Abstract
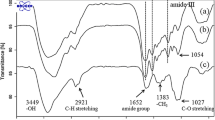
Silk sericin is recently shown to possess various biological activities for biomedical applications. While various sericin carriers were developed for drug delivery system, very few researches considered sericin as a bioactive molecule itself. In this study, sericin incorporated in the chitosan-based microspheres was introduced as a bioactive molecule and bioactive carrier at the same time. The chitosan/sericin (CH/SS) microspheres at different composition (80/20, 70/30, 60/40, and 50/50) were successfully fabricated using anhydroustri-polyphosphate (TPP) as a polyanionic crosslinker. The microspheres with an average size of 1–4 μm and narrow size distribution were obtained. From FT-IR spectra, the presence of both chitosan and sericin in the microspheres confirmed the occurrence of ionic interaction that crosslink them within the microspheres. We also found that the CH/SS microspheres prepared at 50/50 could encapsulate sericin at the highest percentage (37.28 %) and release sericin in the most sustained behavior, possibly due to the strong ionic interaction of the positively charged chitosan and the negatively charged sericin. On the other hand, the composition of CH/SS had no effect on the degradation rate of microspheres. All microspheres continuously degraded and remained around 20 % after 14 days of enzymatic degradation. This explained that the ionic crosslinkings between chitosan and sericin could be demolished by the enzyme and hydrolysis. Furthermore, we have verified that all CH/SS microspheres at any concentrations showed non-toxicity to L929 mouse fibroblast cells. Therefore, we suggested that the non-toxic ionic-crosslinked CH/SS microspheres could be incorporated in wound dressing material to achieve the sustained release of sericin for accelerated wound healing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Aramwit, S. Kanokpanont, P. Punyarit, T. Srichana, Wounds 21, 198 (2009)
P. Aramwit, S. Kanokpanont, T. Nakpheng, T. Srichana, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11, 2200 (2010a)
P. Aramwit, T. Siritientong, S. Kanokpanont, T. Srichana, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 47, 668 (2010b)
P. Aramwit, T. Siritientong, T. Srichana, Waste Manag. Res. 30, 217 (2012)
P. Aramwit, T. Siritienthong, T. Srichana, J. Ratanavaraporn, Cells Tissues Organs 197, 224 (2013)
R. Dash, C. Acharya, P.C. Bindu, S.C. Kundu, BMB Rep. 41, 236 (2007)
S. Ekgasit, N. Pattayakorn, D. Tongsakul, C. Thammacharoen, T. Kongyou, Anal. Sci. 23, 863 (2007)
J.B. Fan, L.P. Wu, L.S. Chen, X.Y. Mao, F.Z. Ren, J. Food Biochem. 33, 74 (2009)
S. Freiberg, X.X. Zhu, Int. J. Pharm. 282, 1 (2004)
F. Ganji, E. Vasheghani-Farahani, Iran. Polym. J. 18, 63 (2009)
M.R. Khan, M. Tsukada, X. Zhang, H. Morikawa, J. Mater. Sci. 48, 3731 (2013)
T. Kitisin, P. Maneekan, N. Luplertlop, J. Agric. Sci. 5, 1916 (2013)
J.A. Ko, H.J. Park, S.J. Hwang, J.B. Park, J.S. Lee, Int. J. Pharm. 249, 165 (2002)
S.C. Kundu, B.C. Dash, R. Dash, Prog. Polym. Sci. 33, 998 (2008)
K. Lee, H. Kweon, J.H. Yeo, S.O. Woo, Y.W. Lee, C.S. Cho, K.H. Kim, Y.H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 33, 75 (2003)
B.B. Mandal, S.C. Kundu, Nanotechnology 20, 355101 (2009)
B.B. Mandal, A.S. Priya, S.C. Kundu, Acta Biomater. 5, 3007 (2009)
S. Masahiro, Y. Hideyuki, K. Norihisa, Nutr. Res. 20, 1505 (2000)
L.N. Mengatto, I.M. Helbling, J.A. Luna, Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 6, 156 (2012)
F.L. Mi, Y.C. Tan, H.F. Liang, H.W. Sung, Biomaterials 23, 181 (2002)
M. Morikawa, T. Kimura, M. Murakami, K. Katayama, S. Terada, A. Yamaguchi, J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 16, 223 (2009)
T. Mosmann, J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55 (1983)
A. Nascimento, M.C. Laranjeira, V.T. Favere, A. Josue, J. Microencapsul. 18, 679 (2001)
S. Nayak, S. Dey, S.C. Kundu, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 65, 258 (2014)
J. O’Regan, D.M. Mulvihill, Food Chem. 119, 182 (2010)
N. Shanmugasundaram, P. Ravichandran, P.R. Neelakanta, N. Ramamurty, S. Pal, K.P. Rao, Biomaterials 22, 1943 (2001)
X.Z. Shu, K.J. Zhu, Int. J. Pharm. 201, 51 (2000)
X.Z. Shu, K.J. Zhu, J. Microencapsul. 18, 237 (2001)
V.R. Sinha, A.K. Singla, S. Wadhawan, R. Kaushik, R. Kumria, K. Bansal, S. Dhawan, Int. J. Pharm. 274, 1 (2004)
A. Sionkowska, M. Wisniewski, J. Skopinska, C.J. Kennedy, T.J. Wess, Biomaterials 25, 795 (2004)
T. Siritienthong, J. Ratanavaraporn, P. Aramwit, Int. J. Pharm. 439, 175 (2012)
T. Siritienthong, J. Ratanavaraporn, T. Srichana, P. Aramwit, BioMed Research International, Article ID 904314 (2013)
T. Siritienthong, A. Angspatt, J. Ratanavaraporn, P. Aramwit, Pharm. Res. 31, 104 (2014)
Y. Tang, S.Y. Liu, S.P. Armes, N.C. Billingham, Biomacromolecules 4, 1636 (2003)
S. Terada, T. Nishimura, M. Sasaki, H. Yamada, M. Miki, Cytotechnology 40, 3 (2002)
C. Thomas, P. Sharma, Biomater. Artif. Cells Artif. Org 18, 1 (1990)
K. Tsujimoto, H. Takagi, M. Takahashi, H. Yamada, S. Nakamori, J. Biochem. 129, 979 (2001)
R. Voegeli, J. Meier, R. Blust, Cosmetics Toiletries 108, 101 (1993)
Y.Q. Zhang, Biotechnol. Adv. 20, 91 (2002)
Y.Q. Zhang, M.L. Tao, W.D. Shen, Y.Z. Zhou, Y. Ding, Y. Ma, W.L. Zhou, Biomaterials 25, 3751 (2004)
S. Zhaorigetu, N. Yanaka, M. Sasaki, H. Watanabe, N. Kato, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 71, 11 (2003)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledged the financial support from Thailand Research Fund (Contract number RSA5680004) and Chulalongkorn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
The decovoluted FT-IR spectra of the amide I region of CH/SS microspheres prepared at different mixing compositions (80/20, 70/30, 60/40, and 50/50). (GIF 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aramwit, P., Ekasit, S. & Yamdech, R. The development of non-toxic ionic-crosslinked chitosan-based microspheres as carriers for the controlled release of silk sericin. Biomed Microdevices 17, 84 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9991-4
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9991-4