Abstract
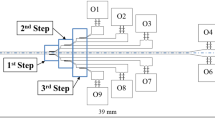
This work presents design, fabrication and test of a microfluidic device which employs Fahraeus-Lindqvist and Zweifach-Fung effects for cell concentration and blood cell-plasma separation. The device design comprises a straight main channel with a series of branched channels placed symmetrically on both sides of the main channel. The design implements constrictions before each junction (branching point) in order to direct cells that would have migrated closer to the wall (naturally or after liquid extraction at a junction) towards the centre of the main channel. Theoretical and numerical analysis are performed for design of the microchannel network to ensure that a minimum flow rate ratio (of 2.5:1, main channel-to-side channels) is maintained at each junction and predict flow rate at the plasma outlet. The dimensions and location of the constrictions were determined using numerical simulations. The effect of presence of constrictions before the junctions was demonstrated by comparing the performances of the device with and without constrictions. To demonstrate the performance of the device, initial experiments were performed with polystyrene microbeads (10 and 15 μm size) and droplets. Finally, the device was used for concentration of HL60 cells and separation of plasma and cells in diluted blood samples. The cell concentration and blood-plasma purification efficiency was quantified using Haemocytometer and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter (FACS). A seven-fold cell concentration was obtained with HL60 cells and a purification efficiency of 70 % and plasma recovery of 80 % was observed for diluted (1:20) blood sample. FACS was used to identify cell lysis and the cell viability was checked using Trypan Blue test which showed that more than 99 % cells are alive indicating the suitability of the device for practical use. The proposed device has potential to be used as a sample preparation module in lab on chip based diagnostic platforms.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Aran, A. Fok, L.A. Sasso, N. Kamdar, Y. Guan, Q. Sun, A. Undar, J.D. Zahn, Microfiltration platform for continuous blood plasma protein extraction from whole blood during cardiac surgery. Lab Chip 11, 2858–2868 (2011)
A.A.S. Bhagat, H. Bow, H.W. Hou, S.J. Tan, J. Han, C.T. Lim, Microfluidics for cell separation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 48, 999–1014 (2010)
P. Bhardwaj, P. Bagdi, A.K. Sen, Microfluidic device based on a microhydrocyclone for particle liquid separation. Lab Chip. 11, 4012–4021 (2011)
C. Blattert, R. Jurischka, A. Schoth, P. Kerth, W. Menz, “Separation of blood cells and plasma in microchannel bend structures”. Lab-on-a-Chip: Plat Dev Appl 5591, 143–151 (2004)
S. Choi, J.K. Park, Continuous hydrophoretic separation and sizing of microparticles using slanted obstacles in a microchannel. Lab Chip 7, 890–897 (2007)
K.H. Chung, Y.H. Choi, J.H. Yang, C.W. Park, W.J. Kim, C.S. Ah, G.Y. Sung, Magnetically-actuated blood filter unit attachable to pre-made biochips. Lab Chip 12(18), 3272–3276 (2012)
T.A. Crowley, V. Pizziconi, Isolation of plasma from whole blood using planar microfilters for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 5, 922–929 (2005)
J.A. Davis, D.W. Inglis, K.J. Morton, D.A. Lawrence, L.R. Huang, S.Y. Chou, J.C. Sturm, R.H. Austin, Deterministic hydrodynamics: taking blood apart. PNAS 103, 14779–14784 (2006)
I.K. Dimov, L. Basabe-Desmonts, J.L. Garcia-Cordero, B.M. Ross, A.J. Ricco, L.P. Lee, Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 11, 845–850 (2011)
V. Doyeux, T. Podgorski, S. Peponas, M. Ismail, G. Coupier, Spheres in the vicinity of a bifurcation:elucidating the zweifach–fung effect. J. Fluid Mech 674, 359–388 (2011)
R. Fahraeus and T. Lindqvist, “The viscosity of the blood in narrow capillary tubes”. Am. J. Physiol. 96, 562–568 (1931)
M. Faivre, M. Abkarian, K. Bickraj, H.A. Stone, Geometrical focusing of cells in a microfluidic device: an approach to separate blood plasma. Biorheology 43, 147–159 (2006)
R. Fan, O. Vermesh, A. Srivastava, B.K.H. Yen, L. Qin, H. Ahmad, G.A. Kwong, C. Liu, J. Gould, L. Hood, J.R. Heath, Integrated barcode chips for rapid, multiplexed analysis of proteins in microliter quantities of blood. Nat. Biotechnol. 26(12), 1373–1378 (2008)
