Abstract
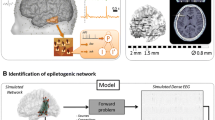
Epilepsy surgery is the most efficient treatment option for patients with refractory epilepsy. Before surgery, it is of utmost importance to accurately delineate the seizure onset zone (SOZ). Non-invasive EEG is the most used neuroimaging technique to diagnose epilepsy, but it is hard to localize the SOZ from EEG due to its low spatial resolution and because epilepsy is a network disease, with several brain regions becoming active during a seizure. In this work, we propose and validate an approach based on EEG source imaging (ESI) combined with functional connectivity analysis to overcome these problems. We considered both simulations and real data of patients. Ictal epochs of 204-channel EEG and subsets down to 32 channels were analyzed. ESI was done using realistic head models and LORETA was used as inverse technique. The connectivity pattern between the reconstructed sources was calculated, and the source with the highest number of outgoing connections was selected as SOZ. We compared this algorithm with a more straightforward approach, i.e. selecting the source with the highest power after ESI as the SOZ. We found that functional connectivity analysis estimated the SOZ consistently closer to the simulated EZ/RZ than localization based on maximal power. Performance, however, decreased when 128 electrodes or less were used, especially in the realistic data. The results show the added value of functional connectivity analysis for SOZ localization, when the EEG is obtained with a high-density setup. Next to this, the method can potentially be used as objective tool in clinical settings.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723
Arnold M, Milner X, Witte H, Bauer R, Braun C (1998) Adaptive AR modeling of nonstationary time series by means of Kalman filtering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 45(5):553–562
Assaf BA, Ebersole JS (1997) Continuous source imaging of scalp ictal rhythms in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 38(10):1114–1123
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, de Vico Fallani F, Tocci A, Colosimo A, Salinari S, Marciani MG, Hesse W, Witte H et al (2008) Tracking the time-varying cortical connectivity patterns by adaptive multivariate estimators. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(3):902–913
Baillet S, Mosher JC, Leahy RM (2001) Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE Signal Process Mag 18(6):14–30
Bastos AM, Schoffelen JM (2015) A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front Syst Neurosci 9:1–23
Baumann SB, Wozny DR, Kelly SK, Meno FM (1997) The electrical conductivity of human cerebrospinal fluid at body temperature. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 44(3):220–223
Boon P, D’Havé M, Vanrumste B, Van Hoey G, Vonck K, Van Walleghem P, Caemaert J, Achten E, De Reuck J (2002) Ictal source localization in presurgical patients with refractory epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol 19(5):461–468
Brodbeck V, Spinelli L, Lascano AM, Wissmeier M, Vargas MI, Vulliémoz S, Pollo C, Schaller K, Michel CM, Seeck M (2011) Electroencephalographic source imaging: a prospective study of 152 operated epileptic patients. Brain 134(10):2887–2897
Brovelli A, Chicharro D, Badier JM, Wang H, Jirsa V (2015) Characterization of cortical networks and corticocortical functional connectivity mediating arbitrary visuomotor mapping. J Neurosci 35(37):12643–12658
Carrette E, Vonck K, Boon P (2011) The management of pharmacologically refractory epilepsy. Int J of Clin Rev 1(02):104–121
Clarke C, Janday B (1989) The solution of the biomagnetic inverse problem by maximum statistical entropy. Inverse Probl 5(4):483
Coito A, Genetti M, Pittau F, Iannotti GR, Thomschewski A, Höller Y, Trinka E, Wiest R, Seeck M, Michel CM et al (2016) Altered directed functional connectivity in temporal lobe epilepsy in the absence of interictal spikes: a high density EEG study. Epilepsia 57(3):402–411
Coito A, Plomp G, Genetti M, Abela E, Wiest R, Seeck M, Michel CM, Vulliémoz S (2015) Dynamic directed interictal connectivity in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 56(2):207–217
Dalal SS, Rampp S, Willomitzer F, Ettl S (2014) Consequences of EEG electrode position error on ultimate beamformer source reconstruction performance. Front Neurosci 8:42
de Tisi J, Bell GS, Peacock JL, McEvoy AW, Harkness WF, Sander JW, Duncan JS (2011) The long-term outcome of adult epilepsy surgery, patterns of seizure remission, and relapse: a cohort study. Lancet 378(9800):1388–1395
