Abstract
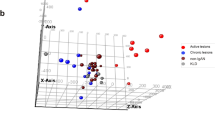
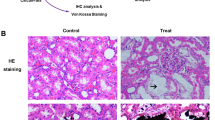
Nephropathic cystinosis is a rare, inherited metabolic disease caused by functional defects of cystinosin associated with mutations in the CTNS gene. The mechanisms underlying the phenotypic alterations associated with this disease are not well known. In this study, gene expression profiles in peripheral blood of nephropathic cystinosis patients (N = 7) were compared with controls (N = 7) using microarray technology. In unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis, cystinosis samples co-clustered, and 1,604 genes were significantly differentially expressed between both groups. Gene ontology analysis revealed that differentially expressed genes in cystinosis were enriched in cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum (p ≤ 0.030). The majority of the differentially regulated genes were involved in oxidative phosphorylation, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, antigen processing and presentation, B-cell-receptor signaling, and oxidative stress (p ≤ 0.003). Validation of selected genes involved in apoptosis and oxidative phosphorylation was performed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Electron microscopy and confocal imaging of cystinotic renal proximal tubular epithelial cells further confirmed anomalies in the cellular organelles and pathways identified by microarray analysis. Further analysis of these genes and pathways may offer critical insights into the clinical spectrum of cystinosis patients and ultimately lead to novel links for targeted therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- CTNS :
-
Cystinosin
- SAM:
-
Significance analysis of microarray
- PAM:
-
Prediction analysis of microarray
- LSD:
-
Lysosomal storage disorders
- RPTE:
-
Renal proximal tubular epithelial
References
Abernathy CO, Liu YP, Longfellow D et al (1999) Arsenic: health effects, mechanisms of actions, and research issues. Environ Health Perspect 107:593–597
Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, Heuser JE, Wang X, Akey CW (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell 9:423–432
Achanzar WE, Diwan BA, Liu J, Quader ST, Webber MM, Waalkes MP (2001) Cadmium-induced malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res 61:455–458
Anikster Y, Shotelersuk V, Gahl WA (1999) CTNS mutations in patients with cystinosis. Hum Mutat 14:454–458
Baum M (1998) The Fanconi syndrome of cystinosis: insights into the pathophysiology. Pediatr Nephrol 12:492–497
Castaneda JA, Lim MJ, Cooper JD, Pearce DA (2008) Immune system irregularities in lysosomal storage disorders. Acta Neuropathol 115:159–174
Chen R, Li L, Butte AJ (2007) AILUN: reannotating gene expression data automatically. Nat Methods 4:879
Cherqui S, Kalatzis V, Trugnan G, Antignac C (2001) The targeting of cystinosin to the lysosomal membrane requires a tyrosine-based signal and a novel sorting motif. J Biol Chem 276:13314–13321
Cherqui S, Sevin C, Hamard G et al (2002) Intralysosomal cystine accumulation in mice lacking cystinosin, the protein defective in cystinosis. Mol Cell Biol 22:7622–7632
Cho HY, Jedlicka AE, Reddy SP, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Zhang LY, Kleeberger SR (2002) Role of NRF2 in protection against hyperoxic lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:175–182
