Abstract
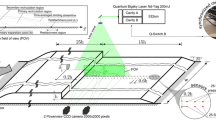
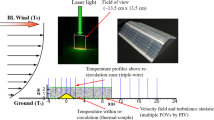
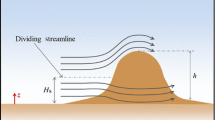
A parametrization method used to account for the effects of flow separation and wall roughness on the lower boundary condition for turbulent boundary layers is investigated against direct numerical simulation and laser Doppler anemometry data. The numerical simulation represents flow over a smooth, flat surface with a prescribed external adverse pressure gradient. The water-channel experiments cover flow over smooth and rough hills for two specified Reynolds numbers. Global optimization algorithms based on four different direct search methods are used to assess the parametrization function, C, in terms of local mean velocity profiles and the parametrization parameters u * (friction velocity), ∂ x p (local pressure gradient), z 0 (effective roughness) and d (zero-plane displacement). The study investigates regions of attached and reversed flows, and forty-two velocity profiles are compared with the proposed expression for the function C, including two profiles that satisfy the solution of Stratford.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya SPS, Capuano ME, Fagen LC (1987) Some fluid modelling studies of flow and dispersion over two-dimensional low hills. Atmos Environ 21: 753–764
Athanassiadou M, Castro IP (2001) Neutral flow over a series of rough hills: a laboratory experiment. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 101: 1–30
Britter RE, Hunt JCR, Richards KJ (1981) Air flow over a two-dimensional hill: studies of velocity speedup, roughness effects and turbulence. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 107: 91–110
Cheng H, Castro IP (2002) Near-wall flow development after a step change in surface roughness. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 105: 411–432
Clauser FH (1954) Turbulent boundary layers in adverse pressure gradients. J Aeronaut Sci 21: 91–108
Cruz DOA, Silva Freire AP (1998) On single limits and the asymptotic behaviour of separating turbulent boundary layers. Int J Heat Mass Transf 41: 2097–2111
Cruz DOA, Silva Freire AP (2002) Note on a thermal law of the wall for separating and recirculating flows. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45: 1459–1465
Garratt JR (1992) The atmospheric boundary layer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 316
Kaimal JC, Finnigan JJ (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flows—their structure and measurement. Oxford University Press, New York, p 289
Loureiro JBR, Soares DV, Fontoura Rodrigues JLA, Pinho FT, Silva Freire AP (2007a) Water tank and numerical model studies of flow over steep smooth two-dimensional hills. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 122: 343–365
Loureiro JBR, Pinho FT, Silva Freire AP (2007b) Near wall characterization of the flow over a two- dimensional steep smooth hill. Exp Fluids 42: 441–457
Loureiro JBR, Monteiro AS, Pinho FT, Silva Freire AP (2008) Water tank studies of separating flow over rough hills. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 129: 289–308
Na Y, Moin P (1998) Direct numerical simulation of a separated turbulent boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 374: 379–405
Ohba R, Hara T, Nakamura S, Ohya Y, Uchida T (2002) Gas diffusion over an isolated hill under neutral, stable and unstable conditions. Atmos Environ 36: 5697–5707
Oke TR (1987) Boundary layer climates. Routledge, London, p 435
Perry AE, Joubert PN (1963) Rough-wall boundary layers in adverse pressure gradients. J Fluid Mech 17: 193–211
Simpson RL (1996) Aspects of turbulent boundary-layer separation. Prog Aero Sci 32: 457–521
Snyder WH, Britter RE (1987) A wind-tunnel study of the flow structure and dispersion from sources upwind of three-dimensional hills. Atmos Environ 21: 735–751
Stratford BS (1959) The prediction of separation of the turbulent boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 5: 1–16
Wood N (1995) The onset of separation in neutral, turbulent flow over hills. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 76: 137–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loureiro, J.B.R., Silva Freire, A.P. Note on a Parametric Relation for Separating Flow over a Rough Hill. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 131, 309–318 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-009-9362-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-009-9362-x