Abstract
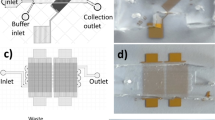
Isolation of exosome from culture medium in an effective way is desired for a less time consuming, cost saving technology in running the diagnostic test on cancer. In this study, we aim to develop an inertial microfluidic channel to separate the nano-size exosome from C666-1 cell culture medium as a selective sample. Simulation was carried out to obtain the optimum flow rate for determining the dimension of the channels for the exosome separation from the medium. The optimal dimension was then brought forward for the actual microfluidic channel fabrication, which consisted of the stages of mask printing, SU8 mould fabrication and ended with PDMS microchannel curing process. The prototype was then used to verify the optimum flow rate with polystyrene particles for its capabilities in actual task on particle separation as a control outcome. Next, the microchip was employed to separate the selected samples, exosome from the culture medium and compared the outcome from the conventional exosome extraction kit to study the level of effectiveness of the prototype. The exosome outcome from both the prototype and extraction kits were characterized through zetasizer, western blot and Transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The microfluidic chip designed in this study obtained a successful separation of exosome from the culture medium. Besides, the extra benefit from this microfluidic channels in particle separation brought an evenly distributed exosome upon collection while the exosomes separated through extraction kit was found clustered together. Therefore, this work has shown the microfluidic channel is suitable for continuous separation of exosome from the culture medium for a clinical study in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Azizah, N. Saleha, N. Hashimah, Z. Asmah, W. Mastulu, Malaysian National Cancer Registry Report 2007–2011 (Vol. 16). (2016). https://www.crc.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/documents/report/MNCRRrepor2007-2011.pdf
T. Baranyai, K. Herczeg, Z. Onódi, I. Voszka, K. Módos, N. Marton, G. Nagy, I. Mäger, M.J. Wood, S. El Andaloussi, Z. Pálinkás, V. Kumar, P. Nagy, Á. Kittel, E.I. Buzás, P. Ferdinandy, Z. Giricz, Isolation of Exosomes from Blood Plasma: Qualitative and Quantitative Comparison of Ultracentrifugation and Size Exclusion Chromatography Methods. PLoS ONE 10(12), e0145686 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145686
K. Boriachek, M.N. Islam, A. Möller, C. Salomon, N.-T. Nguyen, M.S.A. Hossain, Y. Yamauchi, M.J.A. Shiddiky, Biological Functions and Current Advances in Isolation and Detection Strategies for Exosome Nanovesicles. Small 14(6), 1702153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702153
L.T. Brinton, H.S. Sloane, M. Kester, K.A. Kelly, Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 72(4), 659–671 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1764-3
S.T. Cheung, D.P. Huang, A.B.Y. Hui, K.W. Lo, C.W. Ko, Y.S. Tsang, N. Wong, B.M. Whitney, J.C.K. Lee, Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666–1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int. J. Cancer. 83(1), 121–126 (1999)
M. Chiriacò, M. Bianco, A. Nigro, E. Primiceri, F. Ferrara, A. Romano, A. Quattrini, R. Furlan, V. Arima, G. Maruccio, M.S. Chiriacò, M. Bianco, A. Nigro, E. Primiceri, F. Ferrara, A. Romano, A. Quattrini, R. Furlan, V. Arima, G. Maruccio, Lab-on-Chip for Exosomes and Microvesicles Detection and Characterization. Sensors. 18(10), 3175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103175
A.L. Cicero, G. Raposo, The Cell Biology of Exosomes: Historical and Perspectives, in Emerging Concepts of Tumor Exosome? Mediated Cell-Cell Communication. ed. by H.G. Zhang (Springer, New York, 2013), pp. 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3697-3_1
J. De Toro, L. Herschlik, C. Waldner, C. Mongini, Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Normal and Pathological Conditions: New Insights for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Immunol. 6, 203 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00203
D.C. Duffy, J.C. McDonald, O.J.A., Schueller, G.M. Whitesides, Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 70(23), 4974–4984 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac980656z