Cho HY, Reddy SP, Kleeberger SR (2006) Nrf2 defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:76–87
Corcoran GB, Fix L, Jones DP, Moslen MT, Nicotera P, Oberhammer FA et al (1994) Apoptosis: molecular control point in toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 128:169–181
Demarchi F, Schneider C (2007) The calpain system as a modulator of stress/damage response. Cell Cycle 6:136–138
Demarchi F, Bertoli C, Copetti T, Eskelinen EL, Schneider C (2007) Calpain as a novel regulator of autophagosome formation. Autophagy 3:235–237
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14863–14868
Gahl WA, Thoene JG, Schneider JA (2002) Cystinosis. N Engl J Med 347:111–121
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV (1995) The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 81:495–504
Hwang SO, Boswell SA, Seo JS, Lee SW (2008) Novel oxidative stress-responsive gene ERS25 functions as a regulator of the heat-shock and cell death response. J Biol Chem 283:13063–13069
Jackson JD, Smith FG, Litman NN, Yuile CL, Latta H (1962) The Fanconi syndrome with cystinossis. Electron microscopy of renal biopsy specimens from five patients. Am J Med 33:893–910
Kalatzis V, Cherqui S, Antignac C, Gasnier B (2001) Cystinosin, the protein defective in cystinosis, is a H(+)-driven lysosomal cystine transporter. EMBO J 20:5940–5949
Kalatzis V, Nevo N, Cherqui S, Gasnier B, Antignac C (2004) Molecular pathogenesis of cystinosis: effect of CTNS mutations on the transport activity and subcellular localization of cystinosin. Hum Mol Genet 13:1361–1371
Khatri P, Desai V, Tarca AL, Sellamuthu S, Wildman DE, Romero R, Draghici S (2006) New onto-tools: promoter-express, nsSNPCounter and onto-translate. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W626–W631
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M (2006) Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:113–140
Kubo Y, Sekiya S, Ohigashi M et al (2005) ABCA5 resides in lysosomes, and ABCA5 knockout mice develop lysosomal disease-like symptoms. Mol Cell Biol 25:4138–4149
Kwak MK, Egner PA, Dolan PM et al (2001a) Role of phase 2 enzyme induction in chemoprotection by dithiolethiones. Mutat Res 480–481:305–315
Kwak MK, Egner PA, Dolan PM, Ramos-Gomez M, Groopman JD, Itoh K et al (2001b) Role of phase 2 enzyme induction in chemoprotection by dithiolethiones. Mutat Res 480–481:305–315
Levtchenko E, de Graaf-Hess A, Wilmer M, van den Heuvel L, Monnens L, Blom H (2005) Altered status of glutathione and its metabolites in cystinotic cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:1828–1832
Levtchenko EN, Wilmer MJ, Janssen AJ, Koenderink JB, Visch HJ, Willems PH et al (2006) Decreased intracellular ATP content and intact mitochondrial energy generating capacity in human cystinotic fibroblasts. Pediatr Res 59:287–292
Namba T, Homan T, Nishimura T, Mima S, Hoshino T, Mizushima T (2009) Up-regulation of S100P expression by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and its role in anti-tumorigenic effects. J Biol Chem 284:4158–4167
Nevo N, Chol M, Bailleux A, Kalatzis V, Morisset L, Devuyst O et al (2010) Renal phenotype of the cystinosis mouse model is dependent upon genetic background. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1059–1066
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies. NAPRTCS 2008 Annual Report. https://web.emmes.com/study/ped/annlrept/annlrept.html. Accessed May 2009.
