Abstract
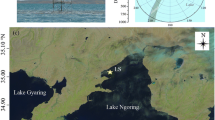
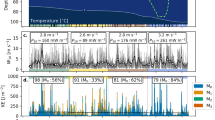
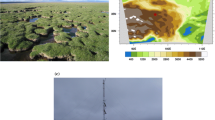
In studies of lake–atmosphere interactions, the fluxes of momentum, water vapour and sensible heat are often parametrized as being proportional to the differences in wind, humidity and air temperature between the water surface and a reference height above the surface. Here, the proportionality via transfer coefficients in these relationships was investigated with the eddy-covariance method at three sites within an eddy-covariance mesonet across Lake Taihu, China. The results indicate that the transfer coefficients decreased with increasing wind speed for weak winds and approached constant values for strong winds. The presence of submerged macrophytes reduced the momentum transfer (drag) coefficient significantly. At the two sites free of submerged macrophytes, the 10-m drag coefficients under neutral stability were 1.8 \((\pm \,0.4) \times \,10^{-3}\) and \(1.7\,(\pm \,0.3) \times \,10^{-3 }\) at the wind speed of \(9\,\text{ m } \text{ s }^{-1}\), which are 38 and 34 % greater than the prediction by the Garratt model for the marine environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ataktürk SS, Katsaros KB (1999) Wind stress and surface waves observed on Lake Washington. J Phys Oceanogr 29:633–650
Barko JW, James WJ (1998) Effects of submerged aquatic macrophytes on nutrient dynamics, sedimentation, and resuspension. In: Jeppesen E et al (eds) The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in lakes. Springer, New York, pp 197–214
Blanken PD, Rouse WR, Culf AD, Spence C, Boudreau LD, Jasper JN, Kochtubajda B, Schertzer WM, Marsh P, Verseghy D (2000) Eddy covariance measurements of evaporation from Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada. Water Resour Res 36:1069–1077
Blanken PD, Rouse WR, Schertzer WM (2003) Enhancement of evaporation from a large northern lake by the entrainment of warm, dry air. J Hydrometeorol 4:680–693
Blanken PD, Spence C, Hedstrom N, Lenters JD (2011) Evaporation from Lake Superior: 1. Physical controls and processes. J Great Lakes Res 37:707–716
Carpenter SR, Lodge DM (1986) Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquat Bot 26:341–370
Chen Y, Qin B, Teubner K, Dokulil MT (2003) Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J Plankton Res 25:445–453
Dale HM, Gillespie TJ (1977) The influence of submersed aquatic plants on temperature gradients in shallow water bodies. Can J Bot 55:2216–2225
Davidan IN, Lopatuhin LI, Rozhkov VA (1985) Waves in the world ocean (in Russian). Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, p 256
Deacon EL (1977) Gas transfer to and across an air–water interface. Tellus 29:363–374
Deng B, S Liu, W Xiao, W Wang, J Jin, X Lee (2013) Evaluation of the CLM4 lake model at a large and shallow freshwater lake. J Hydrometeorol 14:636–649
Donelan MA, Dobson FW, Smith SD, Anderson RJ (1993) On the dependence of sea-surface roughness on wave development. J Phys Oceanogr 23:2143–2149. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1993)023<2143:OTDOSS>2.0.CO;2
Downing JA, Prairie YT, Cole JJ, Duarte CM, Tranvik LJ, Striegl RG, McDowell WH, Kortelainen P, Caraco NF, Melack JM, Middelburg JJ (2006) The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol Oceanogr 51:2388–2397
Fairall CW, Bradley EF, Godfrey JS, Wick GA, Edson JB, Young GS (1996) Cool-skin and warm-layer effects on the sea surface temperature. J Geophys Res 101:1295–1308
Foken T (2008) Micrometeorology. Springer, Berlin
Gao ZQ, Wang Q, Zhou MY (2009) Wave-dependence of friction velocity, roughness length, and drag coefficient over coastal and open water surfaces by using three databases. Adv Atmos Sci 26:887–894
Garratt JR (1992) The atmospheric boundary layer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Geernaert GL, Larsen SE, Hansen F (1987) Measurements of the wind-stress, heat-flux and turbulence intensity during storm conditions over the north sea. J Geophys Res 92:13127–13139
Grachev AA, Fairall CW, Larsen SE (1998) On the determination of the neutral drag coefficient in the convective boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 86:257–278
Grachev AA, Bariteau L, Fairall CW, Hare JE, Helmig D, Hueber J, Lang EK (2011) Turbulent fluxes and transfer of trace gases from ship-based measurements during TexAQS 2006. J Geophys Res 116:D13110