D.W. Greening, R. Xu, H. Ji, B.J. Tauro, R.J. Simpson, A Protocol for Exosome Isolation and Characterization: Evaluation of Ultracentrifugation Density-Gradient Separation and Immunoaffinity Capture Methods (Humana Press, New York, 2015), p. 179–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2550-6_15
H. Haddadi, H. Naghsh-nilchi, D. Di Carlo, Separation of cancer cells using vortical microfluidic flows. Biomicrofluidics 12(1), 014112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5009037
S. Halvaei, S. Daryani, Z. Eslami-S, T. Samadi, N. Jafarbeik-Iravani, T.O., Bakhshayesh, K. Majidzadeh-A, R. Esmaeili, Exosomes in Cancer Liquid Biopsy: A Focus on Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids. 10, 131–141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.11.014
C. He, H. Zeng, J. Chen, Modeling of the Effect of Cell Deformation Associated with Microbubble Collision in Centrifugation Field. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 9(1), 162–174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-015-0416-5
I. Helwa, J. Cai, M.D. Drewry, A. Zimmerman, M.B. Dinkins, M.L. Khaled, M. Seremwe, W.M. Dismuke, E. Bieberich, W.D. Stamer, M.W. Hamrick, Y. Liu, A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents. PLoS ONE 12(1), e0170628 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170628
J.L. Hood, M.J. Scott, S.A. Wickline, Maximizing exosome colloidal stability following electroporation. Anal. Biochem. 448(1), 41–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2013.12.001
K. Houali, X. Wang, Y. Shimizu, D. Djennaoui, J. Nicholls, S. Fiorini, A. Bouguermouh, T. Ooka, A new diagnostic marker for secreted Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and BARF1 oncoproteins in the serum and saliva of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer. Res. 13(17), 4993–5000 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2945
H.J. Huber, P. Holvoet, Exosomes: Emerging roles in communication between blood cells and vascular tissues during atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 26(5), 412–419 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0000000000000214
C. Keryer-Bibens, C. Pioche-Durieu, C. Villemant, S. Souquère, N. Nishi, M. Hirashima, J. Middeldorp, P. Busson, Exosomes released by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells convey the viral Latent Membrane Protein 1 and the immunomodulatory protein galectin 9. BMC Cancer 6, 1–8 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-6-283
M. Kesimer, R. Gupta, Physical characterization and profiling of airway epithelial derived exosomes using light scattering. Methods 87, 59–63 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.03.013
T. Li, Y. Yan, B. Wang, H. Qian, X. Zhang, L. Shen, M. Wang, Y. Zhou, W. Zhu, W., Li, W. Xu, Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Liver Fibrosis. Stem. Cells. Dev. 22(6), 845–854 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2012.0395
W. Li, C. Li, T. Zhou, X. Liu, X. Liu, X. Li, D. Chen, Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol. Cancer. 16(1), 145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8
Y.Q. Li, N.S. Khin, M.L.K. Chua, The evolution of Epstein-Barr virus detection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. Biol. Med. 15(1), 1–5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0176
A. Liga, A.D.B. Vliegenthart, W. Oosthuyzen, J.W. Dear, M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, Exosome isolation: a microfluidic road-map. Lab. Chip. 15(11), 2388–2394 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC00240K
J. Lin, J. Li, B. Huang, J. Liu, X. Chen, X.-M. Chen, Y.-M. Xu, L.-F. Huang, X.-Z. Wang, Exosomes: Novel Biomarkers for Clinical Diagnosis. Sci. World. J. 2015, 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/657086
C. Liu, J. Guo, F. Tian, N. Yang, F. Yan, Y. Ding, J. Wei, G. Hu, G. Nie, J. Sun, Field-Free Isolation of Exosomes from Extracellular Vesicles by Microfluidic Viscoelastic Flows. ACS Nano 11(7), 6968–6976 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02277
M. Lo, J.D. Zahn, Development of a Multi-Compartment Microfiltration Device for Particle Fractionation. in 16th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences. Okinawa, Japan. 28 Oct-1 Nov 2012 (2012), p. 527–529
