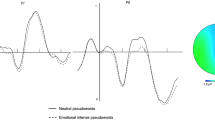
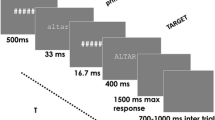
Summary:
A substantial body of research suggests that the cognitive mechanisms for picture and word processes are functionally and anatomically distinct. In spite of significant advancements in the understanding of pictures and words, the electrophysiological activities mediating these processes are not well known. To address this issue, we examined event-related brain potentials (ERPs) to pictures and their printed names in a modified dual-target oddball task. ERPs were recorded while participants classified schematic pictures and their corresponding names into target and nontarget categories. Results showed that pictures and words were associated with electrophysiological responses that differed temporally and topographically. In comparison to words, P300s to pictures were characterized by shorter latency and larger amplitude at parietal electrodes. In contrast, words produced greater P200 amplitude at frontal areas. The results are consistent with the view that categorization of pictures is faster than words. Findings are discussed in relation to stimulus evaluation and the time course for picture and word classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J.E., Porjesz, B., Bauer, L.O., Kuperman, S., Morzorati, S., O'Connor, S.J., Rohrbaugh, J., Begleiter, H. and Polich, J. P300 hemispheric amplitude asymmetries from a visual oddball task. Psychophysiology, 1995, 32: 467–475.
Anderson, J. Arguments concerning representations for mental imagery. Psychological Review, 1989, 85: 249–277.
Berman, S., Friedman, D. and Cramer, M. A developmental study of event-related potentials during explicit and implicit memory. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 1990, 10: 191–197.
Boller, F. and De Reniz, E. Relationship between visual memory defects and hemispheric locus of lesion. Neurology, 1967, 17: 1052–1058.
Bright, P., Moss, H. and Tyler, L.K. Unitary vs multiple semantics: PET studies of word and picture processing. Brain Language, 2004, 89: 417–432.
Budson, A.E., Droller, D.B., Dodson, C.S., Schacter, D.L., Rugg, M.D., Holcomb, P.J. and Daffner, K.R. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 2005, 17: 1181–1193.
Caramazza, A., Hillis, A.E., Rapp, B.C. and Romani, C. The multiple semantics hypothesis: Multiple Confusions? Cognitive Neuropsychology, 1990, 7: 161–189.
Denckla, M.B. Performance on color tasks in kindergarten children. Cortex, 1972, 8: 117–190.
De Renzi, E., Faglioni, P., Previdi, P., Sorgato, P. and Vescovini, E. The differential contribution of the verbal code in the course of visual learning: evidence from hemisphere-damaged patients. Cortex, 1981, 17: 447–452.
Duncan-Johnson, C.C. and Donchin, E. On quantifying surprise: the variation of event-related potentials with subjective probability. Psychophysiology, 1977, 14: 456–467.
Fabiani, M., Karis, D. and Donchin, E. P300 and recall in an incidental memory paradigm. Psychophysiology, 1986, 23: 298–308.
Fraisse, Paul. Motor and verbal reaction times to words and drawings. Psychonomic Science, 1968, 12: 235–236.
Gainotti, G., Cappa, A., Perri, R. and Silveri, M.C. Disorders of verbal and pictorial memory in right and left brain-damaged patients. International Journal of Neuroscience, 1994, 78: 9–20.
Glanzer, M. and Clark, W.H. Accuracy of perceptual recall: An analysis of organization. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 1963, 1: 289–299.
Glaser, W.R. Picture naming. Cognition, 1992, 42: 61–105.
Goldstein, B., Armstrong, C.L., Modestino, E., Ledakis, G., John, C. and Hunter, J.V. The impact of left and right intracranial tumors on picture and word recognition memory. Brain Cognition, 2004, 54: 1–6.
Grady, C.L., McIntosh, A.R., Rajah, M.N. and Craik, F.I. Neural correlates of the episodic encoding of pictures and words. Proceedings National Academy Science, 1998, 95: 2703–2708.
Greenham, S.L., Stelmack, R.M. and Campbell, K.B. Effects of attention and semantic relation on event-related potentials in a picture-word naming task. Biological Psychology, 2000, 55: 79–104.
Greenhouse, W.W and Geisser, S. On methods in the analysis of profile data. Psychometrika, 1959, 24: 95–112.
Hillis, A.E. and Caramazza, A. Cognitive and neural mechanisms underlying visual and semantic processing: Implications from “optic aphasia”. Journal of Cognitive Neuropsychology, 1995, 7: 457–478.
Kim, K.H., Yoon, H.W. and Park, H.W. Spatiotemporal brain activation pattern during word/picture perception by native Koreans. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuropsychology, 2004, 15: 1099–1103.
Johnson, C.J., Paivio, A. and Clark, J.M. Cognitive components of picture naming. Psychology Bulletin, 1996, 120: 113–139.
Kirchhoff, B.A., Wagner, A.D., Maril, A. and Stern, C.E. Prefrontal-temporal circuitry for episodic encoding and subsequent memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 2000, 20: 6173–6180.
Köhler, S., Moscovitch, M., Winocur, G. and McIntosh, A.R. Episodic encoding and recognition of pictures and words: role of the human medial temporal lobes. Acta. Psychologica., 2000, 105: 159–179.
Kok, A. On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology, 2001, 38: 557–577.