Heikinheimo M, Kangas M, Tourula T, Venäläinen A, Tattari S (1999) Momentum and heat fluxes over lakes Tämnaren and Råksjö determined by the bulk-aerodynamic and eddy-correlation methods. Agric For Meteorol 98–99:521–534
Henderson-Sellers B (1986) Calculating the surface energy balance for lake and reservoir modeling: A review. Rev Geophys 24:625–649
Herb WR, Stefan HG (2005) Dynamics of vertical mixing in a shallow lake with submersed macrophytes. Water Resour Res 41:W02023. doi:10.1029/2003WR002613
Hinze JO (1975) Turbulence: an introduction to its mechanism and theory, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Hsieh CI, Katul G, Chi T (2000) An approximate analytical model for footprint estimation of scalar fluxes in thermally stratified atmospheric flows. Adv Water Resour 23:765–772
James WF, Barko JW (2000) Sediment resuspension dynamics in canopy- and meadow-forming submersed macrophyte communities. Rep ERDC/EL SR-00-8, US Army Corps of Engineers, Vicksburg, Miss, USA, 38 pp
Johnson RK, Ostrofsky ML (2004) Effects of sediment nutrients and depth on small-scale spatial heterogeneity of submersed macrophyte communities in Lake Pleasant, Pennsylvania. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 61:1493–1502
Kaimal JC, Finnigan JJ (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flows: their structure and measurement. Oxford University Press, New York
Lee X, Massman W (2011) A perspective on thirty years of the Webb, Pearman and Leuning density corrections. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 139:37–59. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9575-z
Lee X, Massman W, Law B (2004) Handbook of micrometeorology: a guide for surface flux measurement and analysis. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Liu H, Randerson JT, Lindfors J, Chapin III FS (2005) Changes in the surface energy budget after fire in boreal ecosystems of interior Alaska: an annual perspective. J Geophys Res 110:D13101. doi:10.1029/2004JD005158
Liu H, Zhang Y, Liu S, Jiang H, Sheng L, Williams QL (2009) Eddy covariance measurements of surface energy budget and evaporation in a cool season over southern open water in Mississippi. J Geophys Res 114:D04110. doi:10.1029/2008JD010891
Losee RF, Wetzel RC (1993) Littoral flow rates within and around submersed macrophyte communities. Freshwater Biol 29:7–17
MacKay MD, Neale PJ, Arp CD, De Senerpont Domis LN, Fang X, Gal G, Jöhnk KD, Kirillin G, Lenters JD, Litchman E, MacIntyre S, Marsh P, Melack J, Mooij WM, Peeters F, Quesada A, Schladow SG, Schmid M, Spence C, Stokes SL (2009) Modeling lakes and reservoirs in the climate system. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2315–2329
Madsen JD, Chambers PA, James WF, Koch EW, Westlake DF (2001) The interaction between water movement, sediment dynamics and submersed macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 444:71–84
Matt N, Kraan C, Oost WA (1991) The roughness of wind-waves. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 54:89–103. doi:10.1007/BF00119414
Moraes OLL (2000) Turbulence characteristics in the surface boundary layer over the South American pampa. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 96:317–335
Nepf HM (1999) Drag, turbulence, and diffusion in flow through emergent vegetation. Water Resour Res 35:479–489
Nordbo A, Launiainen S, Mammarella I, Leppäranta M, Huotari J, Ojala A, Vesala T (2011) Long-term energy flux measurements and energy balance over a small boreal lake using eddy covariance technique. J Geophys Res 116:D02119. doi:10.1029/2010JD014542
Oleson KW, Dai Y, Bonan G, Bosilovich M, Dickinson R, Dirmeyer P, Hoffman F, Houser P, Levis S, Niu G, Thornton P, Vertenstein M, Yang Z, Zeng X (2004) Technical description of the Community Land Model (CLM). NCAR Technical Note: NCAR/TN-461\(+\)STR. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, USA, p 174
Pahlow M, Parlange M, Porté-Agel F (2001) On Monin–Obukhov similarity in the stable atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 99:225–248
Panin GN, Nasonov AE, Foken Th, Lohse H (2006) On the parameterisation of evaporation and sensible heat exchange for shallow lakes. Theor Appl Climatol 85:123–129. doi:10.1007/s00704-005-0185-5
Pip E (1979) Survey of the ecology of submerged aquatic macrophytes in central Canada. Aquat Bot 7:339–357
