Abstract
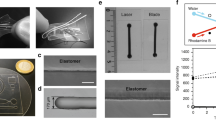
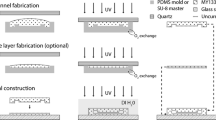
We describe a simple fabrication technique – targeted towards non-specialists – that allows for the production of leak-proof polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic devices that are compatible with live-cell microscopy. Thin PDMS base membranes were spin-coated onto a glass-bottom cell culture dish and then partially cured via microwave irradiation. PDMS chips were generated using a replica molding technique, and then sealed to the PDMS base membrane by microwave irradiation. Once a mold was generated, devices could be rapidly fabricated within hours. Fibronectin pre-treatment of the PDMS improved cell attachment. Coupling the device to programmable pumps allowed application of precise fluid flow rates through the channels. The transparency and minimal thickness of the device enabled compatibility with inverted light microscopy techniques (e.g. phase-contrast, fluorescence imaging, etc.). The key benefits of this technique are the use of standard laboratory equipment during fabrication and ease of implementation, helping to extend applications in live-cell microfluidics for scientists outside the engineering and core microdevice communities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. W. Beh, W. Zhou, T. H. Wang, Lab. Chip 12(20), 4120–4127 (2012)
Q. Chen, G. Li, Y. Nie, S. Yao, J. Zhao, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 16(1), 83–90 (2014)
S. I. Ertel, B. D. Ratner, A. Kaul, M. B. Schway, T. A. Horbett, J. Biomed. Mater. Res 28(6), 667–675 (1994)
B. T. Ginn, O. Steinbock, Langmuir 19(19), 8117–8118 (2003)
M. W. Grol, A. Pereverzev, S. M. Sims, S. J. Dixon, J. Cell Sci 126(Pt 16), 3615–3626 (2013)
P. G. Gross, E. P. Kartalov, A. Scherer, L. P. Weiner, J. Neurol. Sci 252(2), 135–143 (2007)
K. Haubert, T. Drier, D. Beebe, Lab. Chip 6(12), 1548–1549 (2006)
P. M. Hinderliter, K. R. Minard, G. Orr, W. B. Chrisler, B. D. Thrall, J. G. Pounds, J. G. Teeguarden, Part. Fibre Toxicol 7(1), 36 (2010)
A. Y. Hui, G. Wang, B. Lin, W. T. Chan, Lab. Chip 5(10), 1173–1177 (2005)
A. Konda, J. M. Taylor, M. A. Stoller, S. A. Morin, Lab. Chip 15(9), 2009–2017 (2015)
E. Leclerc, B. David, L. Griscom, B. Lepioufle, T. Fujii, P. Layrolle, C. Legallaisa, Biomaterials 27(4), 586–595 (2006)
Y. Lee, J. M. Lee, P. K. Bae, I. Y. Chung, B. H. Chung, B. G. Chung, Electrophoresis 36(7–8), 994–1001 (2015)
G.H. Lee, J.S. Lee, X. Wang and S. Hoon Lee, Adv Healthc Mater 5(1), 56–74 (2016)
K. Loutherback, L. Chen and H.Y. Holman, Anal. Chem. 87(9), 4601–4606 (2015)
I. Meyvantsson, D. J. Beebe, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1, 423–449 (2008)
K. M. Miller, J. M. Anderson, J. Biomed. Mater. Res 22(8), 713–731 (1988)
C. Moraes, M. Likhitpanichkul, C. J. Lam, B. M. Beca, Y. Sun, C. A. Simmons, Integr. Biol. 5(4), 673–680 (2013)
W. J. Polacheck, R. Li, S. G. Uzel, R. D. Kamm, Lab. Chip 13(12), 2252–2267 (2013)
M. A. Unger, H.-P. Chou, T. Thorsen, A. Scherer, S. R. Quake, Science 288(5463), 113–116 (2000)
B. D. Wheal, R. J. Beach, N. Tanabe, S. J. Dixon, S. M. Sims, J. Bone Miner. Res 29(3), 725–734 (2014)
S. Yasotharan, S. Pinto, J. G. Sled, S.-S. Bolz, A. Gunther, Lab. Chip 15(12), 2660–2669 (2015)
E. W. Young, D. J. Beebe, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39(3), 1036–1048 (2010)
H. Yu, G. Zhou, F. Chau, S. Sinha, Microsyst. Technol. 17(3), 443–449 (2011)
Acknowledgments
We thank members of Dixon, Sims, and Holdsworth labs for their contributions, as well as members of the Skeletal Biology and Robarts Imaging Laboratories for their support. We also thank Yoshiyuki Arai for the use of his PTA ImageJ software plugin, and Mike Kovach and colleagues from Horiba-Photon Technology International for valuable advice and infrastructure support. This work was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) grant number 126065. D. Lorusso is supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship and a Transdisciplinary Bone & Joint Training Award from the Collaborative Training Program in Musculoskeletal Health Research. N.M. Ochotny was supported by a Postdoctoral Fellowship Award from The Arthritis Society and by the Joint Motion Program — a CIHR Strategic Training Program in Musculoskeletal Health Research and Leadership. D. W. Holdsworth holds the Dr. Sandy Kirkley Chair in Musculoskeletal Research at The University of Western Ontario.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorusso, D., Nikolov, H.N., Milner, J.S. et al. Practical fabrication of microfluidic platforms for live-cell microscopy. Biomed Microdevices 18, 78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0101-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0101-z