Abstract
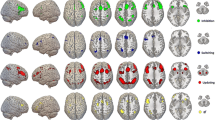
The neurobiological correlates of human fluid intelligence (Gf) remain elusive. Here, we demonstrate that spatiotemporal dynamics of EEG activity correlate with baseline measures of Gf and with its modulation by cognitive training. EEG dynamics were assessed in 74 healthy participants by examination of fast-changing, recurring, topographically-defined electric patterns termed “microstates”, which characterize the electrophysiological activity of distributed cortical networks. We find that the frequency of appearance of specific brain topographies, spatially associated with visual (microstate B) and executive control (microstate C) networks, respectively, is inversely related to Gf scores. Moreover, changes in Gf scores with cognitive training are inversely correlated with changes in microstate properties, indicating that the changes in brain network dynamics are behaviorally relevant. Finally, we find that cognitive training that increases Gf scores results in a posterior shift in the topography of microstate C. These results highlight the role of fast-changing brain electrical states in individual variability in Gf and in the response to cognitive training.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander GE, Furey ML, Grady CL, Pietrini P, Brady DR, Mentis MJ, Schapiro MB (1997) Association of premorbid intellectual function with cerebral metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for the cognitive reserve hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry 154:165–172
Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA (2014) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: one decade on. Trends Cogn Sci 18:177–185
Au J, Sheehan E, Tsai N, Duncan GJ, Buschkuehl M, Jaeggi SM (2014) Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory: a meta-analysis. Psychon Bull Rev 22:366–377
Bartlett MS (1937) The statistical conception of mental factors. Br J Psychol 28:97–104
Beaujean AA, Firmin MW, Michonski JD, Berry T, Johnson C (2010) A multitrait–multimethod examination of the reynolds intellectual assessment scales in a college sample. Assessment 17:347–360
Benedek M, Jauk E, Sommer M, Arendasy M, Neubauer AC (2014) Intelligence, creativity, and cognitive control: the common and differential involvement of executive functions in intelligence and creativity. Intelligence 46:73–83
Bondarenko R, Boehler CN, Stoppel CM, Heinze HJ, Schoenfeld MA, Hopf JM (2012) Separable mechanisms underlying global feature-based attention. J Neurosci 32:15284–15295
Britz J, Van De Ville D, Michel CM (2010a) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 52:1162–1170
Britz J, Van De Ville D, Michel CM (2010b) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 52:1162–1170
Brumback CR, Low KA, Gratton G, Fabiani M (2004) Sensory ERPs predict differences in working memory span and fluid intelligence. Neuroreport 15:373–376
Brunet D, Murray MM, Michel CM (2011) Spatiotemporal analysis of multichannel EEG: CARTOOL. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011:813870
Burgess GC, Gray JR, Conway AR, Braver TS (2011) Neural mechanisms of interference control underlie the relationship between fluid intelligence and working memory span. J Exp Psychol Gen 140:674–692
Buschman TJ, Siegel M, Roy JE, Miller EK (2011) Neural substrates of cognitive capacity limitations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:11252–11255
Carpenter PA, Just MA, Shell P (1990) What one intelligence test measures: a theoretical account of the processing in the Raven Progressive Matrices Test. Psychol Rev 97:404–431
Chiang MC, Barysheva M, Lee AD, Madsen S, Klunder AD, Toga AW, McMahon KL, de Zubicaray GI, Meredith M, Wright MJ, Srivastava A, Balov N, Thompson PM (2008) Brain fiber architecture, genetics, and intelligence: a high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) study. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 11:1060–1067
Choi YY, Shamosh NA, Cho SH, Deyoung CG, Lee MJ, Lee JM, Kim SI, Cho ZH, Kim K, Gray JR, Lee KH (2008) Multiple bases of human intelligence revealed by cortical thickness and neural activation. J Neurosci 28:10323–10329
Cole JC, Lopez BR, Daleo DV (2004) Latent relationships of fluid, visual, and simultaneous cognitive tasks. Psychol Rep 94:547–561
Cole MW, Yarkoni T, Repovs G, Anticevic A, Braver TS (2012) Global connectivity of prefrontal cortex predicts cognitive control and intelligence. J Neurosci 32:8988–8999
Colom R, Jung RE, Haier RJ (2006) Distributed brain sites for the g-factor of intelligence. Neuroimage 31:1359–1365