Plew DR, Cooper GG, Callaghan FM (2008) Turbulence-induced forces in a freshwater macrophyte canopy. Water Resour Res 44:W02414. doi:10.1029/2007WR006064
Radomski P, Perleberg D (2012) Application of a versatile aquatic macrophyte integrity index for Minnesota lakes. Ecol Indic 20:252–268. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.012
Roll HU (1948) Wassernahes windprofil und wellen auf dem wattenmeer. Ann Meteorol 1:139–151
Rouse WR, Blanken PD, Bussières N, Oswald CJ, Schertzer WM, Spence C, Walker AE (2008) An investigation of the thermal and energy balance regimes of Great Slave and Great Bear Lakes. J Hydrometeorol 9:1318–1333. doi:10.1175/2008JHM977.1
Samuelsson P, Tjernström M (2001) Mesoscale flow modification induced by land-lake surface temperature and roughness differences. J Geophys Res 106D:12419–12435
Samuelsson P, Kourzeneva E, Mironov D (2010) The impact of lakes on the European climate as simulated by a regional climate model. Boreal Environ Res 15:113–129
Schertzer WM, Rouse WR, Blanken PD, Walker AE (2003) Over-lake meteorology and estimated bulk heat exchange of Great Slave Lake in 1998 and 1999. J Hydrometeorol 4:649–659
Sheppard PA, Tribble DT, Garratt JR (1972) Studies of turbulence in the surface layer over water (Lough Neagh). Part I. Instrumentation, programme, profiles. Q J R Meteorol Soc 98:627–641
Sills DML, Brook JR, Levy I, Makar PA, Zhang J, Taylor PA (2011) Lake breezes in the southern Great Lakes region and their influence during BAQS-Met 2007. Atmos Chem Phys 11:7955–7973
Smith SD, Anderson RJ, Oost WA, Kraan C, Maat N, DeCosmo J, Katsaros KB, Davidson KL, Bumke K, Hasse L, Chadwick HM (1992) Sea-surface wind stress and drag coefficients: the HEXOS results. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 60:109–142. doi:10.1007/BF00122064
Søndergaard M, Phillips G, Hellsten S, Kolada A, Ecke F, Mäemets H, Mjelde M, Azzella MM, Oggioni A (2013) Maximum growing depth of submerged macrophytes in European lakes. Hydrobiologia 704:165–177. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1389-1
Subin ZM, Riley WJ, Mironov DV (2012) An improved lake model for climate simulations: model structure, evaluation, and sensitivity analyses in CESM1. JAMES 4:M02001
Törnblom K, Bergström H, Jahansson C (2007) Thermally driven mesoscale flows—simulations and measurements. Boreal Environ Res 12:623–641
Vermaat JE, Santamaria L, Roos PJ (2000) Water flow across and sediment trapping in submerged macrophyte beds of contrasting growth form. Arch Hydrobiol 148:549–562
Vesala T, Huotari J, Rannik Ü, Suni T, Smolander S, Sogachev A, Launiainen S, Ojala A (2006) Eddy covariance measurements of carbon exchange and latent and sensible heat fluxes over a boreal lake for a full open-water period. J Geophys Res 111:D11101. doi:10.1029/2005JD006365
Vikers D, Mahrt L (1997) Fetch limited drag coefficients. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 85:53–79. doi:10.1023/A:1000472623187
Wallsten M, Forsgren P (1989) The effects of increased water level on aquatic macrophytes. J Aquat Plant Manag 27:32–37
Webb EK, Pearman GI, Leuning R (1980) Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 106:85–100
Wilson JD (2008) Monin–Obukhov functions for standard deviations of velocity. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 129:353–369. doi:10.1007/s10546-008-9319-5
Zhao L, Jin J, Wang SY, Ek MB (2012) Integration of remote-sensing data with WRF to improve lake-effect precipitation simulations over the Great Lakes region. J Geophys Res 117:D09102. doi:10.1029/2011JD016979
Zilitinkevich SS (1969) On the computation of the basic parameters of the interaction between the atmosphere and the ocean. Tellus 21:17–24
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (grant BK2011830), the Ministry of Education of China (grant PCSIRT), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (grant PAPD) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 41275024). We thank three reviewers whose constructive comments have improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Liu, S., Wang, W. et al. Transfer Coefficients of Momentum, Heat and Water Vapour in the Atmospheric Surface Layer of a Large Freshwater Lake. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 148, 479–494 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-013-9827-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-013-9827-9