Ding L, He B (2006) Spatio-temporal EEG source localization using a three-dimensional subspace fine approach in a realistic geometry inhomogeneous head model. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(9):1732–1739
Ding L, Worrell GA, Lagerlund TD, He B (2007) Ictal source analysis: localization and imaging of causal interactions in humans. Neuroimage 34(2):575–586
Ebersole JS (2000) Noninvasive localization of epileptogenic foci by EEG source modeling. Epilepsia 41(s3):S24–S33
Elshoff L, Muthuraman M, Anwar AR, Deuschl G, Stephani U, Raethjen J, Siniatchkin M (2013) Dynamic imaging of coherent sources reveals different network connectivity underlying the generation and perpetuation of epileptic seizures. PloS ONE 8(10):e78422
Golub GH, Reinsch C (1970) Singular value decomposition and least squares solutions. Numer Math 14(5):403–420
Groß J, Kujala J, Hämäläinen M, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A, Salmelin R (2001) Dynamic imaging of coherent sources: studying neural interactions in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(2):694–699
Groß J, Timmermann L, Kujala J, Dirks M, Schmitz F, Salmelin R, Schnitzler A (2002) The neural basis of intermittent motor control in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(4):2299–2302
Grova C, Daunizeau J, Lina JM, Bénar CG, Benali H, Gotman J (2006) Evaluation of EEG localization methods using realistic simulations of interictal spikes. Neuroimage 29(3):734–753
Haalman I, Vaadia E (1997) Dynamics of neuronal interactions: relation to behavior, firing rates, and distance between neurons. Hum Brain Mapp 5(4):249–253
Habib MA, Ibrahim F, Mohktar MS, Kamaruzzaman SB, Rahmat K, Lim KS (2015) Ictal EEG source imaging for presurgical evaluation of refractory focal epilepsy. World Neurosurg 88:576–585
Hallez H, Vanrumste B, Van Hese P, D’Asseler Y, Lemahieu I, Van de Walle R (2005) A finite difference method with reciprocity used to incorporate anisotropy in electroencephalogram dipole source localization. Phys Med Biol 50(16):3787
Hillebrand A, Barnes GR, Bosboom JL, Berendse HW, Stam CJ (2012) Frequency-dependent functional connectivity within resting-state networks: an atlas-based MEG beamformer solution. Neuroimage 59(4):3909–3921
Jayakar P, Duchowny M, Resnick TJ, Alvarez LA (1991) Localization of seizure foci: pitfalls and caveats. J Clin Neurophysiol 8(4):414–431
Jung KY, Kang JK, Kim JH, Im CH, Kim KH, Jung HK (2009) Spatiotemporospectral characteristics of scalp ictal EEG in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Brain Res 1287:206–219
Koessler L, Benar C, Maillard L, Badier JM, Vignal JP, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Gavaret M (2010) Source localization of ictal epileptic activity investigated by high resolution EEG and validated by SEEG. Neuroimage 51(2):642–653
Lantz G, de Peralta RG, Spinelli L, Seeck M, Michel CM (2003) Epileptic source localization with high density EEG: how many electrodes are needed? Clin Neurophysiol 114(1):63–69
Lantz G, Michel CM, Seeck M, Blanke O, Landis T, Rosén I (1999) Frequency domain EEG source localization of ictal epileptiform activity in patients with partial complex epilepsy of temporal lobe origin. Clin Neurophysiol 110(1):176–184
Lopez J, Litvak V, Espinosa J, Friston K, Barnes GR (2014) Algorithmic procedures for bayesian meg/eeg source reconstruction in spm. Neuroimage 84:476–487
Lu Y, Yang L, Worrell GA, He B (2012) Seizure source imaging by means of fine spatio-temporal dipole localization and directed transfer function in partial epilepsy patients. Clin Neurophysiol 123(7):1275–1283
Makeig S, Bell AJ, Jung TP, Sejnowski TJ et al (1996) Independent component analysis of electroencephalographic data. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 8:145–151
Mégevand P, Spinelli L, Genetti M, Brodbeck V, Momjian S, Schaller K, Michel CM, Vulliémoz S, Seeck M (2014) Electric source imaging of interictal activity accurately localises the seizure onset zone. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85(1):38–43
Michel CM, Murray MM (2012) Towards the utilization of EEG as a brain imaging tool. Neuroimage 61(2):371–385
Montes-Restrepo V, van Mierlo P, Strobbe G, Staelens S, Vandenberghe S, Hallez H (2014) Influence of skull modeling approaches on EEG source localization. Brain Topogr 27(1):95–111
Nolte G, Bai O, Wheaton L, Mari Z, Vorbach S, Hallett M (2004) Identifying true brain interaction from eeg data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clin Neurophysiol 115(10):2292–2307
Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1994) Low resolution electromagnetic tomography: a new method for localizing electrical activity in the brain. Int J Psychophysiol 18(1):49–65
