Abstract
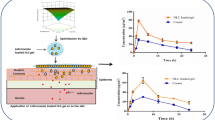
The present study was intended to enhance the permeation of artemether and lumefantrine by encapsulating in dissolvable microneedle arrays for extended action. Lumefantrine-nanoparticles were synthesized using chitosan mediated gelation and optimized by 22 factorial designs. The particle size, zeta potential and % entrapment efficiency of the optimized nanoparticles F5 were 105 ± 3.64 nm, 24.4 ± 0.54 mV and 83.94 ± 1.71%, respectively. The nanoparticles showed a controlled-release of 79.15 ± 2.45% for lumefantrine after 24 h and stability for 6 months. A combination of biocompatible polymers (PVA and PVP K − 12) was used to develop dissolvable microneedle of artemether co-loaded lumefantrine nanoparticles. The SEM and TEM analysis confirmed the needle-shaped morphology with a size of 672 ± 0.99 μm. The in-vitro release of microneedle showed biphasic release pattern for both artemether and lumefantrine, with an initial burst followed by controlled-release profile. The ex-vivo study of optimized formulation showed 70.94 ± 2.45% and 65.87 ± 1.94% permeation for artemether and lumefantrine, respectively, after 24 h. Thus, microneedle-based delivery provides an alternative to painful intravenous administration and a promising approach to increase the penetration of drugs across the skin barrier.

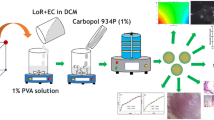
Fabrication of microneedle arrays of artemether co-loaded with lumefantrine nanoparticles.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PVA:
-
Polyvinyl alcohol
- PVP K12:
-
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- ACT:
-
Artemisinin-based combination therapy
- MN:
-
Microneedle
- STPP:
-
Sodium tripolyphosphate
- BKC:
-
Benzalkonium chloride
- HPMC:
-
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
- HPC:
-
Hydroxypropyl cellulose
- MPS:
-
Mean particle size
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- EE:
-
Entrapment efficiency
- HPH:
-
High-pressure homogenizer
References
C. Agbo et al., Formulation design, in vitro characterizations and anti-malarial investigations of artemether and lumefantrine-entrapped solid lipid microparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 42(10), 1708–1721 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2016.1171331
S.W. Ali, S. Rajendran, M. Joshi, Synthesis and characterization of chitosan and silver loaded chitosan nanoparticles for bioactive polyester. Carbohydr. Polym. 83(2), 438–446 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.004
A.Z. Alkilani, M.T. McCrudden, R.F. Donnelly, Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics. 7(4), 438–470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
D. Bhadra, S. Bhadra, N.K. Jain, PEGylated peptide dendrimeric carriers for the delivery of antimalarial drug chloroquine phosphate. Pharm. Res. 23(3), 623–633 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-9396-9
S. Bhatnagar et al., Dissolvable microneedle patch containing doxorubicin and docetaxel is effective in 4T1 xenografted breast cancer mouse model. Int. J. Pharm. 556, 263–275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.12.022
M.D. Bhavsar, S.B. Tiwari, M.M. Amiji, Formulation optimization for the nanoparticles in-microsphere hybrid oral delivery system using factorial design. J. Cont. Rel. 110(2), 422–430 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.11.001
J. Choi et al., Development of a film-based immunochromatographic microfluidic device for malaria diagnosis. Biomed. Microdevices 21(4) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0431-8
M. Cormier et al., Transdermal delivery of desmopressin using a coated microneedle array patch system. J. Cont. Rel. 97(3), 503–511 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.04.003
K. Derakhshandeh, M. Erfan, S. Dadashzadeh, Encapsulation of 9-nitrocamptothecin, a novel anticancer drug, in biodegradable nanoparticles: Factorial design, characterization and release kinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 66(1), 34–41 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.09.004
R.F. Donnelly, M.T. McCrudden, A.Z. Alkilani, et al., Hydrogel-forming microneedles prepared from super swelling polymers combined with lyophilized wafers for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS One 9(10), e111547 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111547
O. Egunsola, K.A. Oshikoya, Comparative safety of artemether-lumefantrine and other artemisinin-based combinations in children: a systematic review. Malar. J. 12(1), 385 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-12-385
R. Fule et al., Solubility and dissolution rate enhancement of lumefantrine using hot melt extrusion technology with physicochemical characterization. J. Pharm. Investig. 43(4), 305–321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0078-z
A. Garg, K. Bhalala, D.S. Tomar, In-situ single pass intestinal permeability and pharmacokinetic study of developed lumefantrine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 516(1–2), 120–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.064
M.J. Garland et al., Dissolving polymeric microneedle arrays for electrically assisted transdermal drug delivery. J. Cont. Rel. 159(1), 52–59 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.003
M. Gharib et al., Micro-needle drug delivery systems. California Instit. of Technol. 2016 U.S. Patent Application 20160144100A1
S. Henry et al., Microfabricated microneedles: A novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 87(8), 922–925 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/js980042+
P.P. Ige, S.N. Dipsingh, Preparation and in vitro–in vivo evaluation of surface-modified poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles as controlled release carriers for flutamide delivery. J. Microencapsul. 32(3), 231–239 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2014.995731
A. Jain et al., Fabrication, characterization and cytotoxicity studies of ionically cross-linked docetaxel loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 137, 65–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.012
K.A. Janes et al., Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Cont. Rel. 73, 255–267 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(01)00294-2