Colom R, Karama S, Jung RE, Haier RJ (2010) Human intelligence and brain networks. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 12:489–501
Colom R, Burgaleta M, Roman FJ, Karama S, Alvarez-Linera J, Abad FJ, Martinez K, Quiroga MA, Haier RJ (2013) Neuroanatomic overlap between intelligence and cognitive factors: morphometry methods provide support for the key role of the frontal lobes. Neuroimage 72:143–152
Crone EA, Wendelken C, van LL, Honomichl RD, Christoff K, Bunge SA (2009) Neurocognitive development of relational reasoning. Dev Sci 12:55–66
da Rocha AF, Rocha FT, Massad E (2011) The brain as a distributed intelligent processing system: an EEG study. PLoS ONE 6:e17355
Damoiseaux JS, Rombouts SA, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Stam CJ, Smith SM, Beckmann CF (2006) Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13848–13853
Dang CP, Braeken J, Colom R, Ferrer E, Liu C (2014) Why is working memory related to intelligence? Different contributions from storage and processing. Memory 22:426–441
Deary I (2008) Why do intelligent people live longer? Nature 456:175–176
Deary IJ, Penke L, Johnson W (2010) The neuroscience of human intelligence differences. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:201–211
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–21
Engle RW, Tuholski SW, Laughlin JE, Conway AR (1999) Working memory, short-term memory, and general fluid intelligence: a latent-variable approach. J Exp Psychol Gen 128:309–331
Filmer HL, Dux PE, Mattingley JB (2014) Applications of transcranial direct current stimulation for understanding brain function. Trends Neurosci 37:742–753
Gaspar JM, McDonald JJ (2014) Suppression of salient objects prevents distraction in visual search. J Neurosci 34:5658–5666
Gazzaley A, Cooney JW, Rissman J, D’Esposito M (2005) Top-down suppression deficit underlies working memory impairment in normal aging. Nat Neurosci 8:1298–1300
Gazzaley A, Rissman J, Cooney J, Rutman A, Seibert T, Clapp W, D’Esposito M (2007) Functional interactions between prefrontal and visual association cortex contribute to top-down modulation of visual processing. Cereb Cortex 17(Suppl 1):i125–i135
Goh S, Bansal R, Xu D, Hao X, Liu J, Peterson BS (2011) Neuroanatomical correlates of intellectual ability across the life span. Dev Cogn Neurosci 1:305–312
Gong QY, Sluming V, Mayes A, Keller S, Barrick T, Cezayirli E, Roberts N (2005) Voxel-based morphometry and stereology provide convergent evidence of the importance of medial prefrontal cortex for fluid intelligence in healthy adults. Neuroimage 25:1175–1186
Gray JR, Thompson PM (2004a) Neurobiology of intelligence: health implications? Discov Med 4:157–162
Gray JR, Thompson PM (2004b) Neurobiology of intelligence: science and ethics. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:471–482
Gray JR, Chabris CF, Braver TS (2003) Neural mechanisms of general fluid intelligence. Nat Neurosci 6:316–322
Haier RJ (2014) Increased intelligence is a myth (so far). Front Syst Neurosci 8:34
Haier RJ, Jung RE, Yeo RA, Head K, Alkire MT (2004) Structural brain variation and general intelligence. Neuroimage 23:425–433
Hambrick DZ, Altmann EM (2015) The role of placekeeping ability in fluid intelligence. Psychon Bull Rev 22:1104–1110
Hossiep R, Turck D, Hasella M (1999) Bochumer Matrizentest: BOMAT advanced-short version. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Houde O, Zago L, Mellet E, Moutier S, Pineau A, Mazoyer B, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2000) Shifting from the perceptual brain to the logical brain: the neural impact of cognitive inhibition training. J Cogn Neurosci 12:721–728
Jacob SN, Nieder A (2014) Complementary roles for primate frontal and parietal cortex in guarding working memory from distractor stimuli. Neuron 83:226–237
Jaeggi SM, Buschkuehl M, Jonides J, Perrig WJ (2008) Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6829–6833
Jung RE, Haier RJ (2007) The Parieto-Frontal Integration Theory (P-FIT) of intelligence: converging neuroimaging evidence. Behav Brain Sci 30:135–154
Kaiser FH (1958) The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 23:187–200
Khanna A, Pascual-Leone A, Farzan F (2014) Reliability of resting-state microstate features in electroencephalography. PLoS ONE 9:e114163
Khanna A, Pascual-Leone A, Michel CM, Farzan F (2015) Microstates in resting-state EEG: current status and future directions. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 49:105–113
