ic-effect) to the final assembling of a meaningful shape (closure-effect).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler T, Molholm S, Russo N, Snyder A, Brandwein A, Blanco D, Foxe J (2012) Early electrophysiological indices of illusory contour processing within the lateral occipital complex are virtually impervious to manipulations of illusion strength. Neuroimage 59:4074–4085
Altschuler T, Molholm S, Butler J, Mercier M, Brandwein A, Foxe J (2014) The effort to close the gap: tracking the development of illusory contour processing in childhood to adulthood with high-density electrical mapping. Neuroimage 90:360–373
Barlasov-loffe A, Hochstein S (2008) Perceiving illusory contours: Figure detection and shape discrimination. J Vision 8(11): 1–15
Barlasov-loffe A, Hochstein S (2009) Illusory-contours figures prime matching of real shapes. Perception 38:1118–1131
Clark VP, Fan S, Hiilyard SA (1995) Identification of early visually evoked potential generators by retinotopic and topographic analyses. Hum Brain Mapp 2:170–187
Di Russo F, Martinez A, Sereno MI, Pitzalis S, Hillyard SA (2002) Cortical sources of the early components of the visual evoked potential. Hum Brain Mapp 15:95–111
Doniger G, Foxe J, Murray M, Higgins B, Snodgrass J, Schroeder C, Javitt D (2000) Activation timecourse of ventral visual stream object-recognition areas: high density electrical mapping of perceptual closure processes. J Cog Neurosci 12:4:615–621
Doniger G, Foxe J, Schroeder C, Murray M, Higgins B, Javitt D (2001) Visual perceptual learning in human object recognition areas: a repetition priming study using high-density electrical mapping. Neuroimage 13:2:305–313
Doniger G, Foxe J, Murray M, Higgins B, Javitt D (2002) Impaired visual object recognition and dorsal/ventral stream interaction in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:11:1011–1020
Foxe J, Murray M, Javitt D (2005) Filling-in in schizophrenia: a high-density electrical mapping and source-analysis investigation of illusory contour processing. Cereb Cortex 15(12):1914–1927
Grill-Spector K, Kanwisher N (2001) The lateral occipital complex and its role in object recognition. Vision Res 41:1409–1422
Halgren E, Mendola J, Ching CDR, Dale AM (2003) Cortical activation to illusory shapes as measured with magnetoencephalography. Neuroimage 18:1001–1009
Hermann CS, Mecklinger A, Pfeifer E (1999) Gamma responses and ERPs in a visual classification task. Clin Neurophysiol 110:636–642
Herrmann CS, Boch V (2001) IC perception modulates early visual processing. Cog Neurosci 12(5):901–904
Hillyard SA, Anllo-Vento L (1998) Event-related brain potentials in the study of visual selective attention. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:781–787
Hochstein S, Ahissar M (2002) View from the top: hierarchies and reverse hierarchies in the visual system. Neuron 36:791–804
Jennings JR, Wood CC (1976) The e-adjustment procedure for repeated-measures analyses of variance. Psychophysiology 13:277–278
Kanizsa G (1987) Quasi-perceptual margins in homogeneously stimulated fields. In: Petry S, Meyer G (eds) The perception of illusory contours. Springer, New York, pp 40–49 (Original work published1955)
Kobatake E, Tanaka K (1994) Neuronal selectivities to complex object features in the ventral visual pathway of the macaque cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 71:856–867
Lesher GW, Mingolla E (1993) The role of edges and line-ends in illusory contours formation. Vision Res 33(16):2253–2270
Luck SJ (2005) An introduction to the event-related potential technique. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 34–38
Marr D (1982) Vision: a computational investigation into the human representation and processing of visual information. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, pp 51–74
Mendola JD, Dale AM, Fischl B, Liu AK, Tottel R. B. H. (1999) The representation of illusory contours in human cortical visual areas revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 19(19):8560–8572
Murray M, Herrmann C (2013) Illusory contours: a window onto the neurophysiology of constructing perception. Trends Cog Sci 17(9):471–481
Murray MM, Wylie GR, Higgins BA, Javitt DC, Schroeder CE, Foxe JJ (2002). The spatiotemporal dynamics of illusory contour processing: combined high-density electrical mapping, source analysis, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 22(12):5055–5073
Murray M, Foxe D, Javitt D, Foxe J (2004) Setting boundaries: Brain dynamics of modal and amodal illusory shape completion in humans. J Neurosci 24(31):6898–6903
Murray M, Imber M, Javitt D, Foxe J (2006) Boundary completion is automatic and dissociable from shape discrmination. J Neurosci 26:46:12043–12054
Noesselt T, Hillyard S, Woldorff M, Shoenfeld A, Hagner T, Jancke L, Tempelmann C, Hinrichs H, Heinze H (2002) Delayed striate cortical activation during spatial attention. Neuron 35:575–587
Pegna A, Khateb A, Murray M, Landis T, Michel C (2002) Neural processing of illusory and real contours revealed by high-density ERP mapping. Cog Neurosci Neuropsych 13(7):965–968
Perrin F, Pernier J, Bertrand O, Echallier JF (1989) Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 72:184–187
Seghier M, Vuilleumier P (2006) Functional neuroimaging findings on the human perception of illusory contours. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:595–612
Sehatpour P, Molholm S, Javitt D, Foxe J (2006) Spatiotemporal dynamics of human object recognition processing: an integrated high-density electrical mapping and functional imaging study of “closure” processes. Neuroimage 29(2):605–618
Shpaner M, Murray M, Foxe J (2009) Early processing in the human lateral occipital complex is highly responsive to illusory contours but not to salient regions. Eur J Neurosci 30:2018–2028
Stanley DA, Rubin N (2003). fMRI activation in response to illusory contours and salient regions in the human lateral occipital complex. Neuron 37, 323–331
Stanley DA, Rubin N (2005) Rapid detection of salient region: evidence from apparent motion. J Vision 5:690–701
Sugawara M, Morotomi T (1991) Visual evoked potentials elicited by subjective contour figures. Scand J Psychol 32:352–357
Acknowledgements
The study was supported, in part, by research funding of the University of Verona. We are grateful to three anonymous referees who contributed to greatly improve the paper with their comments and criticisms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poscoliero, T., Girelli, M. Electrophysiological Modulation in an Effort to Complete Illusory Figures: Configuration, Illusory Contour and Closure Effects. Brain Topogr 31, 202–217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0582-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0582-y