F. Kesisoglou, S. Panmai, Y. Wu, Nanosizing-oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59(7), 631–644 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.003
R. Kudarha et al., Box–Behnken study design for optimization of bicalutamide-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier: Stability assessment. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 20(5), 608–618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3109/10837450.2014.908305
J.W. Lee, J.H. Park, M.R. Prausnitz, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 29(13), 2113–2124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.12.048
I.C. Lee et al., Fabrication of a novel partially dissolving polymer microneedle patch for transdermal drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 3(2), 276–285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01555J
Y. Luo et al., Preparation, characterization and evaluation of selenite-loaded chitosan/TPP nanoparticles with or without zein coating. Carbohydr. Polym. 82(3), 942–951 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.029
C.J. Martin et al., Low temperature fabrication of biodegradable sugar glass microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. J. Cont. Rel. 158(1), 93–101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.10.024
N. Martinho, C. Damgé, C.P. Reis, Recent advances in drug delivery systems. J Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2, 510 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/jbnb.2011.225062
S.N. Murthy, S.M. Sammeta, C. Bowers, Magnetophoresis for enhancing transdermal drug delivery: Mechanistic studies and patch design. J. Cont. Rel. 148(2), 197–203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.08.015
H.X. Nguyen et al., Poly (vinyl alcohol) microneedles: Fabrication, characterization, and application for transdermal drug delivery of doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 129, 88–103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.05.017
D. Parashar, N.P. Aditya, R.S.R. Murthy, Development of artemether and lumefantrine co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Physicochemical characterization and in-vivo antimalarial activity. Drug Deliv. 23(1), 123–129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.905883
C.V. Pardeshi et al., Novel surface modified solid lipid nanoparticles as intranasal carriers for ropinirole hydrochloride: Application of factorial design approach. Drug Deliv. 20(1), 47–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2012.752421
K. Patel, V. Sarma, P. Vavia, Design and evaluation of lumefantrine–oleic acid self nanoemulsifying ionic complex for enhanced dissolution. Daru 21(1), 27 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-27
J.K. Patra, G. Das, L.F. Fraceto, et al., Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16, 71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
R. Pignatello et al., Flurbiprofen-loaded acrylate polymer nanosuspensions for ophthalmic application. Biomaterials. 23(15), 3247–3255 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00080-7
A. Ripolin, J. Quinn, E. Larraneta, et al., Successful application of large microneedle patches by human volunteers. Int. J. Pharm. 521(1–2), 92–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.02.011
A.H. Sabri et al., Expanding the applications of microneedles in dermatology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 140, 121–140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.05.001
H.M. Shapiro et al., Cytometry in malaria-a practical replacement for microscopy? Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 65(1), 11–20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142956.cy1120s65
P. Shende, M. Salunke, Transepidermal microneedles for co-administration of folic acid with methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express. 5(2), 025023 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2057-1976/aafbbb
P. Shende et al., Physicochemical investigation of engineered nanosuspensions containing model drug lansoprazole. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 37(4), 504–511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1046553
P. Shende et al., Engineering of microcomplex of artemether and lumefantrine for effective drug treatment in malaria. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 45(8), 1597–1604 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1267012
S.P. Singh et al., Intravenous pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, dose proportionality and in situ permeability of anti-malarial lumefantrine in rats. Malar. J. 10(1), 293 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-10-293
R. Watkins, L. Wu, C. Zhang, et al., Natural product-based nanomedicine: Recent advances and issues. Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 6055 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S92162
N.J. White, M. van Vugt, F.D. Ezzet, Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of artemether-lumefantrine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 37(2), 105–125 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199937020-00002
World Malaria Report 2010 https://www.who.int/malaria/world_malaria_report_2010/en/
R. Yoksan, J. Jirawutthiwongchai, K. Arpo, Encapsulation of ascorbyl palmitate in chitosan nanoparticles by oil-in-water emulsion and ionic gelation processes. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces. 76(1), 292–297 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.11.007
K. Zhao, J. Singh, In vitro percutaneous absorption enhancement of propranolol hydrochloride through porcine epidermis by terpenes/ethanol. J. Cont. Rel. 62(3), 359–366 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00171-6
L.J. Zhou et al., Risk of drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria therapy-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Parasitol. Res. 116(2), 781–788 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5353-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawar, S., Shende, P. 22 factorial design-based biocompatible microneedle arrays containing artemether co-loaded with lumefantrine nanoparticles for transepidermal delivery. Biomed Microdevices 22, 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-0476-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-0476-8