Kievit RA, Davis SW, Mitchell DJ, Taylor JR, Duncan J, Henson RN (2014) Distinct aspects of frontal lobe structure mediate age-related differences in fluid intelligence and multitasking. Nat Commun 5:5658
Koenig T, Lehmann D (1996) Microstates in language-related brain potential maps show noun-verb differences. Brain Lang 53:169–182
Koenig T, Melie-Garcia L (2009) Statistical analysis of multichannel scalp field data. In: Koenig T, Melie-Garcia L, Electrical neuroimaging. Cambridge University, Cambridge 53:169–190
Koenig T, Kochi K, Lehmann D,(1998) Event-related electric microstates of the brain differ between words with visual and abstract meaning. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106:535–546
Koenig T, Prichep L, Lehmann D, Sosa PV, Braeker E, Kleinlogel H, Isenhart R, John ER (2002) Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. Neuroimage 16:41–48
Kundu B, Sutterer DW, Emrich SM, Postle BR (2013) Strengthened effective connectivity underlies transfer of working memory training to tests of short-term memory and attention. J Neurosci 33:8705–8715
Kush JC, Spring MB, Barkand J (2012) Advances in the assessment of cognitive skills using computer-based measurement. Behav Res Methods 44:125–134
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L, Kochunov PV, Nickerson D, Mikiten SA, Fox PT (2000) Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10(3):120–131
Langer N, von Bastian CC, Wirz H, Oberauer K, Jancke L (2013) The effects of working memory training on functional brain network efficiency. Cortex 49:2424–2438
Lehmann D (1971) Multichannel topography of human alpha EEG fields. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 31:439–449
Lehmann D, Faber PL, Galderisi S, Herrmann WM, Kinoshita T, Koukkou M, Mucci A, Pascual-Marqui RD, Saito N, Wackermann J, Winterer G, Koenig T (2005) EEG microstate duration and syntax in acute, medication-naive, first-episode schizophrenia: a multi-center study. Psychiatry Res 138:141–156
Malhotra P, Coulthard EJ, Husain M (2009) Role of right posterior parietal cortex in maintaining attention to spatial locations over time. Brain 132:645–660
Martinez A, Anllo-Vento L, Sereno MI, Frank LR, Buxton RB, Dubowitz DJ, Wong EC, Hinrichs H, Heinze HJ, Hillyard SA (1999) Involvement of striate and extrastriate visual cortical areas in spatial attention. Nat Neurosci 2:364–369
Matsuda O, Saito M (1998) Crystallized and fluid intelligence in elderly patients with mild dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int Psychogeriatr 10:147–154
Matzen LE, Benz ZO, Dixon KR, Posey J, Kroger JK, Speed AE (2010) Recreating Raven’s: software for systematically generating large numbers of Raven-like matrix problems with normed properties. Behav Res Methods 42:525–541
Mazziotta J, Toga A, Evans A, Fox P, Lancaster J, Zilles K et al (2001) A four-dimensional probabilistic atlas of the human brain. J Am Med Inf Assoc, 8(5):401–430
Melara RD, Tong Y, Rao A (2012) Control of working memory: effects of attention training on target recognition and distractor salience in an auditory selection task. Brain Res 1430:68–77
Melnick MD, Harrison BR, Park S, Bennetto L, Tadin D (2013) A strong interactive link between sensory discriminations and intelligence. Curr Biol 23:1013–1017
Michel CM, Lehmann D (1993) Single doses of piracetam affect 42-channel event-related potential microstate maps in a cognitive paradigm. Neuropsychobiology 28:212–221
Micheloyannis S, Pachou E, Stam CJ, Vourkas M, Erimaki S, Tsirka V (2006) Using graph theoretical analysis of multi channel EEG to evaluate the neural efficiency hypothesis. Neurosci Lett 402:273–277
Milz P, Faber PL, Lehmann D, Koenig T, Kochi K, Pascual-Marqui RD (2015) The functional significance of EEG microstates-associations with modalities of thinking. Neuroimage 125:643–656
Mognon A, Jovicich J, Bruzzone L, Buiatti M (2011) ADJUST: an automatic EEG artifact detector based on the joint use of spatial and temporal features. Psychophysiology 48:229–240
Moody S (2009) Can intelligence be increased by training on a task of working memory? Intelligence 7:327–328
Narr KL, Woods RP, Thompson PM, Szeszko P, Robinson D, Dimtcheva T, Gurbani M, Toga AW, Bilder RM (2007) Relationships between IQ and regional cortical gray matter thickness in healthy adults. Cereb Cortex 17:2163–2171
Neubauer AC, Fink A (2009) Intelligence and neural efficiency. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:1004–1023
Neubauer AC, Grabner RH, Freudenthaler HH, Beckmann JF, Guthke J (2004) Intelligence and individual differences in becoming neurally efficient. Acta Psychol 116:55–74