Plummer C, Harvey AS, Cook M (2008) EEG source localization in focal epilepsy: where are we now? Epilepsia 49(2):201–218
Rémi J, Vollmar C, de Marinis A, Heinlin J, Peraud A, Noachtar S (2011) Congruence and discrepancy of interictal and ictal EEG with MRI lesions in focal epilepsies. Neurology 77(14):1383–1390
Richardson MP (2012) Large scale brain models of epilepsy: dynamics meets connectomics. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(12):1238–1248
Rosenow F, Lüders H (2001) Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain 124(9):1683–1700
Schlögl A, Roberts S, Pfurtscheller G (2000) A criterion for adaptive autoregressive models. Proc Ann Int IEEE EMBS 1581–1582
Schoffelen JM, Gross J (2009) Source connectivity analysis with meg and eeg. Hum Brain Map 30(6):1857–1865
Smith S (2005) EEG in the diagnosis, classification, and management of patients with epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(Suppl 2):ii2–ii7
Song J, Tucker DM, Gilbert T, Hou J, Mattson C, Luu P, Holmes MD (2013) Methods for examining electrophysiological coherence in epileptic networks. Front Neurol 4:55
Spencer SS (2002) Neural networks in human epilepsy: evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia 43(3):219–227
Sprengers M, Vonck K, Carrette E, Marson AG, Boon P (2014) Deep brain and cortical stimulation for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 6:CD008497
Strobbe G, Carrette E, López JD, Van Roost D, Meurs A, Vonck K, Boon P, Vandenberghe S, van Mierlo P (2016) Electrical source imaging of interictal spikes using multiple sparse volumetric priors for presurgical epileptogenic focus localization. Neuroimage Clin 11:252–263
Strobbe G, van Mierlo P, De Vos M, Mijović B, Hallez H, Van Huffel S, López JD, Vandenberghe S (2014) Multiple sparse volumetric priors for distributed EEG source reconstruction. Neuroimage 100:715–724
Téllez-Zenteno JF, Dhar R, Wiebe S (2005) Long-term seizure outcomes following epilepsy surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain 128(5):1188–1198
Van Hoey G, Vanrumste B, D’Havé M, Van de Walle R, Lemahieu I, Boon P (2000) Influence of measurement noise and electrode mislocalisation on EEG dipole-source localisation. Med Biol Eng Comput 38(3):287–296
van Mierlo P, Carrette E, Hallez H, Raedt R, Meurs A, Vandenberghe S, Roost D, Boon P, Staelens S, Vonck K (2013) Ictal-onset localization through connectivity analysis of intracranial EEG signals in patients with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 54(8):1409–1418
van Mierlo P, Carrette E, Hallez H, Vonck K, Van Roost D, Boon P, Staelens S (2011) Accurate epileptogenic focus localization through time-variant functional connectivity analysis of intracranial electroencephalographic signals. Neuroimage 56(3):1122–1133
Vorwerk J, Cho JH, Rampp S, Hamer H, Knösche TR, Wolters CH (2014) A guideline for head volume conductor modeling in EEG and MEG. Neuroimage 100:590–607
Wang Y, Gotman J (2001) The influence of electrode location errors on EEG dipole source localization with a realistic head model. Clin Neurophysiol 112(9):1777–1780
Wennberg R, Cheyne D (2014) EEG source imaging of anterior temporal lobe spikes: validity and reliability. Clin Neurophysiol 125(5):886–902
Wennberg R, Valiante T, Cheyne D (2011) EEG and MEG in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: where do the spikes really come from? Clin Neurophysiol 122(7):1295–1313
Xu XL, Xu B, He B (2004) An alternative subspace approach to EEG dipole source localization. Phys Med Biol 49(2):327
Yang L, Wilke C, Brinkmann B, Worrell GA, He B (2011) Dynamic imaging of ictal oscillations using non-invasive high-resolution eeg. Neuroimage 56(4):1908–1917
Acknowledgements
The research was funded by a Ph.D. grant of the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT). We acknowledge the support of the Swiss National Science Foundation, Grant No. 33CM30-140332 (G. Birot, M. Seeck), 141165 (S. Vulliémoz) and the Foundation Gertrude von Meissner (S. Vulliémoz). This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Grant No. 660230 (P. van Mierlo).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Model Orders
Appendix: Model Orders
See Table 3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staljanssens, W., Strobbe, G., Holen, R.V. et al. Seizure Onset Zone Localization from Ictal High-Density EEG in Refractory Focal Epilepsy. Brain Topogr 30, 257–271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0537-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0537-8