Ott M, Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2002) Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1259–1263
Park M, Helip-Wooley A, Thoene J (2002) Lysosomal cystine storage augments apoptosis in cultured human fibroblasts and renal tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2878–2887
Park MA, Pejovic V, Kerisit KG, Junius S, Thoene JG (2006) Increased apoptosis in cystinotic fibroblasts and renal proximal tubule epithelial cells results from cysteinylation of protein kinase Cdelta. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3167–3175
Racusen LC, Wilson PD, Hartz PA, Fivush BA, Burrow CR (1995) Renal proximal tubular epithelium from patients with nephropathic cystinosis: immortalized cell lines as in vitro model systems. Kidney Int 48:536–543
Rech VC, Feksa LR, Arevalo do Amaral MF et al (2007) Promotion of oxidative stress in kidney of rats loaded with cystine dimethyl ester. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1121–1128
Sansanwal P, Kambham N, Sarwal MM (2009) Caspase-4 may play a role in loss of proximal tubules and renal injury in nephropathic cystinosis. Pediatr Nephrol
Sansanwal P, Yen B, Gahl WA, Ma Y, Ying L, Wong LJ, Sarwal MM (2010) Mitochondrial autophagy promotes cellular injury in nephropathic cystinosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:272–283
Sasaki H, Sato H, Kuriyama-Matsumura K et al (2002) Electrophile response element-mediated induction of the cystine/glutamate exchange transporter gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:44765–44771
Spear GS, Slusser RJ, Tousimis AJ, Taylor CG, Schulman JD (1971) Cystinosis. An ultrastructural and electron-probe study of the kidney with unusual findings. Arch Pathol 91:206–221
Stypmann J, Glaser K, Roth W et al (2002) Dilated cardiomyopathy in mice deficient for the lysosomal cysteine peptidase cathepsin L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6234–6239
Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B, Chu G (2002) Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6567–6572
Town M, Jean G, Cherqui S et al (1998) A novel gene encoding an integral membrane protein is mutated in nephropathic cystinosis. Nat Genet 18:319–324
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G (2001) Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5116–5121
Vij N, Fang S, Zeitlin PL (2006) Selective inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation rescues DeltaF508-cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator and suppresses interleukin-8 levels: therapeutic implications. J Biol Chem 281:17369–17378
Wang X, Venable J, LaPointe P et al (2006) Hsp90 cochaperone Aha1 downregulation rescues misfolding of CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Cell 127:803–815
Weber SM, Chambers KT, Bensch KG, Scarim AL, Corbett JA (2004) PPARgamma ligands induce ER stress in pancreatic beta-cells: ER stress activation results in attenuation of cytokine signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:E1171–E1177
Wei H, Kim SJ, Zhang Z, Tsai PC, Wisniewski KE, Mukherjee AB (2008) ER and oxidative stresses are common mediators of apoptosis in both neurodegenerative and non-neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorders and are alleviated by chemical chaperones. Hum Mol Genet 17:469–477
Whitney ML, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR (2009) ATF4 is necessary and sufficient for ER stress-induced upregulation of REDD1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:451–455
Wilmer MJ, de Graaf-Hess A, Blom HJ et al (2005) Elevated oxidized glutathione in cystinotic proximal tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:610–614
Wilmer MJ, van den Heuvel LP, Rodenburg RJ et al (2008) Mitochondrial complex V expression and activity in cystinotic fibroblasts. Pediatr Res 64:495–497
Xu W, Liu L, Charles IG, Moncada S (2004) Nitric oxide induces coupling of mitochondrial signalling with the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Nat Cell Biol 6:1129–1134
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Cystinosis Foundation, Ireland, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA. We are indebted to Dr. L.C. Racusen (Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University) for generating an incredible resource of cystinotic renal proximal tubular epithelial cells; to Dr. Benedict Yen (Department of Pathology, University of California, San Francisco) for support with electron microscopy experiments, and to Dr. William A. Gahl (Section on Human Biochemical Genetics, Medical Genetics Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health), for providing us with cystinotic RPTE cells and for helpful advice and review of the manuscript.
Funding Sources
The work was supported by grants from the Cystinosis Foundation Ireland and the Intramural Research Program of the National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institute of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by: Jean-Marie Saudubray
Competing interest:
None declared.
Poonam Sansanwal and Li Li contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table S1
(DOC 77 kb)
Supplemental Table S2
(DOC 139 kb)
Supplemental Table S3
(DOC 33 kb)
Supplemental Table S4
(DOC 191 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S1
(JPEG 1022 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S2
(JPEG 1816 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S3
(JPEG 4895 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S4
(JPEG 827 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S5
(JPEG 1031 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S6
(JPEG 913 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S7
(JPEG 1009 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S8
(JPEG 799 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sansanwal, P., Li, L., Hsieh, SC. et al. Insights into novel cellular injury mechanisms by gene expression profiling in nephropathic cystinosis. J Inherit Metab Dis 33, 775–786 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9203-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9203-6