Y. C. Fung, Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues, Springer, 1993.
E.P. Furlani, Magnetophoretic separation of blood cells at the microscale. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 40, 1313–1319 (2007)
T.M. Geislinger, T. Franke, Hydrodynamic lift of vesicles and red blood cells in flow--from fåhræus & lindqvist to microfluidic cell sorting. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 208, 161–176 (2014)
D.R. Gossett, W.M. Weaver, A.J. Mach, S.C. Hur, H.T.K. Tse, W. Lee, H. Amini, D. Di Carlo, Label-free cell separation and sorting in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 397, 3249–3267 (2010)
S. Haeberle, T. Brenner, R. Zengerle, J. Ducre’e, “Centrifugal extraction of plasma from whole blood on a rotating disk”. Lab Chip 6, 776–781 (2006)
A. Homsy, P.D. van der Wal, W. Doll, R. Schaller, S. Korsatko, M. Ratzer, M. Ellmerer, T.R. Pieber, A. Nicol, N.F. de Rooij, “Development and validation of a low cost blood filtration element separating plasma from undiluted whole blood,”. Biomicrofluidics 6, 012804–1-9 (2012)
H.W. Hou, A.A.S. Bhagat, W.C. Lee, S. Huang, J. Han, C.T. Lim, “Microfluidic devices for blood fractionation”. Micro Mach. 2, 319–343 (2011)
R.D. Jaggi, R.S. Carlo, S. Effenhauser, Microfluidic depletion of red blood cells from whole blood in high-aspect-ratio microchannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 3, 47–53 (2007)
H. Jiang, X. Weng, C. H. Chon, X. Wu and D. Li, “A microfluidic chip for blood plasma separation using electro-osmotic flow control,” J. Micromech. Microeng., vol. 21, pp. 085019-1-8, 2011
M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, E. Sollier, Micro-scale blood plasma separation: from acoustophoresis to egg-beaters. Lab Chip 13, 3323–3346 (2013)
M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, R. Dhariwal, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, Recent advances in microparticle continuous separation. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2(1), 1–13 (2008)
M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, R. Dhariwal, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, L. Jouvet, Hydrodynamic blood plasma separation in microfluidic channels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 8, 105–114 (2010a)
M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, D.M. Kavanagh, R.S. Dhariwal, C.J. Campbell, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, Validation of a blood plasma separation system by biomarker detection. Lab Chip 10, 1587–1595 (2010b)
A. Lenshof, T. Laurell, Continuous separation of cells and particles in microfluidic systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 1203–1217 (2010)
A. Lenshof, A. Ahmad-Tajudin, K. Järås, A. Swärd-Nilsson, L. Åberg, G. Marko-Varga, J. Malm, H. Lilja, T. Laurell, “Acoustic whole blood plasmapheresis chip for prostate specific antigen microarray diagnostics”. Anal. Chem. 81, 6030–6037 (2009)
C. Li, C. Liu, Z. Xu, J. Li, Extraction of plasma from whole blood using a deposited microbead plug (DMBP) in a capillary-driven microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices 14, 565–572 (2012)
S. Liao, C. Chang, H. Chang, “A capillary dielectrophoretic chip for real-time blood cell separation from a drop of whole blood”. Biomicrofluidics 7, 024110–1-9 (2013)
A.J. Mach, D. Di Carlo, Continuous scalable blood filtration device using inertial microfluidics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 107(2), 302–311 (2010)
J. Moorthy, D.J. Beebe, In situ fabricated porous filters for microsystems. Lab Chip 3, 62–66 (2003)
Y. Nakashima, S. Hata, T. Yasuda, Blood plasma separation and extraction from a minute amount of blood using dielectrophoretic and capillary forces. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 145, 561–569 (2010)
J. Nam, H. Lim, C. Kim, J.Y. Kang, S. Shin, “Density-dependent separation of encapsulated cells in a microfluidic channel by using a standing surface acoustic wave”. Biomicrofluidics 6, 024120–1-10 (2012)
V. Narsimhan, H. Zhao, E.S.G. Shaqfeh, Coarse- grained theory to predict the concentration distribution of red blood cells in wall-bounded couette flow at zero Reynolds number. Phys. Fluids 25, 1–10 (2013)
N. Nivedita, I. Papautsky, “Continuous separation of blood cells in spiral microfluidic devices”. Biomicrofluidics 7, 054101–1-14 (2013)
N. Pamme, Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7, 1644–1659 (2007)
A. Prabhakar, B.V. Kumar, S. Tripathi, A. Agrawal, “A novel, compact and efficient microchannel arrangement with multiple hydrodynamic effects for blood plasma separation,”. Microfluid. Nanofluid. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1488-6
A.R. Pries, D. Neuhaus, P. Gaehtgens, “Blood viscosity in tube flow: dependence on diameter and haematocrit,”. Am. J. Physiol. 263(6Pt2), H1770–1778 (1992)
P. Sajeesh, A.K. Sen, Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 17, 1–52 (2014)
P. Sajeesh, M. Doble and A. K. Sen, “Hydrodynamic resistance and mobility of deformable objects in microfluidic channels,” Biomicrofluidics, vol. 8, no. 5, 2014.