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002) Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15(1):1–25
Nishida K, Morishima Y, Yoshimura M, Isotani T, Irisawa S, Jann K, Dierks T, Strik W, Kinoshita T, Koenig T (2013) EEG microstates associated with salience and frontoparietal networks in frontotemporal dementia, schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 124(6):1106–1114
Oelhafen S, Nikolaidis A, Padovani T, Blaser D, Koenig T, Perrig WJ (2013) Increased parietal activity after training of interference control. Neuropsychologia 51:2781–2790
Pahor A, Jausovec N (2014) The effects of theta transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) on fluid intelligence. Int J Psychophysiol 93:322–331
Pascual-Marqui RD (2007) Discrete, 3D distributed, linear imaging methods of electric neuronal activity. Part 1: exact, zero error localization. arXiv:0710.3341 [Math-Ph, Physics:physics, Q-Bio], October
Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1995) Segmentation of brain electrical activity into microstates: model estimation and validation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 42:658–665
Pascual-Marqui RD, Lehmann D, Faber P, Milz P, Kochi K, Yoshimura M, Nishida K, Isotani T, Kinoshita T (2014) The resting microstate networks (RMN): cortical distributions, dynamics, and frequency specific information flow. http://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1949v2
Pereira J, Wang XJ (2015) A tradeoff between accuracy and flexibility in a working memory circuit endowed with slow feedback mechanisms. Cereb Cortex 25:3586–3601
Perfetti B, Saggino A, Ferretti A, Caulo M, Romani GL, Onofrj M (2009) Differential patterns of cortical activation as a function of fluid reasoning complexity. Hum Brain Mapp 30:497–510
Peters JC, Roelfsema PR, Goebel R (2012) Task-relevant and accessory items in working memory have opposite effects on activity in extrastriate cortex. J Neurosci 32:17003–17011
Prado J, Noveck IA (2007) Overcoming perceptual features in logical reasoning: a parametric functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Cogn Neurosci 19:642–657
Prado J, Kaliuzhna M, Cheylus A, Noveck IA (2008) Overcoming perceptual features in logical reasoning: an event-related potentials study. Neuropsychologia 46:2629–2637
Prado J, Van Der Henst JB, Noveck IA (2010) Recomposing a fragmented literature: how conditional and relational arguments engage different neural systems for deductive reasoning. Neuroimage 51:1213–1221
Raven J, Raven JC, Court JH (2003) Manual for Raven’s progressive matrices and vocabulary scales. Section 1: general overview. Harcourt Assessment, San Antonia
Raz N, Lindenberger U, Ghisletta P, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Acker JD (2008) Neuroanatomical correlates of fluid intelligence in healthy adults and persons with vascular risk factors. Cereb Cortex 18:718–726
Rushton JP, Ankney CD (2009) Whole brain size and general mental ability: a review. Int J Neurosci 119:691–731
Santarnecchi E, Rossi S (2016b) Advances in the neuroscience of intelligence: from brain connectivity to brain perturbation. Span J Psychol. doi:10.1017/sjp.2016.89
Santarnecchi E, Polizzotto NR, Godone M, Giovannelli F, Feurra M, Matzen L, Rossi A, Rossi S (2013) Frequency-dependent enhancement of fluid intelligence induced by transcranial oscillatory potentials. Curr Biol 23:1449–1453
Santarnecchi E, Galli G, Polizzotto NR, Rossi A, Rossi S (2014) Efficiency of weak brain connections support general cognitive functioning. Hum Brain Mapp 35:4566–4582
Santarnecchi E, Brem AK, Levenbaum E, Thompson T, Kadosh RC, Pascual-Leone A (2015a) Enhancing cognition using transcranial electrical stimulation. Curr Opin Behav Sci 4:171–178
Santarnecchi E, Rossi S, Rossi A (2015b) The smarter, the stronger: intelligence level correlates with brain resilience to systematic insults. Cortex 64:293–309
Santarnecchi E, Tatti E, Rossi S, Serino V, Rossi A (2015c) Intelligence-related differences in the asymmetry of spontaneous cerebral activity. Hum Brain Mapp 36:3586–3602
Santarnecchi E, Muller T, Rossi S, Sarkar A, Polizzotto NR, Rossi A, Kadosh RC (2016a) Individual differences and specificity of prefrontal gamma frequency-tACS on fluid intelligence capabilities. Cortex 23:1449–1453
Sitaram R, Ros T, Stoeckel L, Haller S, Scharnowski F, Lewis-Peacock J, Weiskopf N et al (2016) Closed-loop brain training: the science of neurofeedback. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(2):86–100
