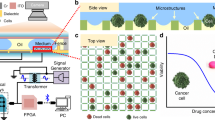
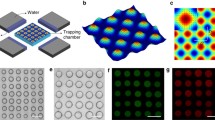
Abstract
We present a new method for the distinct specific chemical stimulation of single cells and small cell clusters within their natural environment. By single-drop release of chemical agents with droplets in size of typical cell diameters (d <30 μm) on-demand micro gradients can be generated for the specific manipulation of single cells. A single channel and a double channel agent release cartridge with integrated fluidic structures and integrated agent reservoirs are shown, tested, and compared in this publication. The single channel setup features a fluidic structure fabricated by anisotropic etching of silicon. To allow for simultaneous release of different agents even though maintaining the same device size, the second type comprises a double channel fluidic structure, fabricated by photolithographic patterning of TMMF. Dispensed droplet volumes are V = 15 pl and V = 10 pl for the silicon and the TMMF based setups, respectively. Utilizing the agent release cartridges, the application in biological assays was demonstrated by hormone-stimulated premature bud formation in Physcomitrella patens and the individual staining of one single L 929 cell within a confluent grown cell culture.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Andersson, A. van den Berg, Lab. Chip 4(2), 98–103 (2004)
H. Andersson, A. van den Berg, Lab. Chip 7, 544–546 (2007)
T. Boland, T. Xu, B. Damon, X. Cui, Biotechnol. J. 1, 910–917 (2006)
S. Boyden, J. Exp. Med. 115(3), 453–466 (1962)
V. Braun, K. Rehn, Eur. J. Biochem. 10, 426–438 (1969)
Cellectricon, Dynaflow®Pro II System – High Quality Automated Patch Clamping (Cellectricon AB, Mölndal, Sweden). http://www.cellectricon.se. Accessed Feb. 2011
B. Dadacz-Narloch et al., Plant Cell 23, 2696–2707 (2011)
E.L. Decker, W. Frank, E. Sarnighausen, R. Reski, Plant Biol. 8, 397–405 (2006)
H.G. Drexler, et al. DSMZ Catalogue of Human and Animal Cell Lines, Eighth Edition. (2001)
U. Egert et al., Brain Res. Protocol. 2, 229–242 (1998)
J. El-Ali et al., Anal. Chem. 77, 3629–3636 (2005)
R. Elmqvist, Measuring instrument of the recording type, US Patent 2566443, 1951
Eppendorf, Microinjectors FemtoJet and FemtoJet express Product Sheet (Eppendorf AG Hamburg, Germany). http://www.eppendorf.de. Accessed Feb. 2011
P. Jonas, Fast application of agonists to isolated membrane patches. In Single-Channel Recording, eds. B. Sakmann & E. Neher (Plenum press, 1995), pp. 231–243
T.M. Keenan, A. Folch, Lab. Chip 8, 34–57 (2008)
T. Kraus et al., Lab. Chip 6, 218–229 (2006)
H.P. Le, J. Imag. Sci. Tech. 42, 49–62 (1998)
L. Leoni, D. Attiah, T.A. Desai, Sensors 2, 111–120 (2002)
X. Liu et al., (IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 7(3), 315–326 (1999)
J. Noolandi et al., Biomed. Microdev. 5(3), 195–199 (2003)
Pam3Cys-SKKKK(Rhodamin), (EMC microcollections GmbH, Tübingen, Germany). http://www.microcollections.de. Accessed Feb. 2011
M.C. Peterman, J. Noolandi, M.S. Blumenkranz, H.A. Fishman, PNAS 101(27), 9951–9954 (2004)
S.A. Rani et al., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49(2), 728–732 (2005)
R. Reski, Botanica Acta 111, 1–15 (1998)
R. Reski, W.O. Abel, Planta 165, 354–358 (1985)
E.A. Roth, T. Xu, M. Das, C. Gregory, J.J. Hickman, T. Boland, Biomaterials 25, 3707–3715 (2004)
J. Steigert et al., Lab. Chip 9(12), 1801–1805 (2009)
U. Stöhr, P. Vulto, P. Hoppe, G. Urban, H. Reinecke, Journal of Micro/Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS. 7, 033009 (2008)
S. Takayama, E. Ostuni, P. Leduc, K. Naruse, D.E. Ingber, G.M. Whitesides, Nature 411(6841), 1016 (2001)
D.A. Wagenaar, J. Pine, S.M. Potter, J. Neurosci. Met. 138, 27–37 (2004)
N. Wangler et al., Proceedings of Thirteenth International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences November 1–5. (2009), 679–81
N. Wangler et al., J. Micromech. Microeng. 21(095009), 9 (2011)
S. Zibek et al., Biophys. J. 92(1), L04–L06 (2006)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank the German Research Foundation (DFG, ZE 527/4 and EXC 294) for financial support of this project. We also appreciate the good cooperation with the Cleanroom Service Center at IMTEK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 614 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wangler, N., Welsche, M., Blazek, M. et al. Bubble Jet agent release cartridge for chemical single cell stimulation. Biomed Microdevices 15, 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9681-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9681-4