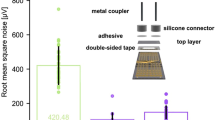
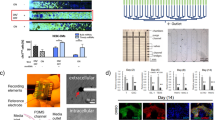
Abstract
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is an emerging genetic model for regenerative medicine. In humans, myocardial infarction results in the irreversible loss of cardiomyocytes. However, zebrafish hearts fully regenerate after a 20% ventricular resection, without either scarring or arrhythmias. To study this cardiac regeneration, we developed implantable flexible multi-microelectrode membrane arrays that measure the epicardial electrocardiogram signals of zebrafish in real-time. The microelectrode electrical signals allowed for a high level of both temporal and spatial resolution (~20 μm), and the signal to noise ratio of the epicardial ECG was comparable to that of surface electrode ECG (7.1 dB vs. 7.4 dB, respectively). Processing and analysis of the signals from the microelectrode array demonstrated distinct ECG signals: namely, atrial conduction (P waves), ventricular contraction (QRS), and ventricular repolarization (QT interval). The electrical signals were in synchrony with optically measured Calcium concentration gradients in terms of d[Ca2+]/dt at both whole heart and tissue levels. These microelectrodes therefore provide a real-time analytical tool for monitoring conduction phenotypes of small vertebral animals with a high temporal and spatial resolution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Bergmann, R.D. Bhardwaj, S. Bernard, S. Zdunek, F. Barnabe-Heider, S. Walsh et al., Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science 324(5923), 98 (2009). doi:10.1126/science.1164680
K. Bersell, S. Arab, B. Haring, B. Kuhn, Neuregulin1/ErbB4 signaling induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and repair of heart injury. Cell 138(2), 257 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.060
E. Braunwald, D.P. Zipes, P. Libby, R. Bonow (eds.), Braunwald’s heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 7th edn. (Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 2004)
C.S. Burrus, R.A. Gopinath, H. Guo, Introduction to wavelets and wavelet transforms: a primer (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 1997)
F. Chen, T.S. Klitzner, J.N. Weiss, Autonomic regulation of calcium cycling in developing embryonic mouse hearts. Cell Calcium 39(5), 375 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2005.12.004
D.L. Donoho, De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 41(3), 613 (1995)
A.S. Forouhar, J.R. Hove, C. Calvert, J. Flores, H. Jadvar, M. Gharib, Electrocardiographic characterization of embryonic zebrafish. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 5, 3615 (2004)
C. Hahn, M.A. Schwartz, The role of cellular adaptation to mechanical forces in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28(12), 2101 (2008)
P.C. Hsieh, V.F. Segers, M.E. Davis, C. MacGillivray, J. Gannon, J.D. Molkentin et al., Evidence from a genetic fate-mapping study that stem cells refresh adult mammalian cardiomyocytes after injury. Nat. Med. 13(8), 970 (2007). doi:10.1038/nm1618
D.H. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ma, Y.S. Kim, R.H. Kim, S. Wang et al., Epidermal electronics. Science 333(6044), 838 (2011)
D.J. Milan, C.A. MacRae, Animal models for arrhythmias. Cardiovasc. Res. 67(3), 426 (2005)
J.S. Mitcheson, J. Chen, M. Lin, C. Culberson, M.C. Sanguinetti, A structural basis for drug-induced long QT syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97(22), 12329 (2000)
K.D. Poss, L.G. Wilson, M.T. Keating, Heart regeneration in zebrafish. Science 298(5601), 2188 (2002)
A. Raya, A. Consiglio, Y. Kawakami, C. Rodriguez-Esteban, J.C. Izpisua-Belmonte, The zebrafish as a model of heart regeneration. Clon. Stem Cell. 6(4), 345 (2004)
J.L. Reeve, A.M. Duffy, T. O’Brien, A. Samali, Don’t lose heart–therapeutic value of apoptosis prevention in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9(3), 609 (2005)
J. Rihel, D.A. Prober, A. Arvanites, K. Lam, S. Zimmerman, S. Jang et al., Zebrafish behavioral profiling links drugs to biological targets and rest/wake regulation. Science 327(5963), 348 (2010)