A.K. Sen, T. Harvey, J. Clausen, T. Cox, “A microsystem for extraction, capture and detection of E-Coli O157:H7”. Biomedical Microdevices 13, 705–715 (2011)
M. Sun, Z.S. Khan, S.A. Vanapalli, Blood plasma separation in a long two-phase plug flowing through disposable tubing. Lab Chip 12, 5225–5230 (2012)
M. Toner, D. Irimia, Blood-on-a-chip. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 77–103 (2005)
S. Tripathi, A. Prabhakar, N. Kumar, S.G. Singh, A. Agrawal, “Blood plasma separation in elevated dimension T-shaped microchannel”. Biomed. Microdevices 15(3), 415–425 (2013)
S. Tripathi, Y.V. Bala Varun Kumar, P. Amit, S.S. Joshi, A. Amit, Performance study of microfluidic devices for blood plasma separation—a designer’s perspective. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 084004 (2015a) (15 pp)
S. Tripathi, Y.V.B.V. Kumar, A. Prabhakar, S.S. Joshi, A. Agrawal, Passive blood plasma separation at the microscale: a review of design principles and microdevices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 083001 (2015b) (24 pp)
V. VanDelinder, A. Groisman, Separation of plasma from whole human blood in a continuous cross-flow in a molded microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 76(11), 3765–3771 (2006)
A.P. Wong, M. Gupta, S.S. Shevkoplyas, G.M. Whitesides, Egg beater as centrifuge: isolating human blood plasma from whole blood in resource-poor settings. Lab Chip 8, 2032–2037 (2008)
Xiangdong Xue, MayurK Patel and Chris Bailey, Challenges in Modelling Biofluids in Microchannels”, 2nd Electronics Systemintegration Technology Conference Greenwich, UK. 2007.
C. Xu, Y. Wang, M. Cao, Z. Lu, Dielectrophoresis of human red cells in microchips. Electrophoresis 20, 1829–1831 (1999)
X. Xue, M.K. Patel, M. Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, C. Bailey, D. Topham, Analysis of fluid separation in microfluidic T-channels. Appl. Math. Model. 36(2), 743–755 (2012)
M. Yamada, M. Nakashima, M. Seki, Pinched flow fractionation: continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal. Chem. 76, 5465–5471 (2004)
S. Yang, A. Undar, J.D. Zahn, A microfluidic device for continuous, real time blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 6, 871–880 (2006)
L.Y. Yeo, J.R. Friend, D.R. Arifin, “Electric tempest in a teacup: the tea leaf analogy to microfluidic blood plasma separation”. Phys. Lett. 89, 103516–1-3 (2006)
Y. S. Yoon, S. Yang, Y. Moon and K. C. Kim, presented in part at MicroTas 2006, Tokyo, Japan, 2006
X.B. Zhang, Z.Q. Wu, K. Wang, J. Zhu, J.J. Xu, X.H. Xia, H.Y. Chen, Gravitational sedimentation induced blood delamination for continuous plasma separation on a microfluidics chip. Anal. Chem. 84, 3780–3786 (2012)
R. Zhong, N. Wu, Y. Liub, Microfluidic human blood plasma separation for Lab on chip based heavy metal detection. ECS Trans. 41(38), 11–16 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Indian Institute of Technology Madras and the Department of Science & Technology (DST), India for providing the financial support for the project. We also acknowledge CNNP, IIT Madras for supporting the photolithography work. We thank Prof. Mukesh Doble and Ms. S. Manasi, Bio Engineering and Drug Design Lab, IIT Madras for the help with HL60 cell culture used in this study. The authors also thank the Department of Biotechnology, IIT Madras for supporting with the FACS studies. Our special thanks to Interdisciplinary Program, IIT Madras which enabled this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maria, M.S., Kumar, B.S., Chandra, T.S. et al. Development of a microfluidic device for cell concentration and blood cell-plasma separation. Biomed Microdevices 17, 115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-0017-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-0017-z