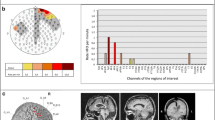
Abstract
The stochastic behavior of the phase synchronization index (SI) in different EEG bands was examined for noninvasive localization of the epileptogenic areas from the short duration (30–60 s), seizure-free and spike-free high density (256 channel) scalp EEG data. We also examined the cross-frequency and cross-electrode coupling in different EEG bands. EEG data of four subjects was used. The seizure areas were localized with subdural recordings with an 8×8 grid electrode array. It was found that the stochastic behavior of the SI in low gamma band (30–50 Hz) was higher in epileptogenic areas. The beta (12–30 Hz) band also showed similar tendencies. The stochastic behavior in theta (3–7 Hz) band was depressed in the seizure area while it was widespread in large areas over the scalp in the alpha (7–12 Hz) band. The stochastic behavior of the cross-frequency and cross-electrode couplings in theta–gamma, alpha–gamma and beta–gamma bands were decreased in the seizure areas for all four subjects. These findings suggest that it is possible to localize the epileptogenic areas from the short duration seizure-free and spike-free high density scalp EEG data.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canolty RT, Knight RT (2010) The functional role of cross-frequency coupling. Trends Cogn Sci 14(11):506–515
Canolty RT, Edwards E, Dalal SS, Soltani M, Nagarajan SS, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Knight RT (2006) High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex. Science 313(5793):1626–1628
Freeman WJ (2004) Origin, structure, and role of background EEG activity. Part 2. Analytic phase. Clin Neurophysiol 115(9):2089–2107
Freeman WJ, Rogers LJ (2002) Fine temporal resolution of analytic phase reveals episodic synchronization by state transitions in gamma EEGs. J Neurophysiol 87(2):937–945
Gratkowski M, Haueisen J, Arendt-Nielsen L, Chen AC, Zanow F (2006) Time–frequency filtering of MEG signals with matching pursuit. J Physiol Paris 99:47–57
Linkenkaer-Hansen K, Monto S, Rytsälä H, Suominen K, Isometsä E, Kähkönen S (2005) Breakdown of long-range temporal correlations in theta oscillations in patients with major depressive disorder. J Neurosci 25(44):10131–10137
Monto S, Vanhatalo S, Holmes MD, Palva JM (2007) Epileptogenic neocortical networks are revealed by abnormal temporal dynamics in seizure-free subdural EEG. Cereb Cortex 17(6):1386–1393
Palva JM, Palva S, Kaila K (2005) Phase synchrony among neuronal oscillations in the human cortex. J Neurosci 25(15):3962–3972
Peng CK, Havlin S, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL (1995) Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos 5(1):82–87
Ramon C, Preissl H, Murphy P, Wilson JD, Lowery C, Eswaran H (2005) Synchronization analysis of the uterine magnetic activity during contractions. Biomed Eng Online 4:55
Ramon C, Holmes MD, Freeman WJ, McElroy R, Rezvanian E (2008) Comparative analysis of temporal dynamics of EEG and phase synchronization of EEG to localize epileptic sites from high density scalp EEG interictal recordings. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2008:4548–4550
Ramon C, Holmes M, Freeman WJ, Gratkowski M, Eriksen KJ, Haueisen J (2009) Power spectral density changes and language lateralization during covert object naming tasks measured with high-density EEG recordings. Epilepsy Behav 14(1):54–59
Tass P, Rosenblum MG, Weule J, Kurths J, Pikovsky AS, Volkmann J, Schnitzler A, Freund H-J (1998) Detection of n:m phase locking from noisy data: application to magnetoencephalography. Phys Rev Lett 81:3291–3294
Viswanathan GM, Peng CK, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL (1997) Deviations from uniform power law scaling in nonstationary time series. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Top 55(1):845–849
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by a Seed Grant provided by the Pacific Northwest Center for Neural Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramon, C., Holmes, M.D. Noninvasive Epileptic Seizure Localization from Stochastic Behavior of Short Duration Interictal High Density Scalp EEG Data. Brain Topogr 25, 106–115 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-011-0188-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-011-0188-8