Abstract
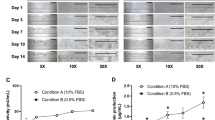
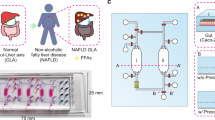
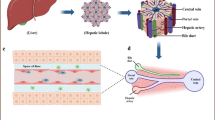
Non-parenchymal cells play a key role in the occurrence and development of alcoholic liver disease. However, this cellular behaviour has not been fully characterized, and it is inconvenient to observe in traditional in vitro alcoholic liver disease (ALD) models and animal models. Herein we developed a demountable liver-on-chip device for investigation of pathophysiological process of individual non-parenchymal cells in alcohol induced ALD. This liver-device comprised of HepG2, LX-2, EAhy926 and U937 cells, which were ordered in a physiological distribution under perfuse. This device allows improved HepG2 cells activities and maintained high liver functions which including albumin synthesis and urea secretion. This novel liver-device is able to recreate the damage process of hepatic non-parenchymal cell lines induced by alcohol, and to understand the intercellular communication between different types of hepatic cells during ALD by measuring multiple biomarkers of each types of hepatic non-parenchymal cell lines, including Ve-cadherin, eNOS, VEGF and α-SMA. The proposed liver-device is able to further studies of pathological analysis and drug- and toxicity-screening.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.I. Cohen, L.E. Nagy, Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: Interactions between parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells. J. Dig. Dis. 12, 3–9 (2011)
J. Deng, Y. Qu, T. Liu, B. Jing, X. Zhang, Z. Chen, Y. Luo, W. Zhao, Y. Lu, B. Lin, Recent organ-on-a-chip advances toward drug toxicity testing. Microphysiol Syst 2, 8 (2018)
J. Deng, X. Zhang, Z. Chen, Y. Luo, Y. Lu, T. Liu, Z. Wu, Y. Jin, W. Zhao, B. Lin, A cell lines derived microfluidic liver model for investigation of hepatotoxicity induced by drug-drug interaction. Biomicrofluidics 13, 024101 (2019)
P. Godoy, N.J. Hewitt, U. Albrecht, M.E. Andersen, N. Ansari, S. Bhattacharya, J.G. Bode, J. Bolleyn, C. Borner, J. Böttger, A. Braeuning, R.A. Budinsky, B. Burkhardt, N.R. Cameron, G. Camussi, C. Cho, Y. Choi, J. Craig Rowlands, U. Dahmen, G. Damm, O. Dirsch, M.T. Donato, J. Dong, S. Dooley, D. Drasdo, R. Eakins, K.S. Ferreira, V. Fonsato, J. Fraczek, R. Gebhardt, A. Gibson, M. Glanemann, C.E.P. Goldring, M.J. Gómez-Lechón, G.M.M. Groothuis, L. Gustavsson, C. Guyot, D. Hallifax, S. Hammad, A. Hayward, D. Häussinger, C. Hellerbrand, P. Hewitt, S. Hoehme, H. Holzhütter, J.B. Houston, J. Hrach, K. Ito, H. Jaeschke, V. Keitel, J.M. Kelm, B. Kevin Park, C. Kordes, G.A. Kullak-Ublick, E.L. LeCluyse, P. Lu, J. Luebke-Wheeler, A. Lutz, D.J. Maltman, M. Matz-Soja, P. McMullen, I. Merfort, S. Messner, C. Meyer, J. Mwinyi, D.J. Naisbitt, A.K. Nussler, P. Olinga, F. Pampaloni, J. Pi, L. Pluta, S.A. Przyborski, A. Ramachandran, V. Rogiers, C. Rowe, C. Schelcher, K. Schmich, M. Schwarz, B. Singh, E.H.K. Stelzer, B. Stieger, R. Stöber, Y. Sugiyama, C. Tetta, W.E. Thasler, T. Vanhaecke, M. Vinken, T.S. Weiss, A. Widera, C.G. Woods, J.J. Xu, K.M. Yarborough, J.G. Hengstler, Recent advances in 2d and 3d in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and adme. Arch. Toxicol. 87, 1315–1530 (2013)
M. Jang, P. Neuzil, T. Volk, A. Manz, A. Kleber, On-chip three-dimensional cell culture in phaseguides improves hepatocyte functions in vitro. Biomicrofluidics 9, 034113 (2015)
T. Kostrzewski, T. Cornforth, S.A. Snow, L. Ouro-Gnao, C. Rowe, E.M. Large, D.J. Hughes, Three-dimensional perfused human in vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 23, 204 (2017)
V.M. Lauschke, D.F.G. Hendriks, C.C. Bell, T.B. Andersson, M. Ingelman-Sundberg, Novel 3d culture systems for studies of human liver function and assessments of the hepatotoxicity of drugs and drug candidates. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 29, 1936–1955 (2016)