Kok, A. and Rooyakkers, J.A. ERPs to laterally presented pictures and words in a semantic categorization task. Psychophysiology, 1986, 23: 672–683.
Kutas, M., McCarthy, G. and Donchin E.Augmenting mental chronometry: the P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science, 1977, 197: 792–795.
Martin, A., Wiggs, C.L. and Weisberg, J. Modulation of human medial temporal lobe activity by form, meaning, and experience. Hippocampus, 1997, 7: 587–593.
McCarthy, G. and Donchin, E. A metric for thought: a comparison of P300 latency and reaction time. Science, 1981, 211: 77–80.
Nelson, T.O., Metzler, J. and Reed, D.A. Role of details in the long-term recognition of pictures and verbal descriptions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1974, 102: 184–186.
Noldy, N.E., Stelmack, R.M. and Campbell, K.B. Event-related potentials and recognition memory for pictures and words: the effects of intentional and incidental learning. Psychophysiology, 1990, 27: 417–428.
Paivio, A. Dual coding theory: Retrospect and current status. Canadian Journal of Psychology, 1991, 45: 255–287.
Paivio, A. Imagery and Verbal Processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1971.
Paivio, A. Mental Representations. New York: Oxford University Press, 1986.
Paivio, A. and Begg, I. Pictures and words in visual search. Memory and Cognition, 1974, 2: 515–521.
Paivio, A. and Begg, I. Imagery and comprehension latencies as a function of sentence concreteness and structure. Perception and Psychophysics, 1971, 10: 408–412.
Paivio, A. and Csapo, K. Concrete image and verbal memory codes. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1969, 80: 279–283.
Paivio, A., Rogers, T.B. and Smythe, P.C. Why are pictures easier to recall than words? Psychonomic Science, 1968, 11: 137–138.
Polich, J. Attention, probability, and task demands as determinants of P300 latency from auditory stimuli. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1986, 63: 2551–2559.
Postman, L. Picture-word differences in the acquisition and retention of paired associates. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1978, 4: 146–157.
Potter, M.C. and Faulconer, B.A. Time to understand pictures and words. Nature, 1975, 253: 437–438.
Reinholz, J. and Pollmann, S. Differential activation of object-selective visual areas by passive viewing of pictures and words. Cognitive Brain Research, 2005, 24: 702–714.
Saffran, E.M., Coslett, H.B., Martin, N. and Boronat, C.B. Access to knowledge from pictures but not words in a patient with progressive fluent aphasia. Language and Cognitive Processes, 2003, 18: 725–757.
Salmelin, R., Hari, R., Lounasmaa, O.V. and Sams, M. Dynamics of brain activation during picture naming. Nature, 1994, 31: 463–465.
Seifert, L.S. Activating Representations in Permanent Memory: Different Benefits for Pictures and Words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, Cognition, 1997, 23: 1106–1121.
Sevostianov, A., Horwitz B., Nechaev, V., Williams, R., Fromm, S. and Braun, A.R. fMRI study comparing names versus pictures of objects. Human Brain Mapping, 2002, 16: 168–175.
Simos, P.G. and Molfese, D.L. Event-related potentials in a two-choice task involving within-form comparisons of pictures and words. International Journal of Neuroscience, 1997, 90: 233–253.
Shepard, R. Recognition memory for words, sentences, and pictures. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Memory, 1967, 6: 156–163.
Shiffrin, R.M. and Schneider, W. Controlled and automatic human information processing: II. Perceptual learning, automatic attending, and a general theory. Psychology Review, 1977, 84: 127–190.
Smith, M.L. Memory disorders associated with temporal-lobe lesions. In: F. Boller and J. Glafman (Eds.), Handbook of Neuropsychology, V3. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1989: 91–106.
Smith, M.C. and Magee, L.E. Tracing the time course of picture-word processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1980, 109: 373–392.
Standing, L., Conezio, J. and Haber, R.N. Perception and memory for pictures: single-trial learning of 2500 visual stimuli. Psychonomic Science, 1970, 19: 73–74.
Sutton, S., Braren, M., Zubin, J. and John, E.R. Evoked potential correlates of stimulus uncertainty. Science, 1965, 150: 1187–1188.
Theios, J. and Amrhein, P.C. Theoretical analysis of the cognitive processing of lexical and pictorial stimuli: Reading, naming, and visual and conceptual comparisons. Psychological Review, 1989, 96: 5–24.
Warrington, E.K. The selective impairment of semantic memory. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1975, 27: 635–657.
Warrington, E.K. and Shallice, T. Category specific semantic impairments. Brain, 1984, 107: 829–854.
Watson, T.D., Azizian, A., Berry, S. and Squires, N.K. Event-related potentials as an index of similarity between words and pictures. Psychophysiology, 2005, 42: 361–368.
Whitehouse, J.P. Imagery and verbal encoding in left and right hemisphere damaged patients. Brain and Language, 1981, 14: 315–332.
Zhang, X.L., Begleiter, H., Porjesz, B. and Litke, A. Visual object priming differs from visual word priming: an ERP study. Electroencephalography Clinical Neurophysiology, 1997, 102(3): 200–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizian, A., Watson, T., Parvaz, M. et al. Time Course of Processes Underlying Picture and Word Evaluation: An Event-Related Potential Approach. Brain Topogr 18, 213–222 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0270-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0270-9