Abstract
Objectives
This paper reports on the national neonatal screening programme for congenital toxoplasmosis (CT) in Denmark conducted from 1999 to 2007, including background, basis for initiation of screening, methods, results, and finally reasons for the discontinuation of the screening.
Methods
A nationwide screening was conducted at Statens Serum Institut, including >98% newborns, and using filter paper eluates (Guthrie card, PKU card) obtained from newborns 5–10 days old. These were analysed for Toxoplasma gondii-specific antibodies (IgM), and if positive, then IgM (ISAGA). Confirmatory serology was performed on children and their mothers (IgM, IgG, IgA, dye test) where infection was suspected, and children with suspected or confirmed CT initiated a 3-month treatment regimen with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine and folinic acid supplements. Selective cohorts were followed with regard to developmental and clinical outcome.
Results
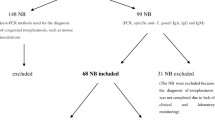
A total of 100 children were diagnosed with CT in the screening period, and only 2 cases were detected outside of the screening programme. CT prevalence was 1.6 per 10,000 live-born infants. Follow-up studies showed new retinochoroidal lesions in affected children despite treatment.
Conclusion
Screening was terminated August 2007, after it became apparent that no benefit of treatment could be shown. CT was evaluated using a Danish adaptation of the Uniform Screening Panel (ACMG), showing CT as an unlikely candidate for screening today. Whereas results might be comparable with other low-endemic countries with similar strains of T. gondii, neonatal screening and treatment might offer different results in regions with either high prevalence or different strains of T. gondii.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACMG (2006) Newborn screening: toward a uniform screening panel and system. Genet Med 8(Suppl 1):1S–252S
Andrade GM, Vasconcelos-Santos DV, Carellos EV, Romanelli RM, Vitor RW, Carneiro AC, Januario JN (2009) Congenital toxoplasmosis from a chronically infected woman with reactivation of retinochoroiditis during pregnancy—an underestimated event? J Pediatr (Rio J) 86(1):85-88
Benard A, Petersen E, Salamon R, Chene G, Gilbert R, Salmi LR (2008) Survey of European programmes for the epidemiological surveillance of congenital toxoplasmosis. Euro Surveill 13(15). http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=18834
Carter AO, Gelmon SB, Wells GA, Toepell AP (1989) The effectiveness of a prenatal education programme for the prevention of congenital toxoplasmosis. Epidemiol Infect 103(3):539–545
Cook AJ, Gilbert RE, Buffolano W, Zufferey J, Petersen E, Jenum PA, Foulon W, Semprini AE, Dunn DT (2000) Sources of toxoplasma infection in pregnant women: European multicentre case-control study. European Research Network on Congenital Toxoplasmosis. BMJ 321(7254):142–147
Di MS, Basevi V, Gagliotti C, Spettoli D, Gori G, D’Amico R, Magrini N (2009) Prenatal education for congenital toxoplasmosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD006171
Dubey JP, Lindsay DS, Speer CA (1998) Structures ofToxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin Microbiol Rev 11(2):267–299
Dunn D, Wallon M, Peyron F, Petersen E, Peckham C, Gilbert R (1999) Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: risk estimates for clinical counselling. Lancet 353(9167):1829–1833
Freeman K, Salt A, Prusa A, Malm G, Ferret N, Buffolano W, Schmidt D, Tan HK, Gilbert RE (2005) Association between congenital toxoplasmosis and parent-reported developmental outcomes, concerns, and impairments, in 3 year old children. BMC Pediatr 5:23
Gilbert R (2009) Treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis: finding out what works. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(2):305–311
Gilbert R, Dezateux C (2006) Newborn screening for congenital toxoplasmosis: feasible, but benefits are not established. Arch Dis Child 91(8):629–631
Gilbert RE, Peckham CS (2002) Congenital toxoplasmosis in the United Kingdom: to screen or not to screen? J Med Screen 9(3):135–141
Gilbert RE, Freeman K, Lago EG, Bahia-Oliveira LM, Tan HK, Wallon M, Buffolano W, Stanford MR, Petersen E (2008) Ocular sequelae of congenital toxoplasmosis in Brazil compared with Europe. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2(8):e277
Guerina NG, Hsu HW, Meissner HC, Maguire JH, Lynfield R, Stechenberg B, Abroms I, Pasternack MS, Hoff R, Eaton RB (1994) Neonatal serologic screening and early treatment for congenital toxoplasma gondii infection. The New England Regional Toxoplasma Working Group. N Engl J Med 330(26):1858–1863
Johannessen JK, Christiansen I, Schmidt DR, Petersen E, Hansen SH (2005) Simultaneous determination of pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine and N-acetyl-sulfadiazine in plasma for monitoring infants in treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36(5):1093–1098