Soulieres I, Dawson M, Samson F, Barbeau EB, Sahyoun CP, Strangman GE, Zeffiro TA, Mottron L (2009) Enhanced visual processing contributes to matrix reasoning in autism. Hum Brain Mapp 30:4082–4107
Stern Y (2002) What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 8:448–460
Stern Y (2009) Cognitive reserve. Neuropsychologia 47:2015–2028
Thompson TW, Waskom ML, Garel KL, Cardenas-Iniguez C, Reynolds GO, Winter R, Chang P, Pollard K, Lala N, Alvarez GA, Gabrieli JD (2013) Failure of working memory training to enhance cognition or intelligence. PLoS ONE 8:e63614
Tibshirania R, Walther G (2005) Cluster validation by prediction strength. J Comput Graph Stat 14:511–528
Tomescu MI, Rihs TA, Becker R, Britz J, Custo A, Grouiller F, Schneider M, Debbane M, Eliez S, Michel CM (2014) Deviant dynamics of EEG resting state pattern in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome adolescents: a vulnerability marker of schizophrenia? Schizophr Res 157:175–181
Vakhtin AA, Ryman SG, Flores RA, Jung RE (2014) Functional brain networks contributing to the Parieto-Frontal Integration Theory of Intelligence. Neuroimage 103:349–354
Van De Ville D, Britz J, Michel CM (2010) EEG microstate sequences in healthy humans at rest reveal scale-free dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:18179–18184
van den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE (2009) Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. J Neurosci 29:7619–7624
Verney SP, Granholm E, Marshall SP, Malcarne VL, Saccuzzo DP (2005) Culture-fair cognitive ability assessment: information processing and psychophysiological approaches. Assessment 12:303–319
Wartenburger I, Heekeren HR, Preusse F, Kramer J, van der Meer E (2009) Cerebral correlates of analogical processing and their modulation by training. Neuroimage 48:291–302
Whalley LJ, Deary IJ, Appleton CL, Starr JM (2004) Cognitive reserve and the neurobiology of cognitive aging. Ageing Res Rev 3:369–382
Yuan Z, Qin W, Wang D, Jiang T, Zhang Y, Yu C (2012) The salience network contributes to an individual’s fluid reasoning capacity. Behav Brain Res 229:384–390
Zhang G, Yao L, Shen J, Yang Y, Zhao X (2015) Reorganization of functional brain networks mediates the improvement of cognitive performance following real-time neurofeedback training of working memory: brain networks mediate post-training behavior. Hum Brain Mapp 36(5):1705–1715
Zook NA, Davalos DB, Delosh EL, Davis HP (2004) Working memory, inhibition, and fluid intelligence as predictors of performance on Tower of Hanoi and London tasks. Brain Cogn 56:286–292
Acknowledgements
This research is based upon work supported by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), via 2014-13121700007. The views and conclusions contained herein are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as necessarily representing the official policies or endorsements, either expressed or implied, of the ODNI, IARPA, or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Governmental purposes notwithstanding any copyright annotation thereon. Dr. Pascual-Leone is further supported by the Berenson-Allen Foundation, the Sidney R. Baer Jr. Foundation, grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01HD069776, R01NS073601, R21 MH099196, R21 NS082870, R21 NS085491, R21 HD07616), and Harvard Catalyst | The Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center (NCRR and the NCATS NIH, UL1 RR025758). The content of this paper is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of Harvard Catalyst, Harvard University and its affiliated academic health care centers, the National Institutes of Health, the Sidney R. Baer Jr. Foundation. The authors would like to thank the members of the larger Honeywell SHARP team for their valuable contributions to this work, including the SHARP Team authors: Harvard Medical School (Ann Connor, Franziska Plessow, Sadhvi Saxena, Erica Levenbaum); Honeywell (Jessamy Almquist, Michael Dillard, Umut Orhan, Santosh Mathan); Northeastern University (James McKanna, Deniz Erdogmus, Misha Pavel); Oxford University (Anna-Katharine Brem, Roi Cohen Kadosh, Nick Yeung); SimCoach Games (Garrett Kimball, Eben Myers).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Emiliano Santarnecchi and Arjun R. Khanna contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santarnecchi, E., Khanna, A.R., Musaeus, C.S. et al. EEG Microstate Correlates of Fluid Intelligence and Response to Cognitive Training. Brain Topogr 30, 502–520 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0565-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0565-z