J. Lee, B. Choi, D.Y. No, G. Lee, S. Lee, H. Oh, S. Lee, A 3d alcoholic liver disease model on a chip. Integr Biol-UK 8, 302–308 (2016)
H. Liu, S. Li, Y. Yan, X. Wang, F. Lin, R. Zhang, A liver analog construct for use as an alcoholic liver disease model. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57, 955–958 (2012)
A. Louvet, P. Mathurin, Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 231–242 (2015)
R.E. Mann, R.G. Smart, R. Govoni, The epidemiology of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 27, 209–219 (2003)
R.S. O'Shea, S. Dasarathy, A.J. McCullough, Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 51, 307–328 (2010)
J.S. Passmore, P.T. Lukey, S.R. Ress, The human macrophage cell line u937 as an in vitro model for selective evaluation of mycobacterial antigen-specific cytotoxic t-cell function. Immunology 102, 146–156 (2001)
J. Poisson, S. Lemoinne, C. Boulanger, F. Durand, R. Moreau, D. Valla, P. Rautou, Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 66, 212–227 (2017)
L. Prodanov, R. Jindal, S.S. Bale, M. Hegde, W.J. McCarty, I. Golberg, A. Bhushan, M.L. Yarmush, O.B. Usta, Long-term maintenance of a microfluidic 3d human liver sinusoid. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 113, 241–246 (2016)
K. Ronaldson-Bouchard, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, Organs-on-a-chip: A fast track for engineered human tissues in drug development. Cell Stem Cell 22, 310–324 (2018)
W. Seo, Hepatic non-parenchymal cells: Master regulators of alcoholic liver disease? World J. Gastroenterol. 22, 1348 (2016)
A. Skardal, T. Shupe, A. Atala, Organoid-on-a-chip and body-on-a-chip systems for drug screening and disease modeling. Drug Discov. Today 21, 1399–1411 (2016)
R.M. Tostões, S.B. Leite, M. Serra, J. Jensen, P. Björquist, M.J.T. Carrondo, C. Brito, P.M. Alves, Human liver cell spheroids in extended perfusion bioreactor culture for repeated-dose drug testing. Hepatology 55, 1227–1236 (2012)
A. Treyer, A. Muesch, Hepatocyte polarity. Compr Physiol 3, 243–287 (2013)
J.P. Wikswo, The relevance and potential roles of microphysiological systems in biology and medicine. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 239, 1061–1072 (2014)
D. Wohlleber, P.A. Knolle, The role of liver sinusoidal cells in local hepatic immune surveillance. Clin. Transl. Immunology 5, e117 (2016)
J. Wu, Pathogenesis mechanism of alcohol liver and associated cell signaling pathways. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology) 31, 514–518 (2017)
F. Zheng, F. Fu, Y. Cheng, C. Wang, Y. Zhao, Z. Gu, Organ-on-a-chip systems: Microengineering to biomimic living systems. Small 12, 2253–2282 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675017), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. SQ2017YFC170204-001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (No. DUT17LK25) and Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZSM201612049). We also thank Dr. Xiaorui Li and Dr. Yu Jin for helping supporting information collecting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. Deng, Z.Z. Chen contributed equally to this work. Y. Luo, J. Deng, B.C. Lin, W.J. Zhao and X.L. Zhang designed the study; J. Deng, Z.Z. Chen and T.J. Liu performed the experiments; J. Deng, X.L. Zhang and Z.Z. Wu analyzed the data; J. Deng, Z.Z. Chen, Y. Luo, Y. Lu and B.C. Lin wrote the paper. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare neither conflict of interest nor competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, J., Chen, Z., Zhang, X. et al. A liver-chip-based alcoholic liver disease model featuring multi-non-parenchymal cells. Biomed Microdevices 21, 57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0414-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0414-9