Koppe JG, Rothova A (1989) Congenital toxoplasmosis. A long-term follow-up of 20 years. Int Ophthalmol 13(6):387–390
Kur J, Holec-Gasior L, Hiszczynska-Sawicka E (2009) Current status of toxoplasmosis vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 8(6):791–808
Lebech M, Andersen O, Christensen NC, Hertel J, Nielsen HE, Peitersen B, Rechnitzer C, Larsen SO, Norgaard-Pedersen B, Petersen E (1999) Feasibility of neonatal screening for toxoplasma infection in the absence of prenatal treatment. Danish Congenital Toxoplasmosis Study Group. Lancet 353(9167):1834–1837
McAuley J, Boyer KM, Patel D, Mets M, Swisher C, Roizen N, Wolters C, Stein L, Stein M, Schey W (1994) Early and longitudinal evaluations of treated infants and children and untreated historical patients with congenital toxoplasmosis: the Chicago collaborative treatment trial. Clin Infect Dis 18(1):38–72
McLeod R, Boyer K, Karrison T, Kasza K, Swisher C, Roizen N, Jalbrzikowski J, Remington J, Heydemann P, Noble AG, Mets M, Holfels E, Withers S, Latkany P, Meier P (2006) Outcome of treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis, 1981–2004: the National Collaborative Chicago-Based Congenital Toxoplasmosis Study. Clin Infect Dis 42(10):1383–1394
McLeod R, Kieffer F, Sautter M, Hosten T, Pelloux H (2009) Why prevent, diagnose and treat congenital toxoplasmosis? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(2):320–344
Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O (2004) Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 363(9425):1965–1976
Nielsen HV, Schmidt DR, Petersen E (2005) Diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis by two-dimensional immunoblot differentiation of mother and child immunoglobulin g profiles. J Clin Microbiol 43(2):711–715
Peyron F (2009) When are we going to celebrate the centenary of the discovery of efficient treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(2):316–319
Remington J, Klein J, Baker C, Wilson C (2006) Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant, 6th ed. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia
Schmidt DR (2005) PhD Thesis: A neonatal screening programme for congenital toxoplasmosis including observations on disease development and its treatment in infants and children. Copenhagen University, Copenhagen Denmark.
Schmidt DR, Hogh B, Andersen O, Fuchs J, Fledelius H, Petersen E (2006a) The national neonatal screening programme for congenital toxoplasmosis in Denmark: results from the initial four years, 1999-2002. Arch Dis Child 91(8):661–665
Schmidt DR, Hogh B, Andersen O, Hansen SH, Dalhoff K, Petersen E (2006b) Treatment of infants with congenital toxoplasmosis: tolerability and plasma concentrations of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine. Eur J Pediatr 165(1):19–25
Sorensen T, Spenter J, Jaliashvili I, Christiansen M, Norgaard-Pedersen B, Petersen E (2002) Automated time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for Toxoplasma gondii-specific IgM and IgA antibodies: study of more than 130,000 filter-paper blood-spot samples from newborns. Clin Chem 48(11):1981–1986
Sundhedsstyrelsen (2008) Biokemisk screening for medfodt sygdom hos nyfodte - Principper, erfaringer, anbefalinger. http://www.ssi.dk/graphics/dk/diagnostik/praenatale/SST%20Biokemisk%20screening.pdf. Accessed 6 Jan 2010
Thiebaut R, Leproust S, Chene G, Gilbert R (2007) Effectiveness of prenatal treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis: a meta-analysis of individual patients’ data. Lancet 369(9556):115–122
Tissot DD, Fricker-Hidalgo H, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Bost-Bru C, Ambroise-Thomas P, Pelloux H (2003) Usefulness of Western blot in serological follow-up of newborns suspected of congenital toxoplasmosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22(2):122–125
WHO (1987) Report of the WHO consultation on public health aspects of toxoplasmosis, Hanover, Federal Republic of Germany, 6-8 October, 1987. WHO, Geneva
Wilson CB, Remington JS, Stagno S, Reynolds DW (1980) Development of adverse sequelae in children born with subclinical congenital Toxoplasma infection. Pediatrics 66(5):767–774
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Lebech, D. Schmidt and the Congenital Toxoplasmosis Screening Group for their work over the years. We thank Rune Stensvold for proofreading and helpful advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Rodney Pollitt
Competing interest: None declared.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9229-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Röser, D., Nielsen, H.V., Petersen, E. et al. Congenital toxoplasmosis—a report on the Danish neonatal screening programme 1999–2007. J Inherit Metab Dis 33 (Suppl 2), 241–247 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9124-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9124-4