J.M. Pitt, G. Kroemer, L. Zitvogel, Extracellular vesicles: masters of intercellular communication and potential clinical interventions. J. Clin. Investig. 126(4), 1139–1143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI87316
P. Sajeesh, A.K. Sen, Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 17(1), 1–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1291-9
A. Sarkar, H.W. Hou, A.E. Mahan, J. Han, G. Alter, Multiplexed Affinity-Based Separation of Proteins and Cells Using Inertial Microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 6, 23589 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23589
S. Shen, C. Tian, T. Li, J. Xu, S.-W. Chen, Q. Tu, M.-S. Yuan, W. Liu, J. Wang, Spiral microchannel with ordered micro-obstacles for continuous and highly-efficient particle separation. Lab. Chip. 17(21), 3578–3591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7LC00691H
A.C. Söderström, M. Nybo, C. Nielsen, P.J. Vinholt, The effect of centrifugation speed and time on pre-analytical platelet activation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 54(12), 1913–1920 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2016-0079
K. Tabuchi, M. Nakayama, B. Nishimura, K. Hayashi, A. Hara, Early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2011, 638058 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/638058
B.W.M. van Balkom, T. Pisitkun, M.C. Verhaar, M.A. Knepper, Exosomes and the kidney: prospects for diagnosis and therapy of renal diseases. Kidney. Int. 80(11), 1138–1145 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/KI.2011.292
B.H. Wunsch, J.T. Smith, S.M. Gifford, C. Wang, M. Brink, R.L. Bruce, R.H. Austin, G. Stolovitzky, Y. Astier, Nanoscale lateral displacement arrays for the separation of exosomes and colloids down to 20 nm. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11(11), 936–940 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2016.134
Y. Yoon, S. Kim, J. Lee, J. Choi, R.-K. Kim, S.-J. Lee, O. Sul, S.-B. Lee, Clogging-free microfluidics for continuous size-based separation of microparticles. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 26531 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26531
C. Yousuff, E. Ho, K.I. Hussain, N. Hamid, Microfluidic Platform for Cell Isolation and Manipulation Based on Cell Properties. Micromachines. 8(1), 15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010015
E. Zeringer, M. Li, T. Barta, J. Schageman, K.W. Pedersen, A. Neurauter, S. Magdaleno, R. Setterquist, A.V. Vlassov, Methods for the extraction and RNA profiling of exosomes. World. J. Methodol. 3(1), 11 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v3.i1.11
Y. Zhou, L. Xia, J. Lin, H. Wang, L. Oyang, S. Tan, Y. Tian, M. Su, H. Wang, D. Cao, Q. Liao, Exosomes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Cancer 9(5), 767–777 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.22505
Funding
This study was supported by UTARRF(IPSR/RMC/UTARRF/2017-C2/T07) and University of Malaya Research grant (RU013-2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation, Teoh B.Y. and Lee P.F.; methodology, Teoh B.Y., Lee P.F. and Lim Y.M.; Simulation, Tan Z.Z. and Teoh B.Y.; Validation, Misni M., Vicit R.E.S. and Menaga S.; formal analysis, Chong W.Y.; investigation, Lim Y.M., Lee P.F.; resources, Lo K.W.; data curation, Teoh B.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Teoh B.Y.; writing—review and editing, Lim Y.M., Lee P.F., Chong W.Y.; visualisation, Tan Z. Z..; supervision, Lee P.F.; project administration, Teoh B.Y.; funding acquisition, Teoh B.Y., Lim Y.M., Lee P.F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Featured application: microfluidic channel used to separate exosome secreted from NPC cancer cells.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teoh, B., Lim, Y.M., Chong, W. et al. Isolation of exosome from the culture medium of Nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) C666-1 cells using inertial based Microfluidic channel. Biomed Microdevices 24, 12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-022-00609-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-022-00609-z