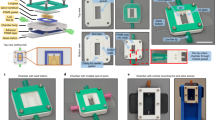
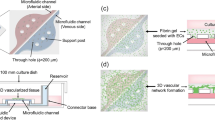
Abstract
Functional endothelialized networks constitute a critical building block for vascularized replacement tissues, organ assist devices, and laboratory tools for in vitro discovery and evaluation of new therapeutic compounds. Progress towards realization of these functional artificial vasculatures has been gated by limitations associated with the mechanical and surface chemical properties of commonly used microfluidic substrate materials and by the geometry of the microchannels produced using conventional fabrication techniques. Here we report on a method for constructing microvascular networks from polystyrene substrates commonly used for tissue culture, built with circular cross-sections and smooth transitions at bifurcations. Silicon master molds are constructed using an electroplating process that results in semi-circular channel cross-sections with smoothly varying radii. These master molds are used to emboss polystyrene sheets which are then joined to form closed bifurcated channel networks with circular cross-sections. The mechanical and surface chemical properties of these polystyrene microvascular network structures enable culture of endothelial cells along the inner lumen. Endothelial cell viability was assessed, documenting nearly confluent monolayers within 3D microfabricated channel networks with rounded cross-sections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.N. Bhatia, C.S. Chen, Biomedical Microdevices 1, 131 (1999)
J.T. Borenstein, H. Terai, K.R. King, E.J. Weinberg, M.R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J.P. Vacanti, Biomed Microdevices 4, 167 (2002)
K. A. Burgess, H.-H. Hu, W. R. Wagner, W. J. Federspiel, Biomedical Microdevices doi:10.1007/s10544-008-9215-2, (2008)
J.P. Camp, T. Stokol, M.L. Shuler, Biomed Microdevices 10, 179–186 (2008)
A. Carraro, W.-M. Hsu et al., Biomedical Microdevices 10, 795 (2008)
G. Dai, M.R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, S. Natarajan, Y. Zhang, S. Vaughn, B.R. Glackman, R.D. Kamm, G. Garcia-Cardeña, M.A. Gimbrone, Proc Nat Acad Sci 101, 14871 (2004)
T.A. Desai, Med Eng Phys 22, 595 (2000)
D.C. Duffy, J.C. McDonald, O.J.A. Schueller, G.M. Whitesides, Anal Chem 70, 4974 (1998)
C. Fidkowski, M.R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J.T. Borenstein, J.P. Vacanti, R. Langer, Y. Wang, Tissue Eng 11, 302 (2005)
G. García-Cardeña, J. Comander, K.R. Anderson, B.R. Blackman, M.A. Gimbrone Jr., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 4478 (2001)
S. Giselbrecht, T. Gietzelt, E. Gottwald, C. Trautmann, R. Truckenmuller, K.F. Weibezahn, A. Welle, Biomed Microdevices 8, 191 (2006)
J. Green, T. Kniazeva, M. Abedi, D.S. Sokhey, M.E. Taslim, S.K. Murthy, Lab Chip 9, 677 (2009)
M. Heckele, W.K. Schomburg, J. Micromech. Microeng 14: R1, 7776 (2007)
S. Hu, X. Ren, M. Bachman, C.E. Sims, G.P. Li, N.L. Allbritton, Langmuir 20, 5569 (2004)
X. Hu, W. Lui, L. Cui, M. Wang, Y. Cao, Tissue Eng 11, 1710 (2005)
B.-H. Jo, D.J. Beebe, SPIE 3877, 222 (1999)
M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, N. J. Krebs, J. P. Vacanti, J. T. Borenstein, Proceedings of the 2004 Hilton Head Sensors and Actuators Conference (2004)
A. Khademhosseini, R. Langer, J.T. Borenstein, J.P. Vacanti, Proc Nat Acad Sci 103, 2480 (2006)
K.R. King, C.J. Wang, M.R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J.P. Vacanti, J.T. Borenstein, Adv Mater 16, 2007 (2004)
D.A. LaVan, P.M. George, R. Langer, Angew Chem Int Ed 42, 1262 (2003)
E. Leclerc, Y. Sakai, T. Fujii, Biomed Microdevices 5, 109 (2003)
D. Lim, Y. Kamotani, B. Cho, J. Mazumder, S. Takayama, Lab Chip 3, 318 (2003)
R. Lima, S. Wada, S. Tanaka, M. Takeda, T. Ishikawa, K.-I. Tsubota, Y. Imai, T. Yamaguchi, Biomed Microdevices 10, 153 (2008)
H. Lu, L.Y. Koo, W.M. Wang, D.A. Lauffenburger, L.G. Griffith, K.F. Jensen, Anal Chem 76, 5257 (2004)
T.C. Marentis, J.P. Vacanti, J. Hsiao, J.T. Borenstein, IEEE JMEMS 2009, in press.
H.L. Prichard, W.M. Reichert, B. Klitzman, Biomaterials 28, 936 (2007)
S.R. Quake, A. Scherer, Science 290, 1536 (2000)
G.M. Riha, P.H. Lin, A.B. Lumsden, Q. Yao, C. Chen, Ann Biomed Eng 33, 772 (2005)
M.K. Runyon, C.J. Kastrup, B.L. Johnson-Kemer, T.G. Ha, R.F. Ismagilov, J Am Chem Soc 130, 3458 (2008)
C.-T. Seo, C.-H. Bae, D.-S. Eun, J.-K. Shin, J.-H. Lee, Jpn J Appl Phys 43, 7773 (2004)
F. Shen, C.L. Kastrup, R.R. Ismagilov, Thrombosis Res 122(Suppl. 1), S27 (2008)
J.W. Song, W. Gu, N. Futai, K.A. Warner, J.E. Nor, S. Takayama, Anal Chem 77, 3993 (2005)
J.P. Vacanti, R. Langer, The Lancet 354(Suppl I), 32SI (1999)
X.F. Walboomers, H.J. Croes, L.A. Ginsel, J.A. Jansen, Biomaterials 19, 1861 (1998)
G.-J. Wang, K.-H. Ho, S.-H. Hsu, K.-P. Wang, Biomed Microdevices 9, 657–663 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the MEMS Technology Group at the Draper Laboratory for fabrication of master molds and use of facilities, and funding provided by Charles Stark Draper Laboratory and Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borenstein, J.T., Tupper, M.M., Mack, P.J. et al. Functional endothelialized microvascular networks with circular cross-sections in a tissue culture substrate. Biomed Microdevices 12, 71–79 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9361-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9361-1