D.C. Rodger, J.D. Weiland, M.S. Humayun, Y.C. Tai, Scalable high lead-count parylene package for retinal prostheses. Sensor. Actuator. B Chem. 117(1), 107 (2006a)
D.C. Rodger, W. Li, H. Fong, A.J. Ameri, E. Meng, J. Burdick et al. Flexible microfabricated parylene multielectrode arrays for retinal stimulation and spinal cord field modulation, in Proc. 4th International IEEE-EMBS Special Topic Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology ((MMB’06), Okinawa, Japan, 2006b), pp. 31
D.C. Rodger, A.J. Fong, W. Li, H. Ameri, I. Lavrov, H. Zhong, et al. High-density Flexible Parylene-based Multielectrode Arrays for Retinal and Spinal Cord Stimulation, (Transducers ’07, Lyon, 2007)
D. Sedmera, M. Reckova, A. deAlmeida, M. Sedmerova, M. Biermann, J. Volejnik et al., Functional and morphological evidence for a ventricular conduction system in zebrafish and Xenopus hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284(4), H1152 (2003)
D.Y. Stainier, Zebrafish genetics and vertebrate heart formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2(1), 39 (2001)
K. Stoletov, L. Fang, S.H. Choi, K. Hartvigsen, L.F. Hansen, C. Hall et al., Vascular lipid accumulation, lipoprotein oxidation, and macrophage lipid uptake in hypercholesterolemic zebrafish. Circ. Res. 104(8), 952 (2009)
P. Sun, Y. Zhang, F. Yu, E. Parks, A. Lyman, Q. Wu et al., Micro-electrocardiograms to study post-ventricular amputation of zebrafish heart. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37(5), 890 (2009)
S.M. Szilagyi, L. Szilagyi, Wavelet transform and neural-network-based adaptive filtering for QRS detection. Proceedings: 22nd Annual IEEE - EMBS International Conference, 2, 1267. (2000)
H.G.R. Tan, A. Tan, P. Khong, & V. Mok, Best wavelet function identification system for ecg signal denoise applications. In International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems, Kuala Lumpur, 2007 (Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems, 2007): IEEE pp. 631
M. Valderrabano, F. Chen, A.S. Dave, S.T. Lamp, T.S. Klitzner, J.N. Weiss, Atrioventricular ring reentry in embryonic mouse hearts. Circulation 114(6), 543 (2006). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.633727
T. Yokogawa, W. Marin, J. Faraco, G. Pézeron, L. Appelbaum, J. Zhang et al., Characterization of Sleep in Zebrafish and Insomnia in Hypocretin Receptor Mutants. PloS Biol. 5(10), 2379 (2007)
H. Yu, L. Ai, M. Rouhanizadeh, D. Patel, E.S. Kim, T.K. Hsiai, Flexible polymer sensors for in vivo intravascular shear stress analysis. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 17(5), 1178 (2008)
F. Yu, R. Li, E. Parks, W. Takabe, T.K. Hsiai, Electrocardiogram signals to assess zebrafish heart regeneration: implication of long QT intervals. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(7), 2346 (2010)
F. Yu, L. Ai, W. Dai, H. Yu, T.K. Hsiai, MEMS thermal sensors to detect changes in heat transfer in the pre-atherosclerotic regions of fat-fed New Zealand white rabbits. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39(6), 1736 (2011)
L.I. Zon, R.T. Peterson, In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4(1), 35 (2005)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to express gratitude for Dr. Fuhua Chen from UCLA School of Medicine for providing the Calcium voltage mapping. This project was supported by the American Heart Association Pre-Doctoral Fellowship (11PRE7370088) (FY), National Institutes of Health, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (HL083015) (TKH), HL091302 (TKH), (HL104239) (NCC) and National Institute of Child Health & Human Development (HD069305) (NCC and TKH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, F., Zhao, Y., Gu, J. et al. Flexible microelectrode arrays to interface epicardial electrical signals with intracardial calcium transients in zebrafish hearts. Biomed Microdevices 14, 357–366 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-011-9612-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-011-9612-9